
In which of the following reactions only a single isomer of alkene is formed on reaction with KOH and ethanol?
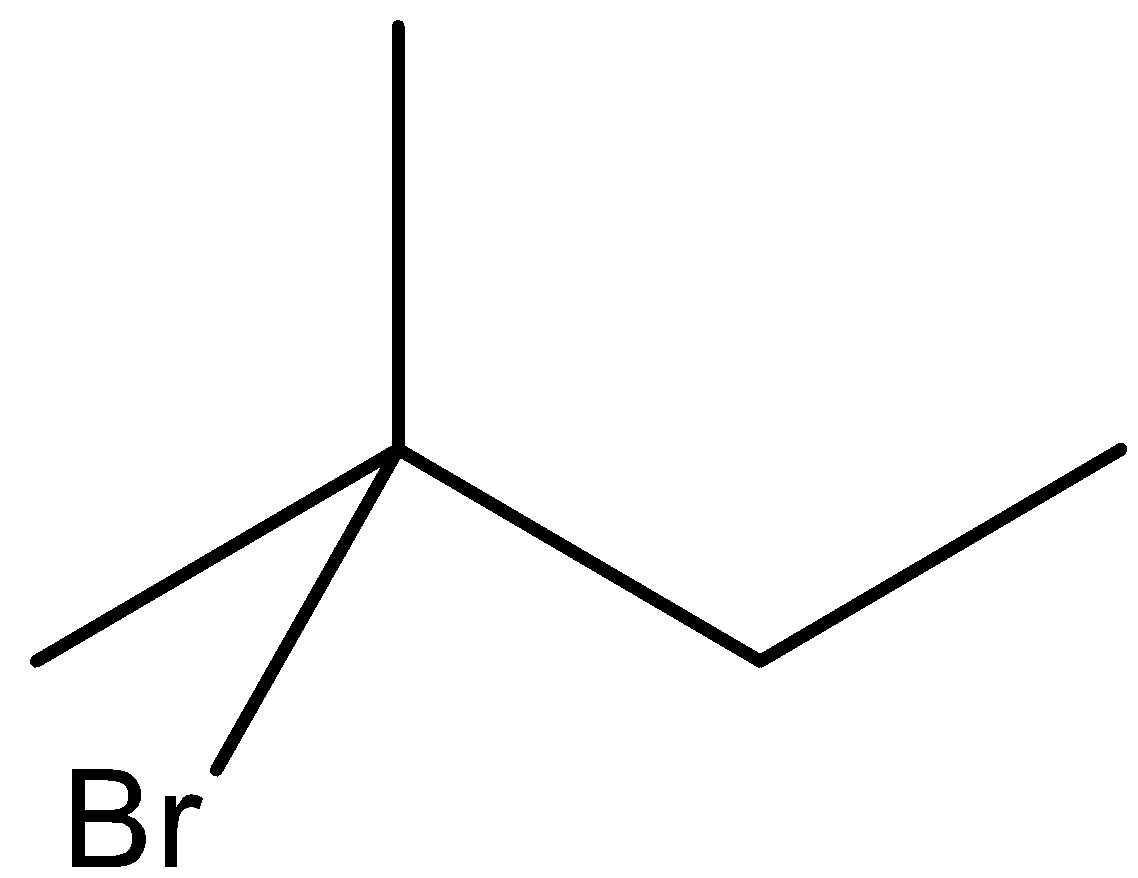
(a)-
(b)- ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-Br$
(c)- ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}-\overset{Br}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,-{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}$
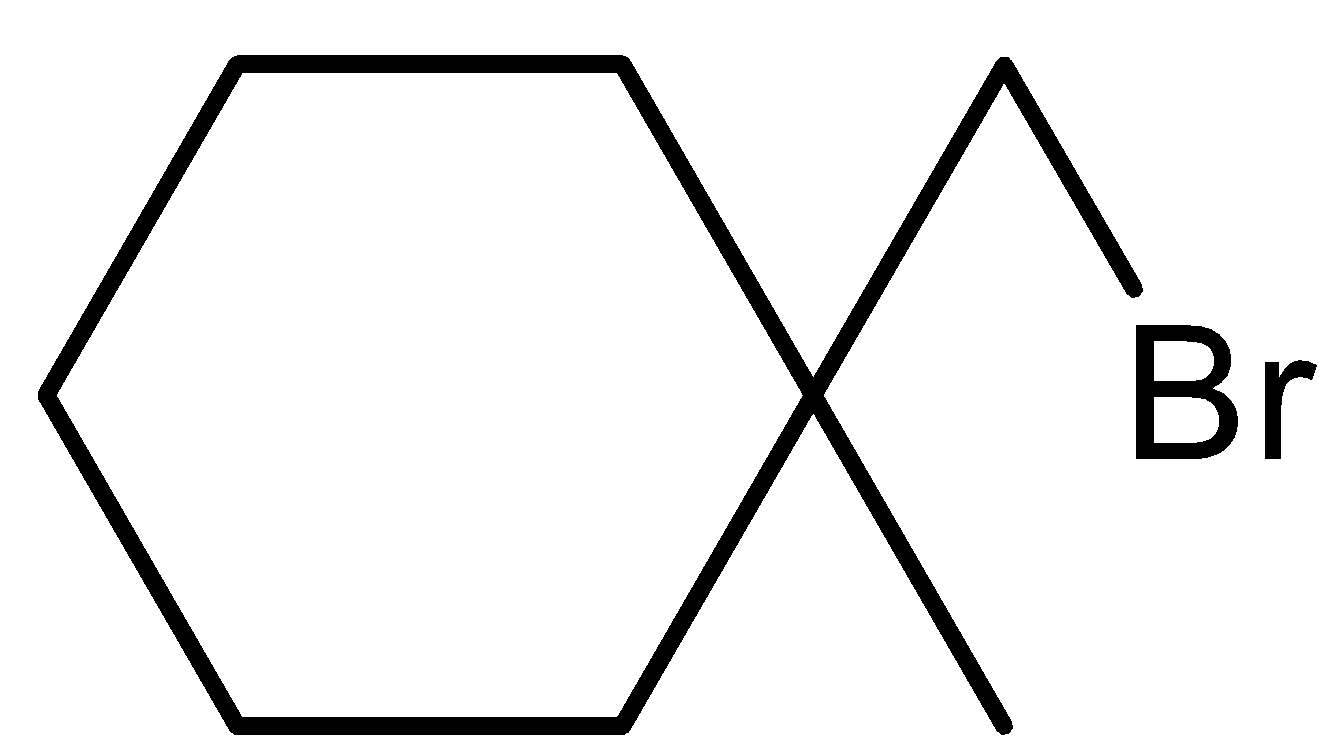
(d)-


Answer
542.4k+ views
Hint: In all the compounds, a bromine atom is present on the carbon chain, which means all are alkyl or aryl halides. When the alkyl or aryl halide reacts with KOH and ethanol, there will be the formation of an alkene by the elimination of bromine atoms and a hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon atom.
