
In which phylum water vascular system is found?
A) Protozoa
B) Arthropoda
C) Porifera
D) Echinodermata (Sea cucumber)
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: This phylum is triploblastic in which larval conditions have bilateral symmetry and adults have radial symmetry.
Complete answer:
Water vascular system is found in Echinoderms. It helps in nutrition, locomotion, respiration, and excretion.
Additional information:
Water vascular system is described as:
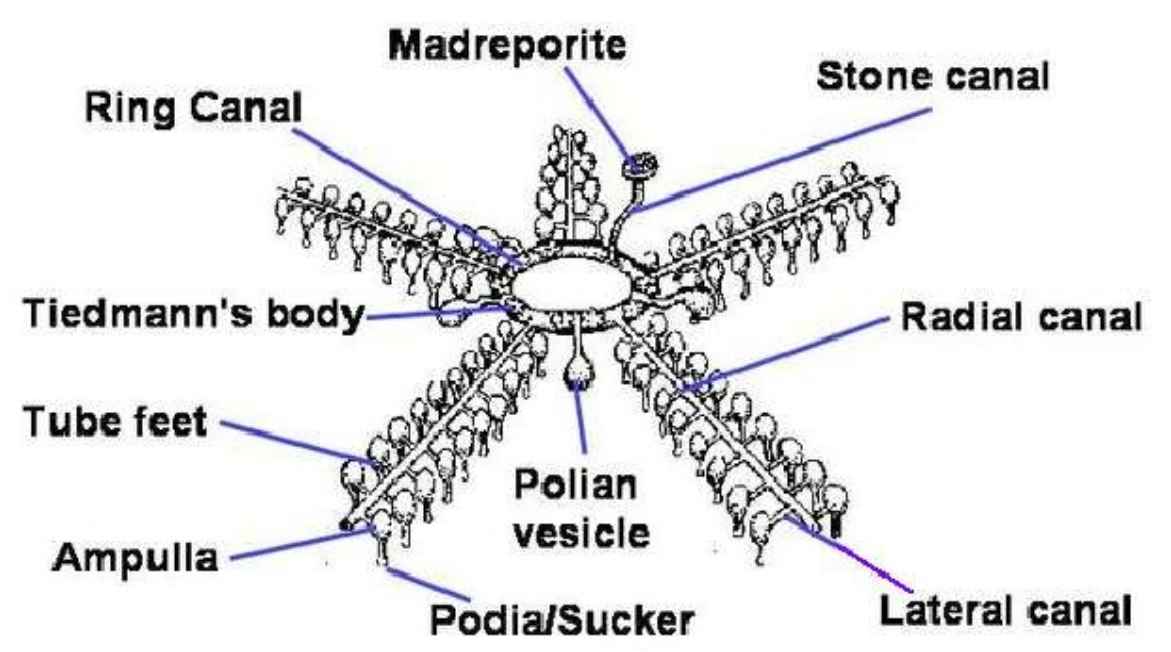
Fig: Water vascular system of Echinoderms
- Water enters the water vascular system through a calcareous opening called Madreporite.
- Madreporite is connected to a canal-like structure called stone canal.
- This stone canal is connected to the centrally located ring-like canal.
- Each arm receives a canal, the ring canal is connected to each arm with a radial canal.
- This radial canal is further divided into several branches known as lateral or transverse canal.
- Further lateral canal is connected to a sac-like structure called tube feet.
- Tube feet are sucker like structures through which the water is going outside. Tube feet help in locomotion, attachment and water to go out.
- Inner side of the ring canal has some specialized structures present which are known as Tiedemann’s bodies. The main function of Tiedemann’s bodies is to produce amoebocytes.
- Towards the outer side of the ring canal large vesicular structures are present on each arm known as Polian vesicles. The main function of Polian vesicles is to store additional amounts of water.
So, the correct answer is ‘Echinodermata (Sea cucumber)’.
Note:
A)Water vascular system is commonly called the ambulacral system.
B) Amoebocyte cells help in excretion.
Complete answer:
Water vascular system is found in Echinoderms. It helps in nutrition, locomotion, respiration, and excretion.
Additional information:
Water vascular system is described as:

Fig: Water vascular system of Echinoderms
- Water enters the water vascular system through a calcareous opening called Madreporite.
- Madreporite is connected to a canal-like structure called stone canal.
- This stone canal is connected to the centrally located ring-like canal.
- Each arm receives a canal, the ring canal is connected to each arm with a radial canal.
- This radial canal is further divided into several branches known as lateral or transverse canal.
- Further lateral canal is connected to a sac-like structure called tube feet.
- Tube feet are sucker like structures through which the water is going outside. Tube feet help in locomotion, attachment and water to go out.
- Inner side of the ring canal has some specialized structures present which are known as Tiedemann’s bodies. The main function of Tiedemann’s bodies is to produce amoebocytes.
- Towards the outer side of the ring canal large vesicular structures are present on each arm known as Polian vesicles. The main function of Polian vesicles is to store additional amounts of water.
So, the correct answer is ‘Echinodermata (Sea cucumber)’.
Note:
A)Water vascular system is commonly called the ambulacral system.
B) Amoebocyte cells help in excretion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




