
It has been given that the radii of the curvature of the faces of a given double convex lens are $10cm$ and $15cm$. If focal length of the lens is $12cm$, find the refractive index of the material of the lens.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: The lens maker’s formula is to be used here in order to solve this question. The reciprocal of the focal length of the lens is found to be equivalent to the product of change in refractive index of the media and the difference of the reciprocal of the radii of the double convex lens. These all will help you to solve this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is already mentioned in the question that the focal length of the lens is,
$F=12cm$
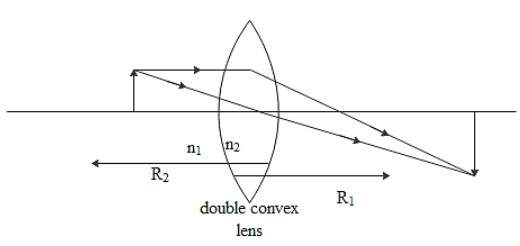
And the radius of the curvature of the first surface of the lens where the light falls is given as,
${{R}_{1}}=10cm$
The radius of the curvature of the second surface of the lens can be written as,
${{R}_{2}}=-15cm$
This will be negative as the radius will be measured in the opposite side of the lens.
The lens is placed in air. Therefore the value of refractive index of the surrounding medium will be,
${{n}_{1}}=1$
According to the lens maker’s equation, we can write that,
$\dfrac{1}{F}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-{{n}_{1}} \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}} \right)$
Substituting the values in the equation will give,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{12}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{-15} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{12}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{15} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Rearranging this equation and then simplifying it will give the answer for the question.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{12}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{25}{150} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{12}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-1 \right)\dfrac{1}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-1 \right) \\
& {{n}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}+1=\dfrac{3}{2}=1.5 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the required answer for the question has been obtained. The refractive index of the lens used is \[1.5\].
Note:
According to the sign convention the parameters which are in the direction of the incident light will be taken as positive. Those which are in the opposite direction of the incident light will be considered as negative. The parameters above the principal axis are considered to be positive and those which are below the principal axis are found to be negative.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is already mentioned in the question that the focal length of the lens is,
$F=12cm$
And the radius of the curvature of the first surface of the lens where the light falls is given as,
${{R}_{1}}=10cm$
The radius of the curvature of the second surface of the lens can be written as,
${{R}_{2}}=-15cm$
This will be negative as the radius will be measured in the opposite side of the lens.
The lens is placed in air. Therefore the value of refractive index of the surrounding medium will be,
${{n}_{1}}=1$
According to the lens maker’s equation, we can write that,
$\dfrac{1}{F}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-{{n}_{1}} \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}-\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}} \right)$
Substituting the values in the equation will give,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{12}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{10}-\dfrac{1}{-15} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{12}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{10}+\dfrac{1}{15} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Rearranging this equation and then simplifying it will give the answer for the question.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{12}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-1 \right)\left( \dfrac{25}{150} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{12}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-1 \right)\dfrac{1}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}=\left( {{n}_{2}}-1 \right) \\
& {{n}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}+1=\dfrac{3}{2}=1.5 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the required answer for the question has been obtained. The refractive index of the lens used is \[1.5\].

Note:
According to the sign convention the parameters which are in the direction of the incident light will be taken as positive. Those which are in the opposite direction of the incident light will be considered as negative. The parameters above the principal axis are considered to be positive and those which are below the principal axis are found to be negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




