
How do you know the hybrid orbitals of a compound? For example, what are the hybrid orbitals of $C{H_2}C{l_2}$, ${C_2}{H_4}$ and ${C_2}{H_2}$?
Answer
557.4k+ views
Hint: We can say that hybridization was used to explain molecular structure when the valence bond theory failed to correctly describe them. It is experimentally observed that bond angles in organic compounds are close to ${109^ \circ },{120^ \circ }$ (or) ${180^ \circ }$. Based on Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory, the pairs of electrons are repelled each other, and unshared pairs and bonds around a central atom are generally separated by largest possible angles.
Complete step by step answer:
At the point when atoms share electrons with other atoms to frame compound bonds, the orbitals that contain the electrons associated with the bonding to form a "hybrid" orbital. The number of hybrid orbitals that is formed is based on the accommodation of the number of electrons in the valence shell.
We can determine the hybrid orbitals by the following ways,
We have to draw the Lewis structure of the compound
We have to determine the geometry of the compound using the VSEPR theory
The corresponding hybridization has to be assigned
We have to know that compound $C{H_2}C{l_2}$ is methylene chloride (or) dichloromethane. So, we can now draw the Lewis structure of this compound,
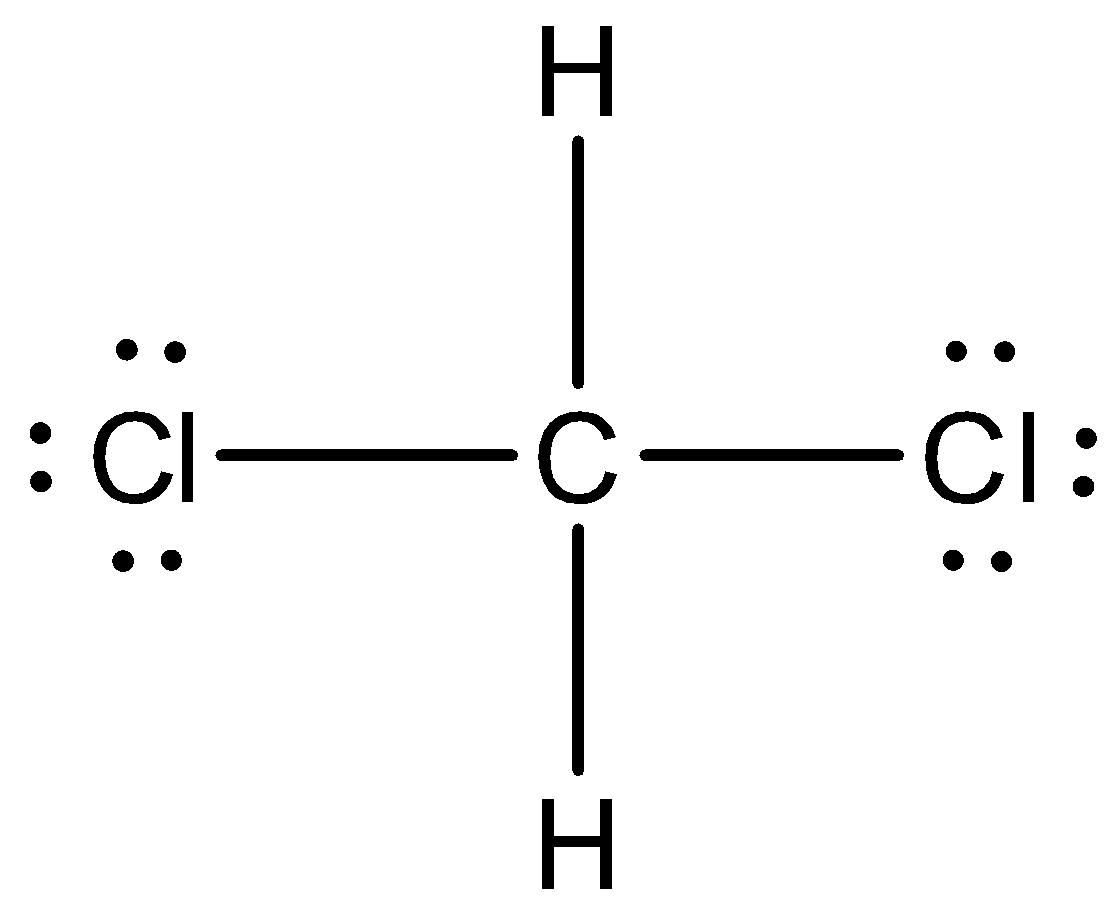
In the above structure, we can observe that there are four domains of electrons around the atom of carbon because the electron geometry is tetrahedral.
