
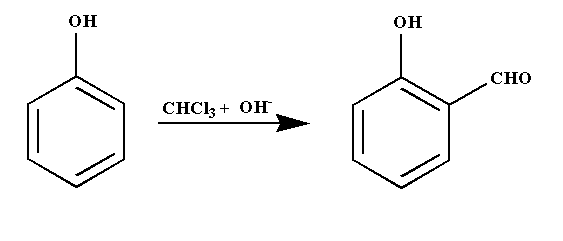
Intermediate of below reaction is:
A. $:CC{l_2}$
B. $:CHCl$
C. $CHC{l_2}$
D. $CC{l_3}$

Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: In Reimer-Tiemann reaction, first the chloroform reacts with the base and deprotonates to form chloroform carbanion which further on alpha elimination forms the reaction species which have neutral carbon atom with unshared valence electrons.
Complete step by step answer: The given reaction is an example of Reimer-Tiemann reaction. It is a type of substitution reaction. In this reaction, phenol is reacted with chloroform in the presence of base sodium hydroxide which results in the substitution of an aldehydic group on the ortho position of the benzene ring forming a compound named ortho hydroxybenzaldehyde.
The Reimer-Tiemann reaction is shown below.

In this reaction first the chloroform is deprotonated by the base to form a chloroform carbanion. The chloroform carbanion undergoes alpha elimination to form dichlorocarbene.
The reaction for the deprotonation of the chloroform is shown below.
$CHC{l_3} + NaOH \to NaCl + {H_2}O + :CC{l_2}$
In this reaction, chloroform reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium chloride, water and dichlorocarbene. The dichlorocarbene is the reactive species of the reaction.
The aqueous hydroxide deprotonates the phenol ring to form the phenoxide anion. The negative charge is delocalized in the benzene ring making it more nucleophilic in nature. The nucleophile then attacks the dichlorocarbene to form an intermediate dichloromethyl substituted phenol. At last on basic hydrolysis, the intermediate yield ortho hydroxybenzaldehyde.
The mechanism of the reaction is shown below.
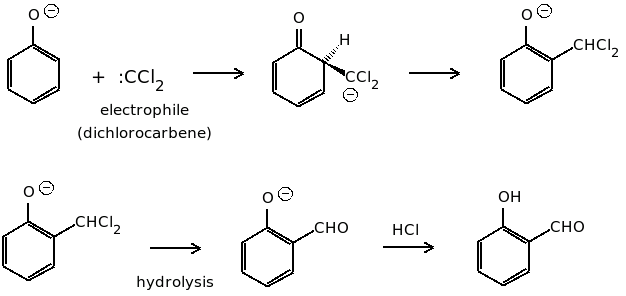
Thus, the intermediate of the reaction is $:CC{l_2}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Carbene is an electron deficient species, as it is electron withdrawing in nature due to the presence of two chlorine groups that’s why it is attracted by electron rich phenoxide ions.
Complete step by step answer: The given reaction is an example of Reimer-Tiemann reaction. It is a type of substitution reaction. In this reaction, phenol is reacted with chloroform in the presence of base sodium hydroxide which results in the substitution of an aldehydic group on the ortho position of the benzene ring forming a compound named ortho hydroxybenzaldehyde.
The Reimer-Tiemann reaction is shown below.

In this reaction first the chloroform is deprotonated by the base to form a chloroform carbanion. The chloroform carbanion undergoes alpha elimination to form dichlorocarbene.
The reaction for the deprotonation of the chloroform is shown below.
$CHC{l_3} + NaOH \to NaCl + {H_2}O + :CC{l_2}$
In this reaction, chloroform reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium chloride, water and dichlorocarbene. The dichlorocarbene is the reactive species of the reaction.
The aqueous hydroxide deprotonates the phenol ring to form the phenoxide anion. The negative charge is delocalized in the benzene ring making it more nucleophilic in nature. The nucleophile then attacks the dichlorocarbene to form an intermediate dichloromethyl substituted phenol. At last on basic hydrolysis, the intermediate yield ortho hydroxybenzaldehyde.
The mechanism of the reaction is shown below.

Thus, the intermediate of the reaction is $:CC{l_2}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Carbene is an electron deficient species, as it is electron withdrawing in nature due to the presence of two chlorine groups that’s why it is attracted by electron rich phenoxide ions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




