
In $x+y+1=0$ and $x+2y+1=0$ are angle bisector of lines ${{L}_{1}}$ and ${{L}_{2}}$ and point $\left( 0,0 \right)$ lies on ${{L}_{1}}$ , then acute angle bisector of ${{L}_{1}}$ and ${{L}_{2}}$ is,
(a) $x+y-1=0$
(b) $x+y+1=0$
(c) $x+2y+1=0$
(d) Data insufficient
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: First find the points A, B, C by intersection of sides given in the question. So given an internal angular bisector, the bisector bisects the angle into 2 equal halves hence, it divides the side opposite into 2 parts with ratio of corresponding sides. Equation of angular bisector of two equation of line $ax+by+c=0,dx+ey+f=0$ is given by
$\dfrac{ax+by+c}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}=\pm \dfrac{dx+ey+f}{\sqrt{{{d}^{2}}+{{e}^{2}}}}$
These 2 lines become the equations of bisectors.
Complete step-by-step answer:
If two lines from an angle then they have 2 angles bisectors because between 2 lines there are 2 angles possible which are acute and obtuse. So, the 2 lines bisecting these 2 angles between lines $ax+by+c=0,dx+ey+f=0$ are given by
$\dfrac{ax+by+c}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}=\pm \dfrac{dx+ey+f}{\sqrt{{{d}^{2}}+{{e}^{2}}}}$
So, the symbol plus or minus denotes 2 equations of bisectors. Out of both any of them may be acute and may be obtuse if one is acute the other is obtuse and vice versa.
The both given bisectors are \[x+y+1=0\] , $x+2y+1=0$ , we need to find out the acute angle bisector from these both.
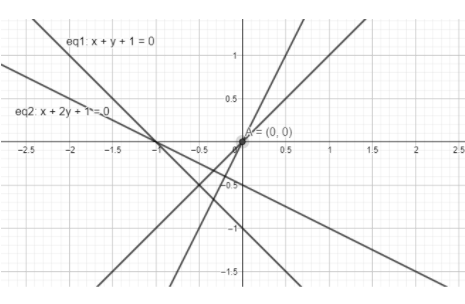
In the figure we are representing 2 lines and perpendiculars from A. The reason we plotted perpendiculars will be understood in the following solution.
As given \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] lies on \[{{L}_{1}}\] . we will find the perpendicular distance of \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] to both the lines.
Perpendicular distance of a line \[ax+by+c=0\] from \[\left( h,k \right)\] :
Let the distance be represented by d (for temporary)
\[d=\left| \dfrac{ah+bk+c}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}} \right|\]
Perpendicular distance of the line \[x+y+1=0\] from \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] .
Let the distance be represented by a.
\[a=\left| \dfrac{0+0+1}{\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}}}} \right|=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]
By simplifying we get the value of a to be $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$. Perpendicular distance of the line $x+2y+1=0$ from \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] .
Let the distance be represented by b.
$b=\left| \dfrac{0+0+1}{\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{2}^{2}}}} \right|=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}$
By simplifying we get b to be $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}$ .
We have $a$$<$$b$ . So, the sin of angle made will be greater in case of a. So, it will be obtuse. The line $x+2y+1=0$ will be acute. Option (c) is correct.
Note:Be careful while relating the distance to angle. Here, it is opposite/hypotenuse. Since the value of sine of angle is directly proportional to distance. Use the above relation properly as the sine of angle we get will be perpendicular from A / hypotenuse. As hypotenuse is the same we can relate directly to the perpendicular distance.
$\dfrac{ax+by+c}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}=\pm \dfrac{dx+ey+f}{\sqrt{{{d}^{2}}+{{e}^{2}}}}$
These 2 lines become the equations of bisectors.
Complete step-by-step answer:
If two lines from an angle then they have 2 angles bisectors because between 2 lines there are 2 angles possible which are acute and obtuse. So, the 2 lines bisecting these 2 angles between lines $ax+by+c=0,dx+ey+f=0$ are given by
$\dfrac{ax+by+c}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}}=\pm \dfrac{dx+ey+f}{\sqrt{{{d}^{2}}+{{e}^{2}}}}$
So, the symbol plus or minus denotes 2 equations of bisectors. Out of both any of them may be acute and may be obtuse if one is acute the other is obtuse and vice versa.
The both given bisectors are \[x+y+1=0\] , $x+2y+1=0$ , we need to find out the acute angle bisector from these both.

In the figure we are representing 2 lines and perpendiculars from A. The reason we plotted perpendiculars will be understood in the following solution.
As given \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] lies on \[{{L}_{1}}\] . we will find the perpendicular distance of \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] to both the lines.
Perpendicular distance of a line \[ax+by+c=0\] from \[\left( h,k \right)\] :
Let the distance be represented by d (for temporary)
\[d=\left| \dfrac{ah+bk+c}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}} \right|\]
Perpendicular distance of the line \[x+y+1=0\] from \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] .
Let the distance be represented by a.
\[a=\left| \dfrac{0+0+1}{\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}}}} \right|=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]
By simplifying we get the value of a to be $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$. Perpendicular distance of the line $x+2y+1=0$ from \[\left( 0,0 \right)\] .
Let the distance be represented by b.
$b=\left| \dfrac{0+0+1}{\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{2}^{2}}}} \right|=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}$
By simplifying we get b to be $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}$ .
We have $a$$<$$b$ . So, the sin of angle made will be greater in case of a. So, it will be obtuse. The line $x+2y+1=0$ will be acute. Option (c) is correct.
Note:Be careful while relating the distance to angle. Here, it is opposite/hypotenuse. Since the value of sine of angle is directly proportional to distance. Use the above relation properly as the sine of angle we get will be perpendicular from A / hypotenuse. As hypotenuse is the same we can relate directly to the perpendicular distance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