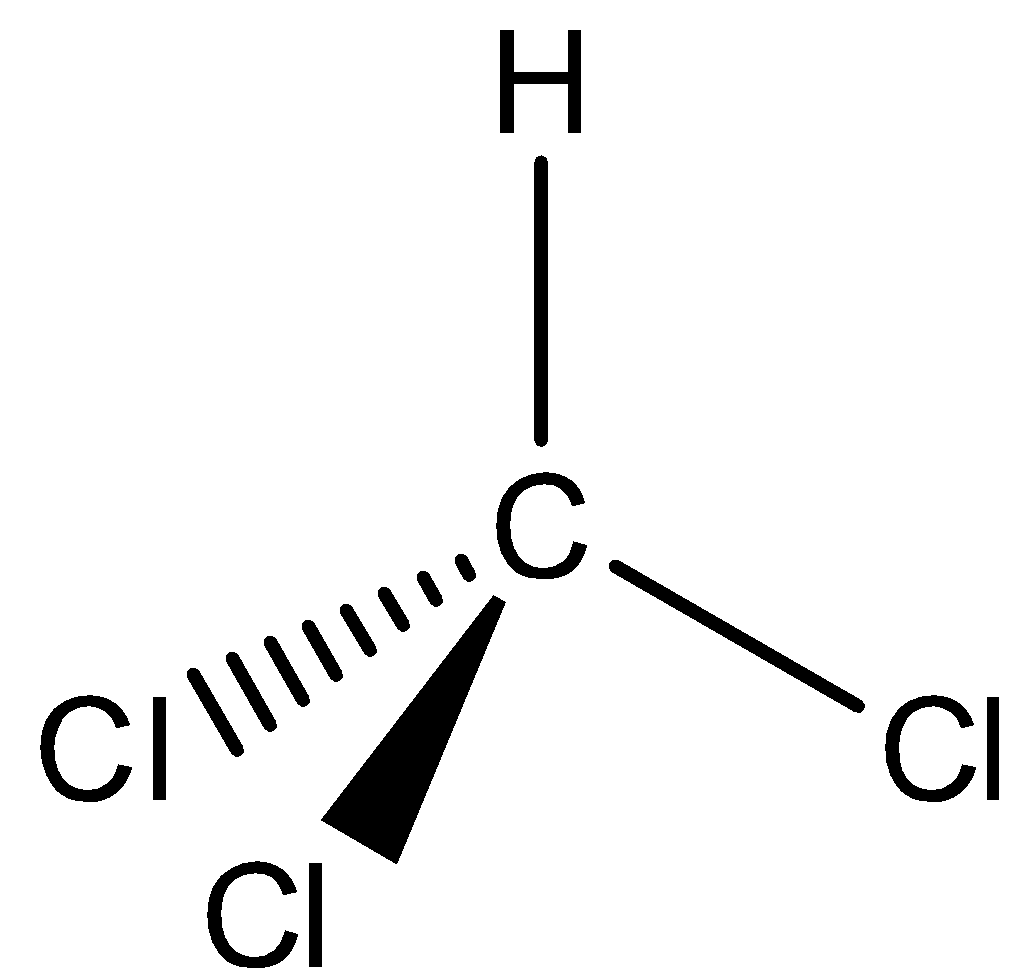
We have to know that the hybridization which corresponds to tetrahedral geometry is $s{p^3}$ and the bond angle is ${109.5^ \circ }$.
