
Ketones $\left( {{R_1}{\text{CO}}{{\text{R}}_2}} \right):{R_1} = {R_2} = $alkyl group, can be obtained in one step by
(1) Hydrolysis of esters
(2) Oxidation of ${1^\circ }$ alcohol
(3) Oxidation of ${2^\circ }$ alcohol
(4) Reaction of acid halides and alcohol
Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: A ketone is a functional group in chemistry that has the form RCOR, where R can be any carbon-containing substituent. Carbonyl groups are found in ketone molecules. Acetone, with the formula \[C{H_3}COC{H_3}\], is the most basic ketone. Ketones play an important role in biology and manufacturing.
Complete answer: Alcohols are a chemical family that includes compounds with one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups bound to a single bonded alkane. The general formula -OH is used to describe alcohols. Alcohols are useful in organic chemistry because they can be converted into and out of a variety of other compounds.
A secondary alcohol is a compound in which a hydroxy group, OH, is attached to a saturated carbon atom that is also attached to two other carbon atoms.
The loss of electrons by a molecule, particle, or ion during a reaction is known as oxidation. When the oxidation state of a molecule, atom, or ion is raised, it is called oxidation. When an atom, molecule, or ion gains electrons or the oxidation state of an atom, molecule, or ion reduces, the mechanism is called reduction.
In organic chemistry, the oxidation of alcohols is a crucial reaction. Aldehydes and carboxylic acids are formed when primary alcohols are oxidised; ketones are formed when secondary alcohols are oxidised.
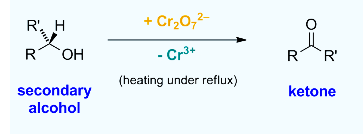
Note:
Ketones are compounds generated by your body when your cells do not receive enough glucose (blood sugar). Glucose is the body's primary energy supply. Ketones may be detected in the blood or urine. High ketone levels could suggest diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a diabetic complication that may result in a coma or even death.
Complete answer: Alcohols are a chemical family that includes compounds with one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups bound to a single bonded alkane. The general formula -OH is used to describe alcohols. Alcohols are useful in organic chemistry because they can be converted into and out of a variety of other compounds.
A secondary alcohol is a compound in which a hydroxy group, OH, is attached to a saturated carbon atom that is also attached to two other carbon atoms.
The loss of electrons by a molecule, particle, or ion during a reaction is known as oxidation. When the oxidation state of a molecule, atom, or ion is raised, it is called oxidation. When an atom, molecule, or ion gains electrons or the oxidation state of an atom, molecule, or ion reduces, the mechanism is called reduction.
In organic chemistry, the oxidation of alcohols is a crucial reaction. Aldehydes and carboxylic acids are formed when primary alcohols are oxidised; ketones are formed when secondary alcohols are oxidised.

Note:
Ketones are compounds generated by your body when your cells do not receive enough glucose (blood sugar). Glucose is the body's primary energy supply. Ketones may be detected in the blood or urine. High ketone levels could suggest diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a diabetic complication that may result in a coma or even death.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




