
l and m are the intersecting lines in the given figure. Find \[x\], \[y\] and \[z\]?
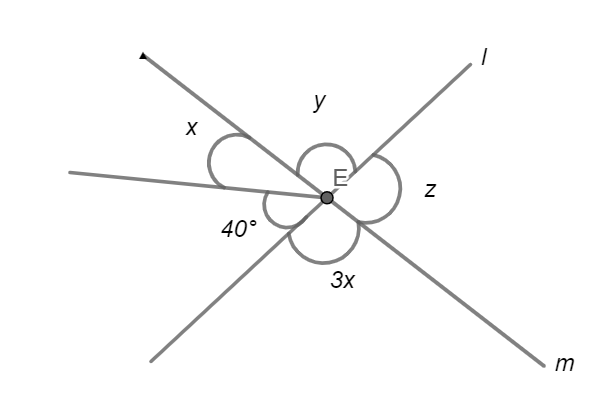

Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: We are given with intersecting lines. There exists a point in the pair of intersecting lines. The angles form around the point. We can assume the point we got as a circle. This can be considered as a \[{{360}^{\circ }}\] angle or a complete angle. The angles around the point should sum up to \[{{360}^{\circ }}\]. This gives us the values of the required angles.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now let us have a brief about intersecting lines. When two or more lines cross each other on a plane, they are called intersecting lines. The intersecting lines share a common point, which exists on all intersecting lines and is called a point of intersection.
Let us find out the angular values from the diagram.
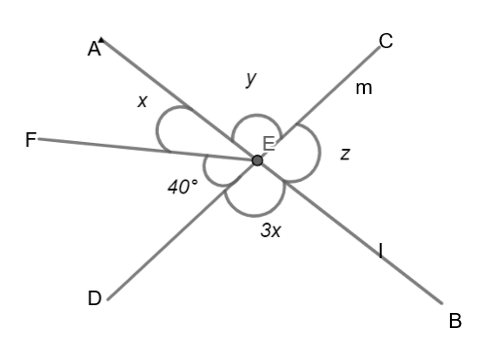
We can apply the angle sum property but since we have three unknown values, we cannot find out the values. So we will be dividing the figure as per convenience such that it includes one unknown and a known value.
Consider \[\angle AED\], we can find that it forms a right angle and it has a known angle and an unknown angle.
Let us find \[x\]
Consider the sum of \[\angle AEF+\angle FED\]
We get,
\[\begin{align}
& x+{{40}^{\circ }}={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& x={{50}^{\circ }} \\
& \therefore \angle AEF={{50}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Since we know the value of \[x\], we can easily find \[\angle BED\] by simply substituting the value of \[x\].
\[\begin{align}
& \angle BED=3x \\
& =3\left( {{50}^{\circ }} \right) \\
& ={{150}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \ angle BED={{180}^{\circ }}\]
Now consider the angles- \[\angle AEC,\angle AEF,\angle FED\]
We can see that all the three angles form a straight angle which says that the sum is \[{{180}^{\circ }}\].
Let us substitute the values now.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle AEC+\angle AEF+\angle FED \\
& \Rightarrow y+{{50}^{\circ }}+{{40}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow y+{{90}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow y={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \therefore \angle AEC={{90}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Now consider the angles \[\angle AEC,\angle CEB\]
We can find that these form a straight angle.
Let us find the value of \[z\] now.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle AEC+\angle CEB \\
& \Rightarrow {{90}^{\circ }}+z={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow z={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \therefore \angle CEB={{90}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
The values of \[x\], \[y\] and \[z\] are \[{{50}^{\circ }}\], \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] and \[{{90}^{\circ }}\].
Note: This can be verified by summing up all the angles to \[{{360}^{\circ }}\] as all the angles are around a point. In a pair of intersecting lines, the opposite pair of angles are congruent which means that they are equal and this pair is termed as vertically opposite angles.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now let us have a brief about intersecting lines. When two or more lines cross each other on a plane, they are called intersecting lines. The intersecting lines share a common point, which exists on all intersecting lines and is called a point of intersection.
Let us find out the angular values from the diagram.

We can apply the angle sum property but since we have three unknown values, we cannot find out the values. So we will be dividing the figure as per convenience such that it includes one unknown and a known value.
Consider \[\angle AED\], we can find that it forms a right angle and it has a known angle and an unknown angle.
Let us find \[x\]
Consider the sum of \[\angle AEF+\angle FED\]
We get,
\[\begin{align}
& x+{{40}^{\circ }}={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& x={{50}^{\circ }} \\
& \therefore \angle AEF={{50}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Since we know the value of \[x\], we can easily find \[\angle BED\] by simply substituting the value of \[x\].
\[\begin{align}
& \angle BED=3x \\
& =3\left( {{50}^{\circ }} \right) \\
& ={{150}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \ angle BED={{180}^{\circ }}\]
Now consider the angles- \[\angle AEC,\angle AEF,\angle FED\]
We can see that all the three angles form a straight angle which says that the sum is \[{{180}^{\circ }}\].
Let us substitute the values now.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle AEC+\angle AEF+\angle FED \\
& \Rightarrow y+{{50}^{\circ }}+{{40}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow y+{{90}^{\circ }}={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow y={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \therefore \angle AEC={{90}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Now consider the angles \[\angle AEC,\angle CEB\]
We can find that these form a straight angle.
Let us find the value of \[z\] now.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle AEC+\angle CEB \\
& \Rightarrow {{90}^{\circ }}+z={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow z={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \therefore \angle CEB={{90}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
The values of \[x\], \[y\] and \[z\] are \[{{50}^{\circ }}\], \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] and \[{{90}^{\circ }}\].
Note: This can be verified by summing up all the angles to \[{{360}^{\circ }}\] as all the angles are around a point. In a pair of intersecting lines, the opposite pair of angles are congruent which means that they are equal and this pair is termed as vertically opposite angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Find the sum of series 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + + 100 class 9 maths CBSE

Distinguish between Conventional and nonconventional class 9 social science CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it