We have to know that compound ${C_2}{H_4}$ is ethene. So, we can now draw the Lewis structure of this compound,
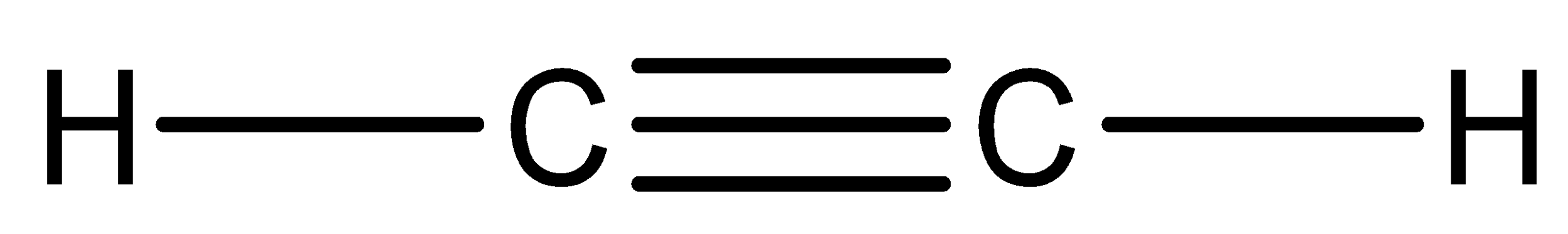
In the above structure, we can observe that there are three domains of electrons around the atom of carbon because the electron geometry is trigonal planar
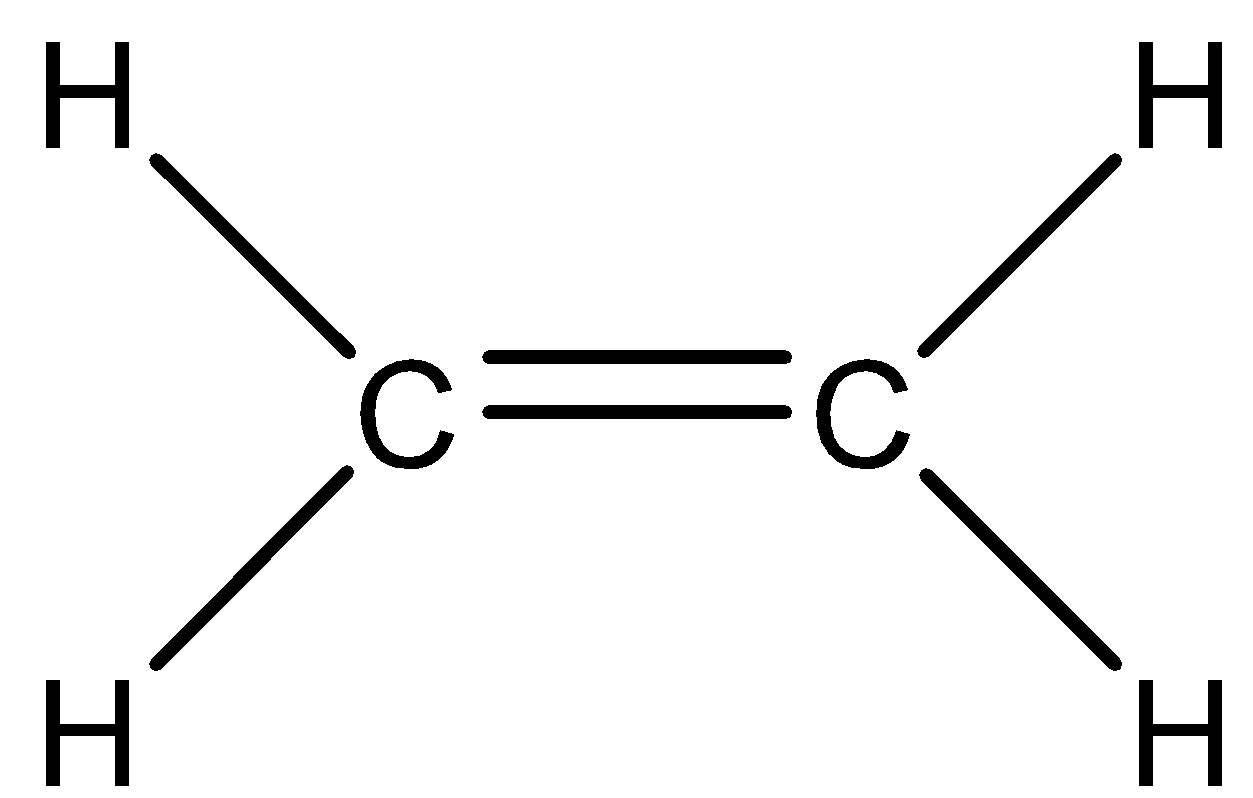
We have to know that the hybridization which corresponds to trigonal geometry is $s{p^2}$ and the bond angle is ${120^ \circ }$.
