
IUPAC name of \[isopropoxymethane\]

A. True
B. False

Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint:Hint:
Ether is the class of the organic compound where the two same or different alkyl groups are attached to single oxygen. IUPAC is the method of naming the organic compound and it refers to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. The ether is represented as follows:
\[R - O - R'\]
\[ - R\,,\, - R'\] = can be the same or different alkyl/aryl group.
Complete step-by-step answer:To find whether the IUPAC name is true or false, before answering we must know the rules of IUPAC for naming the ether. The rules are as follows,
In common names, we use alphabetical order followed by the word “ether” as the suffix.
Suppose two same alkyl groups are attached to the oxygen then those compounds are symmetrical compounds and the name will be given as “Dialkyl ether”.
Suppose two different alkyl groups are attached to the oxygen those are unsymmetrical compounds, and the naming will be according to alphabetical order.
IUPAC naming follows the different guidelines, therefore the rules state when a substituent group containing more number of carbon atoms is present as an alkyl group, and this is chosen as parent hydrocarbon. The substituent group which is attached to the other side of oxygen atom is named with “oxy” as the prefix.
Let’s consider one example,
\[C{H_3} - O - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_3}\]
So, the name will be, \[1 - methoxy\,propane\] .
For determining the structure which is given in question let’s draw and number them,
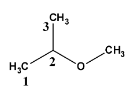
So, here at the second carbon, the methoxy group is attached. Therefore, the name will be
\[2 - methoxy\,propane\] . It follows as “alkoxy alkane”
The answer is \[2 - methoxy\,propane\] not \[isopropoxymethane\] .
Therefore, the answer will be option B. False.
Note:The compound is \[2 - methoxy\,propane\] but not \[isopropoxymethane\] because of the naming rules. So, it is very important to know the rules. However, students may get confused. So, the tip to remember is that having a long chain is parent and then number it accordingly.
Ether is the class of the organic compound where the two same or different alkyl groups are attached to single oxygen. IUPAC is the method of naming the organic compound and it refers to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. The ether is represented as follows:
\[R - O - R'\]
\[ - R\,,\, - R'\] = can be the same or different alkyl/aryl group.
Complete step-by-step answer:To find whether the IUPAC name is true or false, before answering we must know the rules of IUPAC for naming the ether. The rules are as follows,
In common names, we use alphabetical order followed by the word “ether” as the suffix.
Suppose two same alkyl groups are attached to the oxygen then those compounds are symmetrical compounds and the name will be given as “Dialkyl ether”.
Suppose two different alkyl groups are attached to the oxygen those are unsymmetrical compounds, and the naming will be according to alphabetical order.
IUPAC naming follows the different guidelines, therefore the rules state when a substituent group containing more number of carbon atoms is present as an alkyl group, and this is chosen as parent hydrocarbon. The substituent group which is attached to the other side of oxygen atom is named with “oxy” as the prefix.
Let’s consider one example,
\[C{H_3} - O - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_3}\]
So, the name will be, \[1 - methoxy\,propane\] .
For determining the structure which is given in question let’s draw and number them,

So, here at the second carbon, the methoxy group is attached. Therefore, the name will be
\[2 - methoxy\,propane\] . It follows as “alkoxy alkane”
The answer is \[2 - methoxy\,propane\] not \[isopropoxymethane\] .
Therefore, the answer will be option B. False.
Note:The compound is \[2 - methoxy\,propane\] but not \[isopropoxymethane\] because of the naming rules. So, it is very important to know the rules. However, students may get confused. So, the tip to remember is that having a long chain is parent and then number it accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




