
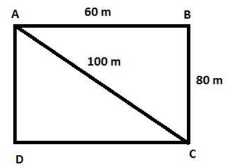
Jayanti takes the shortest route to her home by walking diagonally across a rectangular park. The park measures 60 meters $\times$ 80 meters. How much shorter is the route across the park than the route around its edges?
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: The Pythagorean Theorem states that in any right triangle, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the triangle’s legs is the same as the square of the length of the triangle’s hypotenuse. This theorem is represented by the formula \[{\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2}\].
Put simply, if you know the lengths of two sides of a right triangle, you can apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the third side. Remember, this theorem only works for right triangles.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The park measures 60 meters $\times$ 80 meters
\[Pythagoras{\text{ }}theorem: - {\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2}\]
First scenario if she moves diagonally in the park
As when we cut rectangular park diagonally
We get 2 right angled triangle
The length of the shortest route (the diagonal of the rectangle) =
By using Pythagoras Theorem, (We use it because a diagonal divides a rectangle into two right angled triangles.)
With length and breadth as 2 sides and diagonal as hypotenuse
\[ \Rightarrow lengt{h^{^2}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}breadt{h^{^2}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}diagona{l^{^2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {60^2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{80^2}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}diagona{l^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3600{\text{ }} + {\text{ 6400 }} = {\text{ }}diagona{l^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow diagona{l^2} = 10000\]
\[ \Rightarrow diagonal = \sqrt {10000} = 100\;meters\]
The shortest route is 100 metres.
Second scenario If the person goes around the edges, the distance she will cover = Distance of length + breadth = 80 + 60 = 140 meters
To calculate shorter is the route across the park than the route around its edges = second scenario – first scenario
\[ \Rightarrow 140{\text{ }}meters{\text{ }}-{\text{ }}100{\text{ }}meters{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}40{\text{ }}meters\]
She travels 40 meters less when she travels diagonally.
Jayanti travels a 40 meters shorter route across the park than the route around its edges.
Note: On certain occasions, all 3 sides of a right-angled triangle will be whole numbers as given in this question. This is called a Pythagorean Triad (also called a Pythagorean Triple). Pythagorean triples are relatively prime. Relatively prime means they have no common divisor other than 1, even if the numbers are not prime numbers, like 14 and 15. The number 14 has factors 1, 2, 7, and 14; the number 15 has factors 1, 3, 5, and 15. Their only common factor is 1.
Put simply, if you know the lengths of two sides of a right triangle, you can apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the third side. Remember, this theorem only works for right triangles.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The park measures 60 meters $\times$ 80 meters

\[Pythagoras{\text{ }}theorem: - {\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2}\]
First scenario if she moves diagonally in the park
As when we cut rectangular park diagonally
We get 2 right angled triangle
The length of the shortest route (the diagonal of the rectangle) =
By using Pythagoras Theorem, (We use it because a diagonal divides a rectangle into two right angled triangles.)
With length and breadth as 2 sides and diagonal as hypotenuse
\[ \Rightarrow lengt{h^{^2}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}breadt{h^{^2}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}diagona{l^{^2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {60^2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{80^2}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}diagona{l^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3600{\text{ }} + {\text{ 6400 }} = {\text{ }}diagona{l^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow diagona{l^2} = 10000\]
\[ \Rightarrow diagonal = \sqrt {10000} = 100\;meters\]
The shortest route is 100 metres.
Second scenario If the person goes around the edges, the distance she will cover = Distance of length + breadth = 80 + 60 = 140 meters
To calculate shorter is the route across the park than the route around its edges = second scenario – first scenario
\[ \Rightarrow 140{\text{ }}meters{\text{ }}-{\text{ }}100{\text{ }}meters{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}40{\text{ }}meters\]
She travels 40 meters less when she travels diagonally.
Jayanti travels a 40 meters shorter route across the park than the route around its edges.
Note: On certain occasions, all 3 sides of a right-angled triangle will be whole numbers as given in this question. This is called a Pythagorean Triad (also called a Pythagorean Triple). Pythagorean triples are relatively prime. Relatively prime means they have no common divisor other than 1, even if the numbers are not prime numbers, like 14 and 15. The number 14 has factors 1, 2, 7, and 14; the number 15 has factors 1, 3, 5, and 15. Their only common factor is 1.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