We have to know that compound ${C_2}{H_2}$ is acetylene. So, we can now draw the Lewis structure of this compound,
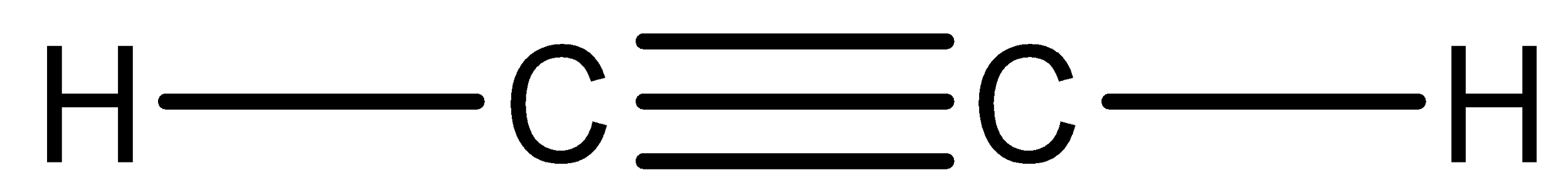
In the above structure, we can observe that there are two domains of electrons around the atom of carbon because the electron geometry is linear.
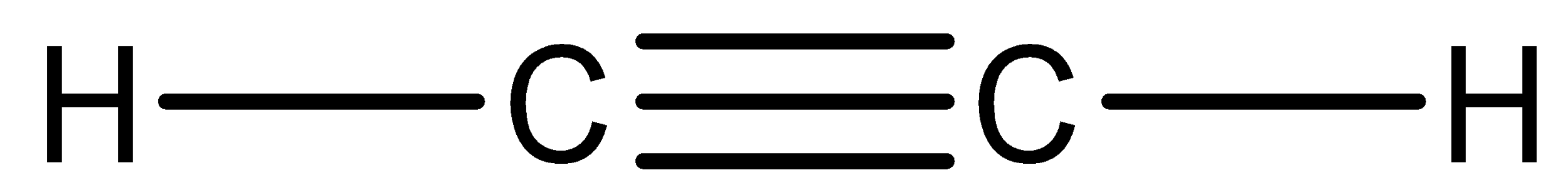
We have to know that the hybridization which corresponds to linear geometry is $sp$ and the bond angle is ${180^ \circ }$.
Note: We have to remember that the formation of a similar number of orbitals containing the same properties of various kinds of orbitals (s and p) of carbon atoms is defined as hybridization and orbitals that are produced are called hybridized orbitals.
In simple ways, we can remember that the,
In $ - C - C$ bond, the kind of hybridization on the carbon atom is $s{p^3}$.
In $ > C = C < $ bond, the kind of hybridization on the carbon atom is $s{p^2}$.
In $ - C \equiv C - $ bond, the kind of hybridization on the carbon atom is $sp$ .
Complete step by step answer:
At the point when atoms share electrons with other atoms to frame compound bonds, the orbitals that contain the electrons associated with the bonding to form a "hybrid" orbital. The number of hybrid orbitals that is formed is based on the accommodation of the number of electrons in the valence shell.
We can determine the hybrid orbitals by the following ways,
We have to draw the Lewis structure of the compound
We have to determine the geometry of the compound using the VSEPR theory
The corresponding hybridization has to be assigned
We have to know that compound $C{H_2}C{l_2}$ is methylene chloride (or) dichloromethane. So, we can now draw the Lewis structure of this compound,

In the above structure, we can observe that there are four domains of electrons around the atom of carbon because the electron geometry is tetrahedral.

We have to know that the hybridization which corresponds to tetrahedral geometry is $s{p^3}$ and the bond angle is ${109.5^ \circ }$.
