
In which stage DNA duplication occurs?
A. G1
B. G2
C. S
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: DNA replication or duplication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule.
There are four phases in a cell cycle- G1, G2, S, and M phase.
G1, G2, and S phase together are known as interphase.
Complete answer: S phase is also known as Synthesis Phase.
1. It is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated. S phase occurs between the G1 phase and the G2 phase. Throughout the M phase and G1 phase, cells assemble inactive pre-replication complexes (pre-RC) on replication origins distributed throughout the genome.
2. During S-phase, the cell converts pre-RCs into active replication forks to initiate DNA replication. This process depends on the kinase activity of Cdc7 and various S-phase CDKs, both of which are upregulated upon S-phase entry.
3. Activation of the pre-RC is a closely regulated and highly sequential process.
After Cdc7 and S-phase CDKs phosphorylate their respective substrates, the second set of replicative factors associate with the pre-RC.
4. The stable association encourages minichromosome maintenance protein complex (MCM) helicase to unwind a small stretch of parental DNA into two strands of ssDNA, which in turn gives work to replication protein A (RPA), an ssDNA binding protein.
5. RPA recruitment primes the replication fork for loading of replicative DNA polymerases and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) sliding clamps.
6. Loading of these factors completes the active replication fork and initiates the synthesis of new DNA.
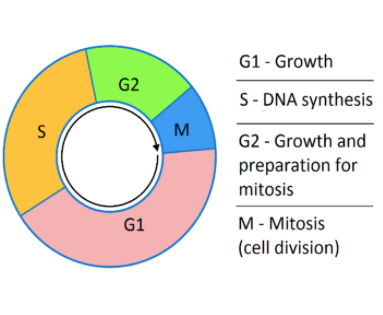
So, the correct answer is C. S phase
Note: DNA must be packaged into nucleosomes to function properly, synthesis of canonical (non-variant) histone proteins occurs alongside DNA replication.
Free histones produced by the cell during S-phase are rapidly incorporated into new nucleosomes.
There are four phases in a cell cycle- G1, G2, S, and M phase.
G1, G2, and S phase together are known as interphase.
Complete answer: S phase is also known as Synthesis Phase.
1. It is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated. S phase occurs between the G1 phase and the G2 phase. Throughout the M phase and G1 phase, cells assemble inactive pre-replication complexes (pre-RC) on replication origins distributed throughout the genome.
2. During S-phase, the cell converts pre-RCs into active replication forks to initiate DNA replication. This process depends on the kinase activity of Cdc7 and various S-phase CDKs, both of which are upregulated upon S-phase entry.
3. Activation of the pre-RC is a closely regulated and highly sequential process.
After Cdc7 and S-phase CDKs phosphorylate their respective substrates, the second set of replicative factors associate with the pre-RC.
4. The stable association encourages minichromosome maintenance protein complex (MCM) helicase to unwind a small stretch of parental DNA into two strands of ssDNA, which in turn gives work to replication protein A (RPA), an ssDNA binding protein.
5. RPA recruitment primes the replication fork for loading of replicative DNA polymerases and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) sliding clamps.
6. Loading of these factors completes the active replication fork and initiates the synthesis of new DNA.

So, the correct answer is C. S phase
Note: DNA must be packaged into nucleosomes to function properly, synthesis of canonical (non-variant) histone proteins occurs alongside DNA replication.
Free histones produced by the cell during S-phase are rapidly incorporated into new nucleosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




