
Is \[B{F_3}\] a hypervalent compound?
Answer
499.5k+ views
Hint: As we know that \[B{F_3}\] is also known as Boron trifluoride. It is named so since it has three fluorine atoms. This pungent colorless toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds. The geometry of a molecule of \[B{F_3}\] is trigonal planar.
Complete answer:
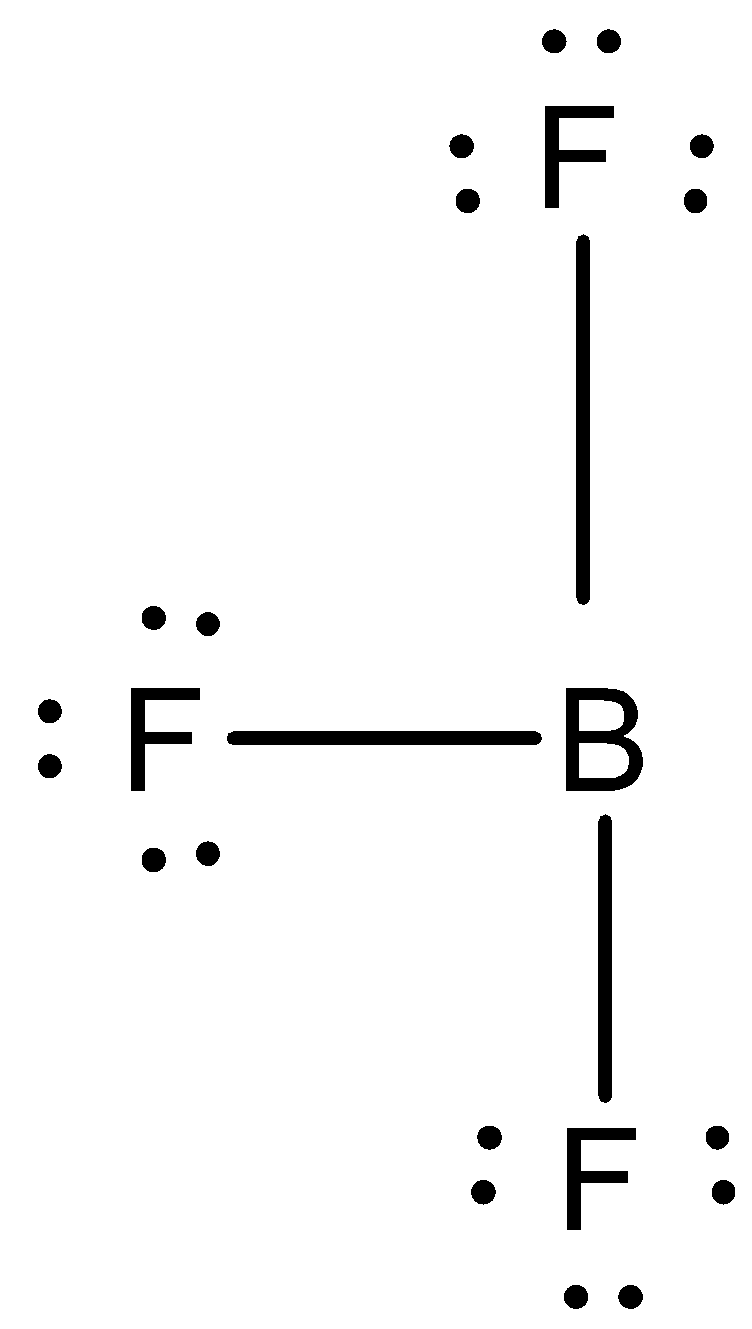
We have to know that the \[B{F_3}\] is not a hypervalent molecule. If we break down \[B{F_3}\] and look at its atomic structure it has $6$ electrons in its outermost shell. Thus, the octet of the central atom is not complete meaning the valence shell has less than \[8{\text{ }}{e^ - }\]electrons. Now if we recall the definition of a hypervalent molecule it is described as a molecule containing one or more main group elements with more than eight electrons in its valence shells. A hypervalent molecule is a molecule that contains one or more main group elements apparently bearing more than eight electrons in their valence shells. For hypervalent compounds in which the ligands are more electronegative than the central, hypervalent atom, resonance structures can be drawn with no more than four covalent electron pair bonds and completed with ionic bonds to obey the octet rule. The covalent bond in \[B{F_3}\] tells us that electrons are shared, rather than lost by boron and gained by fluorine.
Note:
We need to know that the boron trifluoride is most importantly used as a reagent in organic synthesis, typically as a Lewis acid. Examples include: initiates polymerisation reactions of unsaturated compounds, such as polyethers as a catalyst in some isomerization, acylation, alkylation and other reactions.
Complete answer:
We have to know that the \[B{F_3}\] is not a hypervalent molecule. If we break down \[B{F_3}\] and look at its atomic structure it has $6$ electrons in its outermost shell. Thus, the octet of the central atom is not complete meaning the valence shell has less than \[8{\text{ }}{e^ - }\]electrons. Now if we recall the definition of a hypervalent molecule it is described as a molecule containing one or more main group elements with more than eight electrons in its valence shells. A hypervalent molecule is a molecule that contains one or more main group elements apparently bearing more than eight electrons in their valence shells. For hypervalent compounds in which the ligands are more electronegative than the central, hypervalent atom, resonance structures can be drawn with no more than four covalent electron pair bonds and completed with ionic bonds to obey the octet rule. The covalent bond in \[B{F_3}\] tells us that electrons are shared, rather than lost by boron and gained by fluorine.

Note:
We need to know that the boron trifluoride is most importantly used as a reagent in organic synthesis, typically as a Lewis acid. Examples include: initiates polymerisation reactions of unsaturated compounds, such as polyethers as a catalyst in some isomerization, acylation, alkylation and other reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




