
In$\Delta ABC$,$\angle C = 90^\circ $
If $BC = a,AC = b$and$AB = c$, find
(i)$c$when $a = 8cm$and $b = 6cm$
(ii) $a$when $c = 25cm$and $b = 7cm$
(iii) $b$when $c = 13cm$and $a = 5cm$
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Take each of the above cases, then use Pythagoras theorem to find the missing value in that case. Repeat the same procedure to find the missing value in all the cases.
Complete step-by-step answer:
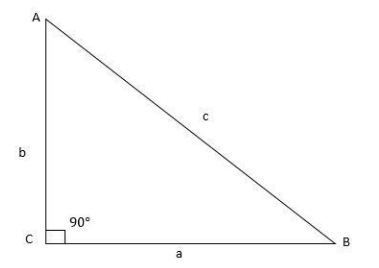
Using Pythagoras theorem,
Hypotenuse2=Perpendicular2+base2
(i) $c$when, $a = 8cm$and $b = 6cm$
Here,
$AC = b = 6cm$
$BC = a = 8cm$
$AB = c = ?$
Applying Pythagoras theorem,
$\Rightarrow A{B^2} = A{C^2} + B{C^2}$
$\Rightarrow {c^2} = {b^2} + {a^2}$
Putting the values,
$\Rightarrow {c^2} = {6^2} + {8^2}$
$\Rightarrow {c^2} = 64 + 36$
$\Rightarrow c = 10$
ii) Find $a$when $c = 25cm$ and $b = 7cm$
$AC = b = 7cm$
$BC = a = ?$
$AB = c = 25cm$
Applying Pythagoras theorem,
$\Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
$\Rightarrow {c^2} = {b^2} + {a^2}$
$\Rightarrow {25^2} = {7^2} + {a^2}$
$\Rightarrow {a^2} = {25^2} - {7^2}$
$\Rightarrow {a^2} = 625 - 49$
$\Rightarrow {a^2} = 576$
$\Rightarrow a = 24$
(iii) $b$when $c = 13cm$and $a = 5cm$
Here,
$ AC = b = ?$
$ BC = a = 5cm$
$ AB = c = 13cm$
Applying Pythagoras theorem,
$\Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
$\Rightarrow {c^2} = {b^2} + {a^2}$
$\Rightarrow {13^2} = {b^2} + {5^2}$
$\Rightarrow {b^2} = 169 - 25$
$\Rightarrow {b^2} = \sqrt {144} $
$\Rightarrow b = 12$
Note: A triangle having 90 Degree is a right angled triangle. The Pythagoras theorem is useful to calculate the values asked to find in a question.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Using Pythagoras theorem,
Hypotenuse2=Perpendicular2+base2
(i) $c$when, $a = 8cm$and $b = 6cm$
Here,
$AC = b = 6cm$
$BC = a = 8cm$
$AB = c = ?$
Applying Pythagoras theorem,
$\Rightarrow A{B^2} = A{C^2} + B{C^2}$
$\Rightarrow {c^2} = {b^2} + {a^2}$
Putting the values,
$\Rightarrow {c^2} = {6^2} + {8^2}$
$\Rightarrow {c^2} = 64 + 36$
$\Rightarrow c = 10$
ii) Find $a$when $c = 25cm$ and $b = 7cm$
$AC = b = 7cm$
$BC = a = ?$
$AB = c = 25cm$
Applying Pythagoras theorem,
$\Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
$\Rightarrow {c^2} = {b^2} + {a^2}$
$\Rightarrow {25^2} = {7^2} + {a^2}$
$\Rightarrow {a^2} = {25^2} - {7^2}$
$\Rightarrow {a^2} = 625 - 49$
$\Rightarrow {a^2} = 576$
$\Rightarrow a = 24$
(iii) $b$when $c = 13cm$and $a = 5cm$
Here,
$ AC = b = ?$
$ BC = a = 5cm$
$ AB = c = 13cm$
Applying Pythagoras theorem,
$\Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
$\Rightarrow {c^2} = {b^2} + {a^2}$
$\Rightarrow {13^2} = {b^2} + {5^2}$
$\Rightarrow {b^2} = 169 - 25$
$\Rightarrow {b^2} = \sqrt {144} $
$\Rightarrow b = 12$
Note: A triangle having 90 Degree is a right angled triangle. The Pythagoras theorem is useful to calculate the values asked to find in a question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





