
In which of the following reactions, the major product alkene is formed by ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ mechanism?
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{Br}}\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{{\text{alc}}{\text{. KOH}}}}$
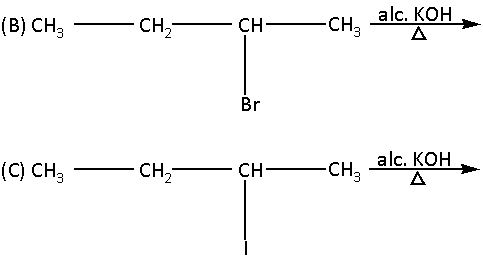
(D) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{F}}\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{{\text{alc}}{\text{. KOH}}}}$

Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this we must know the ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction. ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ stands for elimination of unimolecular conjugate base. ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction is a type of elimination reaction in which a relatively acidic hydrogen is removed and the leaving group is a poor leaving group. The ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction occurs in basic condition.
Complete solution:
We know that ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ stands for elimination of unimolecular conjugate bases. ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction is a type of elimination reaction in which a relatively acidic hydrogen is removed and the leaving group is a poor leaving group. The ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction occurs in basic condition.
The two conditions for ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction are as follows:
The leaving group must be a poor leaving group: The leaving groups that do not leave easily are known as poor leaving groups. Strong bases are poor leaving groups.
The compound must contain beta hydrogen atom: The second carbon that attaches to the functional group is known as beta carbon. And the hydrogen atom attached to a beta carbon is known as beta hydrogen atom.
We know that bromine is a weak base. Thus, bromine is a good leaving group.
Compound (A) and compound (B) has bromine as a leaving group. Thus, compound (A) and compound (B) do not undergo ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction.
Compound (D) does not contain a beta hydrogen atom. Thus, compound (D) does not undergo ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction.
Now, compound (C) has both a poor leaving group i.e. iodine and beta hydrogen atoms. Thus, compound (C) will undergo ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction.
The reaction is as follows:
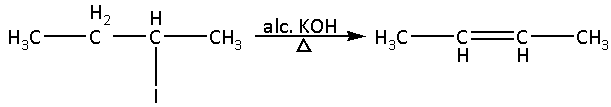
In the reaction, 2-butene is formed as a major product.
Thus, the correct option is (C).
Note: The ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction is a two-step reaction. In the first step, a base abstracts relatively acidic hydrogen and a stabilized anion is formed. In the second step, a lone pair of electrons on the anion moves to the neighbouring atom and thus the leaving group gets eliminated resulting in formation of a double or triple bond.
.
Complete solution:
We know that ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ stands for elimination of unimolecular conjugate bases. ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction is a type of elimination reaction in which a relatively acidic hydrogen is removed and the leaving group is a poor leaving group. The ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction occurs in basic condition.
The two conditions for ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction are as follows:
The leaving group must be a poor leaving group: The leaving groups that do not leave easily are known as poor leaving groups. Strong bases are poor leaving groups.
The compound must contain beta hydrogen atom: The second carbon that attaches to the functional group is known as beta carbon. And the hydrogen atom attached to a beta carbon is known as beta hydrogen atom.
We know that bromine is a weak base. Thus, bromine is a good leaving group.
Compound (A) and compound (B) has bromine as a leaving group. Thus, compound (A) and compound (B) do not undergo ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction.
Compound (D) does not contain a beta hydrogen atom. Thus, compound (D) does not undergo ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction.
Now, compound (C) has both a poor leaving group i.e. iodine and beta hydrogen atoms. Thus, compound (C) will undergo ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction.
The reaction is as follows:

In the reaction, 2-butene is formed as a major product.
Thus, the correct option is (C).
Note: The ${{\text{E}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{CB}}$ reaction is a two-step reaction. In the first step, a base abstracts relatively acidic hydrogen and a stabilized anion is formed. In the second step, a lone pair of electrons on the anion moves to the neighbouring atom and thus the leaving group gets eliminated resulting in formation of a double or triple bond.
.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




