
Is Nuclear envelope derivative of Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: Nuclear envelope separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm and it is made up of two lipoprotein and trilaminar membranes. It consists of two concentric membranes called inner and outer nuclear membranes. There are two sets of intermediate filaments that provide support for the nuclear envelope and it arranges as it internally forms the nuclear lamina and externally forms a loose network to give external support.
Complete answer:
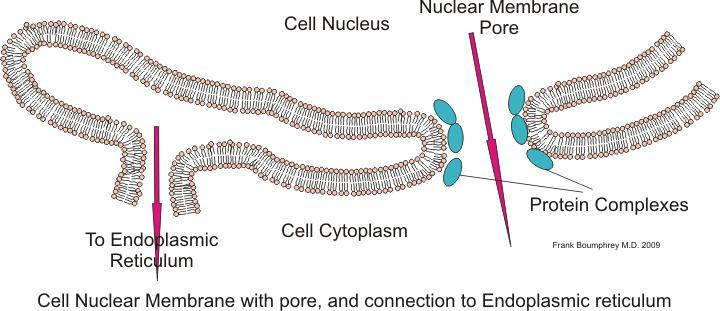
The Nuclear envelope consists of two parallel membranes with a space between (10-50nm) called the perinuclear space which forms barriers between the genetic material and cytoplasm. The nuclear envelope consists of a large number of pores, which help to transport the macromolecules between the cytoplasm and nucleus. These two membranes are continuous in the region of the pores. Each nuclear pore consists of a large multiprotein complex called a nuclear pore complex. The proteins which make up the nuclear pore complex are called nucleoporins. The two membranes are as follows:
Outer membrane: is directly attached with a lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum and is functionally similar to the endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes also attached to its cytoplasmic surface.
Inner membrane: It is connected to the outer membrane through nuclear pores and it carries a unique protein that is specific to the nucleus. It does not bear ribosomes on its surfaces.
Note:
The two membranes outer and inner are fused at the nuclear pore complexes. Rough endoplasmic reticulums produce nuclear envelopes in telophase. The nuclear envelope disappears during cell division and reappears during nuclear reorganization. It provides protection to DNA against the mutagenic effect of cytoplasmic enzymes.
Complete answer:

The Nuclear envelope consists of two parallel membranes with a space between (10-50nm) called the perinuclear space which forms barriers between the genetic material and cytoplasm. The nuclear envelope consists of a large number of pores, which help to transport the macromolecules between the cytoplasm and nucleus. These two membranes are continuous in the region of the pores. Each nuclear pore consists of a large multiprotein complex called a nuclear pore complex. The proteins which make up the nuclear pore complex are called nucleoporins. The two membranes are as follows:
Outer membrane: is directly attached with a lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum and is functionally similar to the endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes also attached to its cytoplasmic surface.
Inner membrane: It is connected to the outer membrane through nuclear pores and it carries a unique protein that is specific to the nucleus. It does not bear ribosomes on its surfaces.
Note:
The two membranes outer and inner are fused at the nuclear pore complexes. Rough endoplasmic reticulums produce nuclear envelopes in telophase. The nuclear envelope disappears during cell division and reappears during nuclear reorganization. It provides protection to DNA against the mutagenic effect of cytoplasmic enzymes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




