
Indicate the $\sigma$ and $\pi$ bonds in the following molecules.
${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$, ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}$, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}$, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$, ${\text{HCONHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: The single bonds in a compound are known as the $\sigma$ bonds. If there are double bonds in a compound then one bond is $\sigma$ bond and one is the $\pi$ bond. If there are triple bonds in a compound then one bond is the $\sigma$ bond and two are the $\pi$ bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the molecule has covalent bonds there are sigma bonds and pi bonds. The sigma bonds are represented by $\sigma$ and the pi bonds are represented by $\pi$.
The bond formed between two atoms by the axial overlap of the atomic orbitals along the intermolecular axis is known as the sigma bond.
The bond formed by the lateral overlap of the atomic orbitals at right angles to the intermolecular axis is known as the pi bond.
1. Consider the compound ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$:
The structure of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ is as follows:
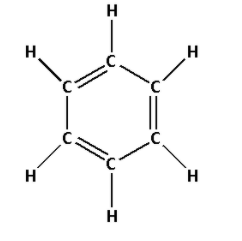
- The structure of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ contains three single bonds and three double bonds.
- Three single bonds indicate that there are three $\sigma$ bonds. And three double bonds indicate that there are three $\sigma$ bonds and three $\pi$ bonds. Thus, there are six $\sigma$ bonds and three $\pi$ bonds.
- Thus, ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ has six $\sigma$ bonds and three $\pi$ bonds.
2. Consider the compound ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}$:
The structure of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}$ is as follows:
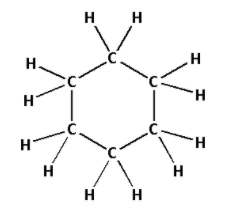
- The structure of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}$ contains eighteen single bonds.
- Eighteen single bonds indicate that there are eighteen $\sigma$ bonds. Thus, there are eighteen $\sigma$ bonds and zero $\pi$ bonds.
- Thus, ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}$ has eighteen $\sigma$ bonds and zero $\pi$ bonds.
3. Consider the compound ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$:
The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as follows:
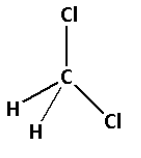
- The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ contains four single bonds.
- Four single bonds indicate that there are four $\sigma$ bonds. Thus, there are four $\sigma$ bonds and zero $\pi$ bonds.
- Thus, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ has four $\sigma$ bonds and zero $\pi$ bonds.
4. Consider the compound ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}$:
The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}$ is as follows:
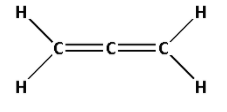
- The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}$ contains four single bonds and two double bonds.
- Four single bonds indicate that there are four $\sigma$ bonds. And two double bonds indicate that there are two $\sigma$ bonds and two $\pi$ bonds. Thus, there are six $\sigma$ bonds and two $\pi$ bonds.
- Thus, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}$ has six $\sigma$ bonds and two $\pi$ bonds.
5. Consider the compound ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$:
The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as follows:
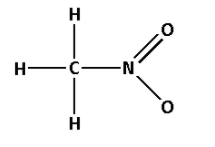
- The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ contains five single bonds and one double bond.
- Five single bonds indicate that there are five $\sigma$ bonds. And one double bond indicates that there is one $\sigma$ bond and one $\pi$ bond. Thus, there are six $\sigma$ bonds and one $\pi$ bond.
- Thus, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ has six $\sigma$ bonds and one $\pi$ bonds.
6. Consider the compound ${\text{HCONHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$:
The structure of ${\text{HCONHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ is as follows:
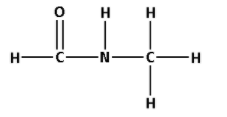
- The structure of ${\text{HCONHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ contains seven single bonds and one double bond.
- Seven single bonds indicate that there are seven $\sigma$ bonds. And one double bond indicates that there is one $\sigma$ bond and one $\pi$ bond. Thus, there are six $\sigma$ bonds and one $\pi$ bond.
- Thus, ${\text{HCONHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ has eight $\sigma$ bonds and one $\pi$ bonds.
Note:
The sigma bond overlapping is very large and thus, the sigma bond is stronger. The overlapping of pi bonds is weak and thus, pi bond is weaker. The sigma bond has one-electron cloud and the pi bond has a two-electron cloud.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the molecule has covalent bonds there are sigma bonds and pi bonds. The sigma bonds are represented by $\sigma$ and the pi bonds are represented by $\pi$.
The bond formed between two atoms by the axial overlap of the atomic orbitals along the intermolecular axis is known as the sigma bond.
The bond formed by the lateral overlap of the atomic orbitals at right angles to the intermolecular axis is known as the pi bond.
1. Consider the compound ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$:
The structure of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ is as follows:

- The structure of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ contains three single bonds and three double bonds.
- Three single bonds indicate that there are three $\sigma$ bonds. And three double bonds indicate that there are three $\sigma$ bonds and three $\pi$ bonds. Thus, there are six $\sigma$ bonds and three $\pi$ bonds.
- Thus, ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ has six $\sigma$ bonds and three $\pi$ bonds.
2. Consider the compound ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}$:
The structure of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}$ is as follows:

- The structure of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}$ contains eighteen single bonds.
- Eighteen single bonds indicate that there are eighteen $\sigma$ bonds. Thus, there are eighteen $\sigma$ bonds and zero $\pi$ bonds.
- Thus, ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}$ has eighteen $\sigma$ bonds and zero $\pi$ bonds.
3. Consider the compound ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$:
The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as follows:

- The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ contains four single bonds.
- Four single bonds indicate that there are four $\sigma$ bonds. Thus, there are four $\sigma$ bonds and zero $\pi$ bonds.
- Thus, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ has four $\sigma$ bonds and zero $\pi$ bonds.
4. Consider the compound ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}$:
The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}$ is as follows:
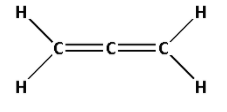
- The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}$ contains four single bonds and two double bonds.
- Four single bonds indicate that there are four $\sigma$ bonds. And two double bonds indicate that there are two $\sigma$ bonds and two $\pi$ bonds. Thus, there are six $\sigma$ bonds and two $\pi$ bonds.
- Thus, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}$ has six $\sigma$ bonds and two $\pi$ bonds.
5. Consider the compound ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$:
The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as follows:

- The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ contains five single bonds and one double bond.
- Five single bonds indicate that there are five $\sigma$ bonds. And one double bond indicates that there is one $\sigma$ bond and one $\pi$ bond. Thus, there are six $\sigma$ bonds and one $\pi$ bond.
- Thus, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ has six $\sigma$ bonds and one $\pi$ bonds.
6. Consider the compound ${\text{HCONHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$:
The structure of ${\text{HCONHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ is as follows:

- The structure of ${\text{HCONHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ contains seven single bonds and one double bond.
- Seven single bonds indicate that there are seven $\sigma$ bonds. And one double bond indicates that there is one $\sigma$ bond and one $\pi$ bond. Thus, there are six $\sigma$ bonds and one $\pi$ bond.
- Thus, ${\text{HCONHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ has eight $\sigma$ bonds and one $\pi$ bonds.
Note:
The sigma bond overlapping is very large and thus, the sigma bond is stronger. The overlapping of pi bonds is weak and thus, pi bond is weaker. The sigma bond has one-electron cloud and the pi bond has a two-electron cloud.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




