
Is $ C{H_3}N{H_2} $ acid or base?
Answer
495k+ views
Hint: Concept of acid and base are explained on the basis of a number of theories like Arrhenius theory, Lewis theory, Bronsted lower. All of these theories explain acidity and basicity with the help of distinctive properties of molecules.
Complete answer:
According to Lewis theory of acid and base any compound which is capable of accepting its lone pair of electrons to other molecules are known as acids. While the compound which is capable of donating its lone pair electron to another molecule is known as base.
As we know nitrogen-containing compounds are commonly known as amines which are either aliphatic or aromatic in nature depending upon the substituents added to nitrogen atoms. Methyl amine $ C{H_3}N{H_2} $ is an example of aliphatic amine. Atomic number of Nitrogen is $ 7 $ and the electronic configuration is $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3} $ . From the electronic configuration it is clear that nitrogen has $ 5 $ electrons in its outermost shell. In the molecule of $ C{H_3}N{H_2} $ , the nitrogen atom shares its two electrons of $ \left( p \right) $ orbital with the hydrogen group and one with methyl group. After the formation of three covalent bonds two electrons of $ \left( {2s} \right) $ orbital remain over the nitrogen atom. This lone pair of electrons participating is available for donation in the chemical reaction and hence imparts the basicity of the methylamine. Methyl group is also electron donating $ \left( { + {\rm I}} \right) $ and increases the basicity of the compound.
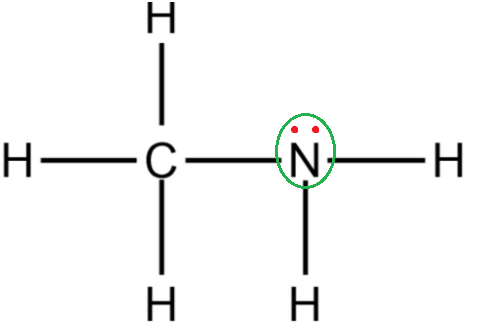
The strength of the basicity depends upon the ease of donation of lone pair electrons present at nitrogen atoms. Molecules which easily donate the lone pair of electrons are strong bases. Hence order of basicity is $ {3^ \circ } > {2^ \circ } > {1^ \circ } $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ C{H_3}N{H_2} $ is basic in nature.
Note:
Secondary amines and tertiary amines are stronger than primary amines due to the presence of a large number of electrons donating methyl groups. But in aqueous phase the tertiary amine shows minimum basicity and order will change to $ {2^ \circ } > {1^ \circ } > {3^ \circ } $ .
Complete answer:
According to Lewis theory of acid and base any compound which is capable of accepting its lone pair of electrons to other molecules are known as acids. While the compound which is capable of donating its lone pair electron to another molecule is known as base.
As we know nitrogen-containing compounds are commonly known as amines which are either aliphatic or aromatic in nature depending upon the substituents added to nitrogen atoms. Methyl amine $ C{H_3}N{H_2} $ is an example of aliphatic amine. Atomic number of Nitrogen is $ 7 $ and the electronic configuration is $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3} $ . From the electronic configuration it is clear that nitrogen has $ 5 $ electrons in its outermost shell. In the molecule of $ C{H_3}N{H_2} $ , the nitrogen atom shares its two electrons of $ \left( p \right) $ orbital with the hydrogen group and one with methyl group. After the formation of three covalent bonds two electrons of $ \left( {2s} \right) $ orbital remain over the nitrogen atom. This lone pair of electrons participating is available for donation in the chemical reaction and hence imparts the basicity of the methylamine. Methyl group is also electron donating $ \left( { + {\rm I}} \right) $ and increases the basicity of the compound.

The strength of the basicity depends upon the ease of donation of lone pair electrons present at nitrogen atoms. Molecules which easily donate the lone pair of electrons are strong bases. Hence order of basicity is $ {3^ \circ } > {2^ \circ } > {1^ \circ } $
$ \Rightarrow $ $ C{H_3}N{H_2} $ is basic in nature.
Note:
Secondary amines and tertiary amines are stronger than primary amines due to the presence of a large number of electrons donating methyl groups. But in aqueous phase the tertiary amine shows minimum basicity and order will change to $ {2^ \circ } > {1^ \circ } > {3^ \circ } $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