We have to know that compound ${C_2}{H_4}$ is ethene. So, we can now draw the Lewis structure of this compound,
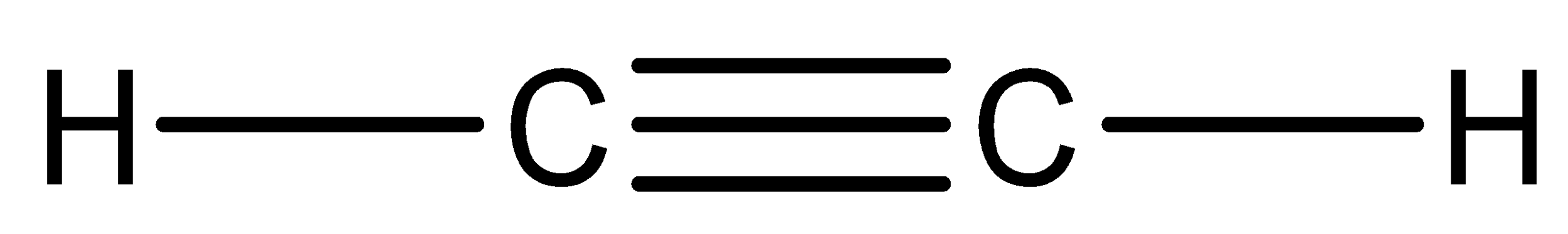
In the above structure, we can observe that there are three domains of electrons around the atom of carbon because the electron geometry is trigonal planar

We have to know that the hybridization which corresponds to trigonal geometry is $s{p^2}$ and the bond angle is ${120^ \circ }$.
We have to know that compound ${C_2}{H_2}$ is acetylene. So, we can now draw the Lewis structure of this compound,
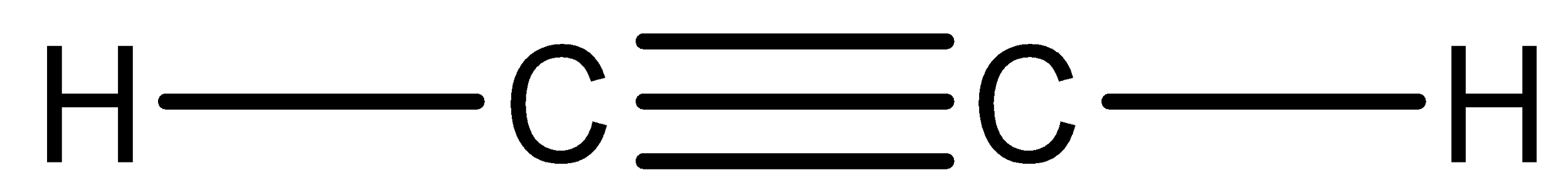
In the above structure, we can observe that there are two domains of electrons around the atom of carbon because the electron geometry is linear.
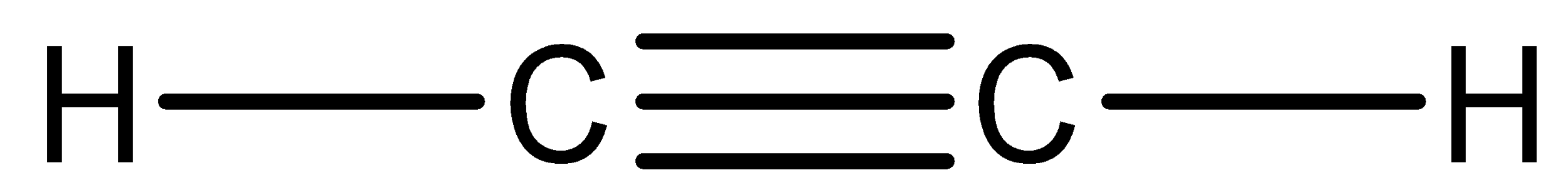
We have to know that the hybridization which corresponds to linear geometry is $sp$ and the bond angle is ${180^ \circ }$.
Note: We have to remember that the formation of a similar number of orbitals containing the same properties of various kinds of orbitals (s and p) of carbon atoms is defined as hybridization and orbitals that are produced are called hybridized orbitals.
In simple ways, we can remember that the,
In $ - C - C$ bond, the kind of hybridization on the carbon atom is $s{p^3}$.
In $ > C = C < $ bond, the kind of hybridization on the carbon atom is $s{p^2}$.
In $ - C \equiv C - $ bond, the kind of hybridization on the carbon atom is $sp$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




