
Is cyclopropenyl cation, $ {C_3}{H_3}^ + $ aromatic?
Answer
492.6k+ views
Hint: Cyclopropenyl cation is a cyclopropane with a positive charge on one carbon atom formed by the loss of one hydrogen atom. The compounds that are cyclic, planar, conjugation of pi-electrons and obeying Huckel’s rule can be defined as aromatic compounds, these are stable compounds.
Complete answer:
Cycloalkenes are alkenes arranged in a cyclic manner. Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons consisting of double bonded carbon atoms. When one hydrogen atom is removed from the cyclopropene, it forms a compound known as cyclopropenyl cation which is represented by a formula of $ {C_3}{H_3}^ + $ .
Aromatic compounds are the compounds that are cyclic, planar which means all the carbon atoms have $ s{p^2} $ hybridization, conjugation of $ \pi $ electrons, and obeying Huckel’s rule. Huckel's rule states that the compound must contain $ \left( {4n + 2} \right)\pi $ electrons, where n is a positive whole number.
The structure of cyclopropenyl cation $ \left( {{C_3}{H_3}^ + } \right) $ is
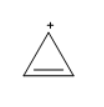
The above molecule is in cyclic arrangement, all the carbon atoms are $ s{p^2} $ hybridized, as the double bonded are $ s{p^2} $ hybridized and the carbocation is also $ s{p^2} $ hybridized, the double bond and the positive charge are in conjugation, and the compound has two pi-electrons which obeys Huckel’s rule as $ \left( {4\left( 0 \right) + 2} \right)\pi = 2\pi $ electrons. cyclopropenyl cation obeys all the conditions required to be an aromatic compound.
Thus, cyclopropenyl cation, $ {C_3}{H_3}^ + $ is an aromatic compound.
Note:
Conjugation means the two double bonds or one double bond and charge separated by a single bond. In the above molecule, charge and double bond are separated by a single bond. Carbocation is the carbon bearing a positive charge and involves in $ s{p^2} $ hybridization.
Complete answer:
Cycloalkenes are alkenes arranged in a cyclic manner. Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons consisting of double bonded carbon atoms. When one hydrogen atom is removed from the cyclopropene, it forms a compound known as cyclopropenyl cation which is represented by a formula of $ {C_3}{H_3}^ + $ .
Aromatic compounds are the compounds that are cyclic, planar which means all the carbon atoms have $ s{p^2} $ hybridization, conjugation of $ \pi $ electrons, and obeying Huckel’s rule. Huckel's rule states that the compound must contain $ \left( {4n + 2} \right)\pi $ electrons, where n is a positive whole number.
The structure of cyclopropenyl cation $ \left( {{C_3}{H_3}^ + } \right) $ is

The above molecule is in cyclic arrangement, all the carbon atoms are $ s{p^2} $ hybridized, as the double bonded are $ s{p^2} $ hybridized and the carbocation is also $ s{p^2} $ hybridized, the double bond and the positive charge are in conjugation, and the compound has two pi-electrons which obeys Huckel’s rule as $ \left( {4\left( 0 \right) + 2} \right)\pi = 2\pi $ electrons. cyclopropenyl cation obeys all the conditions required to be an aromatic compound.
Thus, cyclopropenyl cation, $ {C_3}{H_3}^ + $ is an aromatic compound.
Note:
Conjugation means the two double bonds or one double bond and charge separated by a single bond. In the above molecule, charge and double bond are separated by a single bond. Carbocation is the carbon bearing a positive charge and involves in $ s{p^2} $ hybridization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