Complete answer:
In all the compounds, bromine atoms are present on the carbon chain, which means all are alkyl or aryl halides. When the alkyl or aryl halide reacts with KOH and ethanol, there will be the formation of an alkene by the elimination of bromine atoms and a hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon atom.
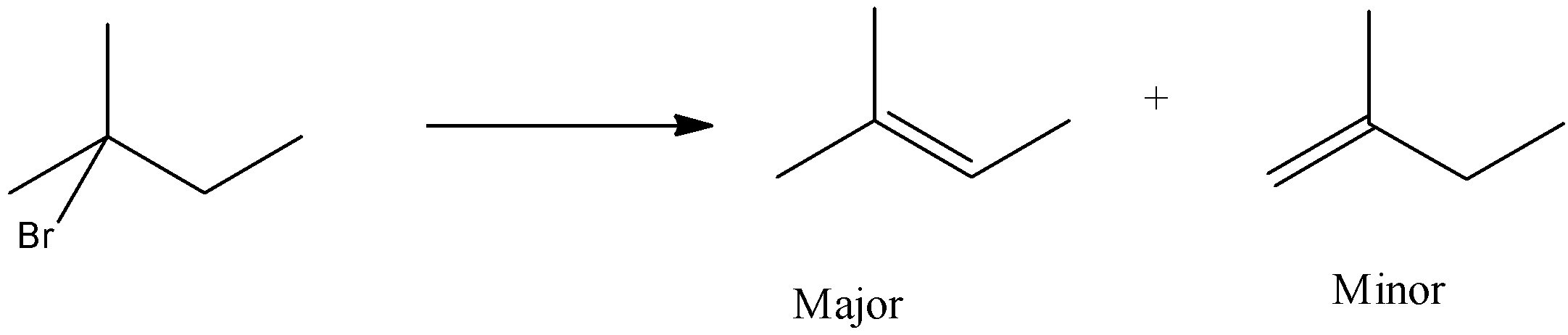
In option (a), the bromine is present on the second carbon atom, when it reacts with KOH and ethanol, then one product will be formed in which the hydrogen atom will be removed from the third carbon atom and the other from the first carbon atom.
In option (b), the bromine is present only on the terminal carbon atom, so the hydrogen atom will be removed from the carbon atom attached with the bromine atom.
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-Br\xrightarrow[ethanol]{KOH}{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}=CH$
In option (c), the bromine is present on the carbon atom between the phenyl groups, when it reacts with KOH and ethanol, then one product will be formed in which the hydrogen atom will be removed from the third carbon atom and the other from the first carbon atom.
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}-\overset{Br}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,-{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}\xrightarrow[ethanol]{KOH}{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}=CH-{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}+{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH={{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}$
In option (d), there will be no reaction because there is no hydrogen atom on the carbon atom that contains the bromine atom.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (b).
Note:
The reaction of an alkyl or aryl halide with the KOH and ethanol, then there is the formation of an alkene or when the alkyl or aryl halide reacts with KOH solution then there is the formation of alcohol.
Complete answer:
In all the compounds, bromine atoms are present on the carbon chain, which means all are alkyl or aryl halides. When the alkyl or aryl halide reacts with KOH and ethanol, there will be the formation of an alkene by the elimination of bromine atoms and a hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon atom.
In option (a), the bromine is present on the second carbon atom, when it reacts with KOH and ethanol, then one product will be formed in which the hydrogen atom will be removed from the third carbon atom and the other from the first carbon atom.

In option (b), the bromine is present only on the terminal carbon atom, so the hydrogen atom will be removed from the carbon atom attached with the bromine atom.
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-Br\xrightarrow[ethanol]{KOH}{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}=CH$
In option (c), the bromine is present on the carbon atom between the phenyl groups, when it reacts with KOH and ethanol, then one product will be formed in which the hydrogen atom will be removed from the third carbon atom and the other from the first carbon atom.
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}-\overset{Br}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,-{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}\xrightarrow[ethanol]{KOH}{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}=CH-{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}+{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH={{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}$
In option (d), there will be no reaction because there is no hydrogen atom on the carbon atom that contains the bromine atom.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (b).
Note:
The reaction of an alkyl or aryl halide with the KOH and ethanol, then there is the formation of an alkene or when the alkyl or aryl halide reacts with KOH solution then there is the formation of alcohol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




