
How is junctional rhythm characterised?
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: When the electrical stimulation of the heart occurs close or within the atrioventricular node rather than the sinoatrial node, it is called a junctional rhythm. The QRS complex is usually narrow because the normal ventricular conduction pathway is employed.
A junctional rhythm is typically sluggish, with a beat rate of fewer than 60 per minute. It's called an accelerated junctional rhythm when it's faster.
Complete answer:
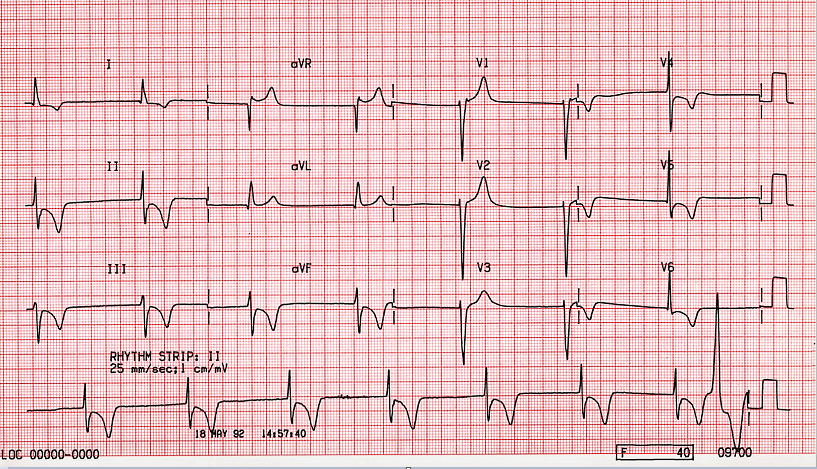
It is distinguished by QRS complexes that have the same shape as the sinus rhythm but do not precede the P waves. This rhythm is slower than the sinus rate expected. The retrograde P waves and atrioventricular dissociation can be noticed when this rhythm entirely overtakes the pacemaker's activity on the heart. Junctional beats are frequently the result of dissection or manipulation around the right atrium during heart surgery. As a result of the loss of AV synchronisation, the central venous pressure contour usually shows obvious v waves (right atrial pressure wave near the end of systole). A decrease in systemic arterial blood pressure can be caused by a lack of atrial contribution to ventricular filling.
A junctional rhythm may be seen in the strip below, with retrograde P waves appearing right before the QRS complex. Just after the QRS complex, the second rhythm strip reveals retrograde P waves.
Note:
Junctional Escape Rhythm ECG Features:
A junctional rhythm with a tempo of \[40 - 60\] beats per minute (bpm).
QRS complexes are usually short (less than \[120\] milliseconds).
There is no link between the QRS complexes and previous atrial activity (e.g. P-waves, flutter waves, fibrillatory waves).
A junctional rhythm is typically sluggish, with a beat rate of fewer than 60 per minute. It's called an accelerated junctional rhythm when it's faster.
Complete answer:
It is distinguished by QRS complexes that have the same shape as the sinus rhythm but do not precede the P waves. This rhythm is slower than the sinus rate expected. The retrograde P waves and atrioventricular dissociation can be noticed when this rhythm entirely overtakes the pacemaker's activity on the heart. Junctional beats are frequently the result of dissection or manipulation around the right atrium during heart surgery. As a result of the loss of AV synchronisation, the central venous pressure contour usually shows obvious v waves (right atrial pressure wave near the end of systole). A decrease in systemic arterial blood pressure can be caused by a lack of atrial contribution to ventricular filling.
A junctional rhythm may be seen in the strip below, with retrograde P waves appearing right before the QRS complex. Just after the QRS complex, the second rhythm strip reveals retrograde P waves.

Note:
Junctional Escape Rhythm ECG Features:
A junctional rhythm with a tempo of \[40 - 60\] beats per minute (bpm).
QRS complexes are usually short (less than \[120\] milliseconds).
There is no link between the QRS complexes and previous atrial activity (e.g. P-waves, flutter waves, fibrillatory waves).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




