
In which of the following reactions a new C-C bond is formed in the preparation of ethane?
A) Sabatier-Senderens reaction.
B) Reduction of ethyl iodide.
C) Decarboxylation.
D) Kolbe’s electrolysis.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: We know that The Kolbe electrolysis or Kolbe reaction is an organic reaction named after Hermann Kolbe. The Kolbe reaction is formally a decarboxylative dimerization of two carboxylic acids (or carboxylate ions).
Complete step by step answer:
We must remember that the Sabatier-Senderens reaction is a reaction in which the large quantity of ethane is prepared by the catalytic hydrogenation of ethylene.
The example of this reaction is given as,
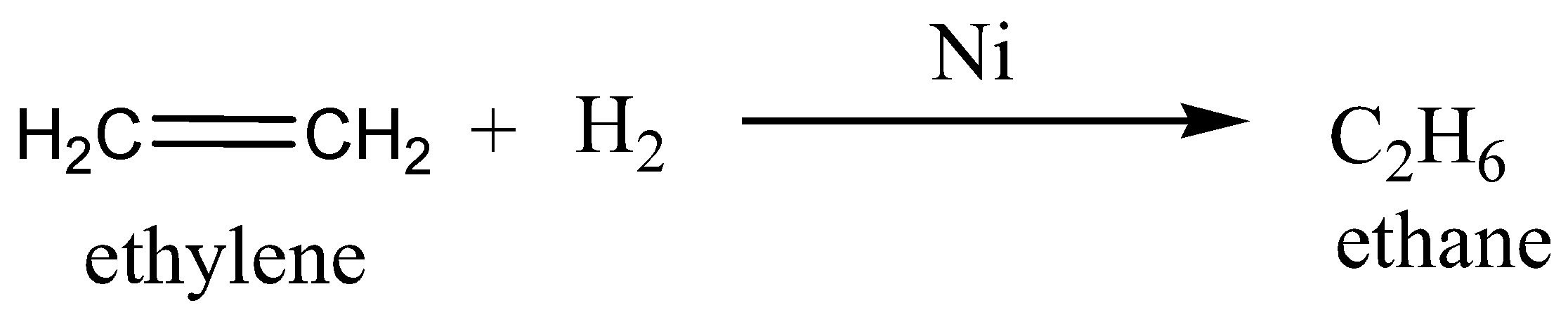
Therefore, the option A is incorrect.
When ethyl iodide reacts with \[\;Zn - {\text{ }}Cu\] couple and ethyl alcohol, iodide is reduced to yield ethane. We can write a chemical equation for the above reaction as,
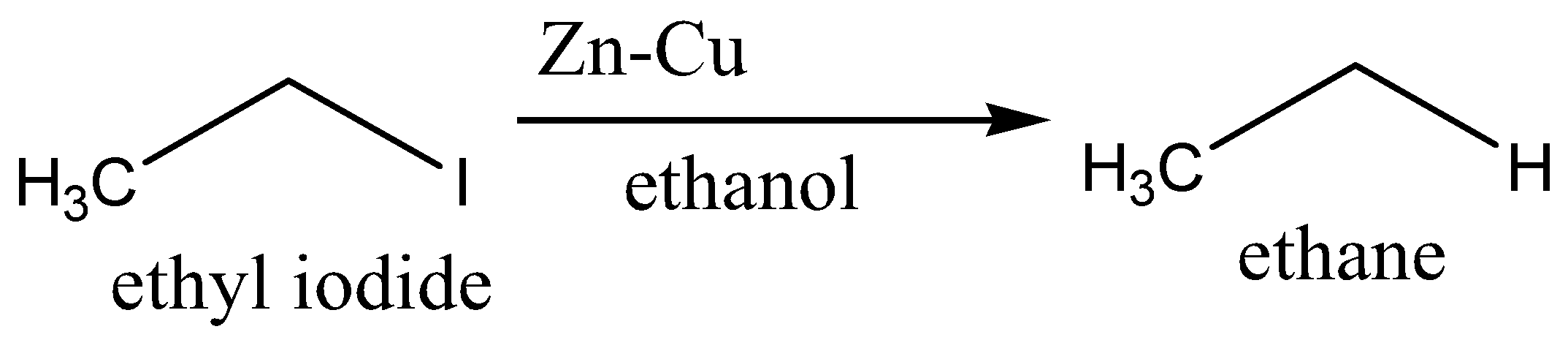
Therefore, the option B is incorrect.
As we know that the Decarboxylation reaction is defined as a reaction to eliminate a carboxyl and releases carbon dioxide. Decarboxylation generally refers to a reaction in which carboxylic acids remove an atom from a series of carbons. Carboxylation may be a total process which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, where Carbon dioxide is added to the compound. Whereas, Enzymes like zymase that catalyse decarboxylation are referred to as decarboxylases. We can write a chemical equation for the above reaction as,
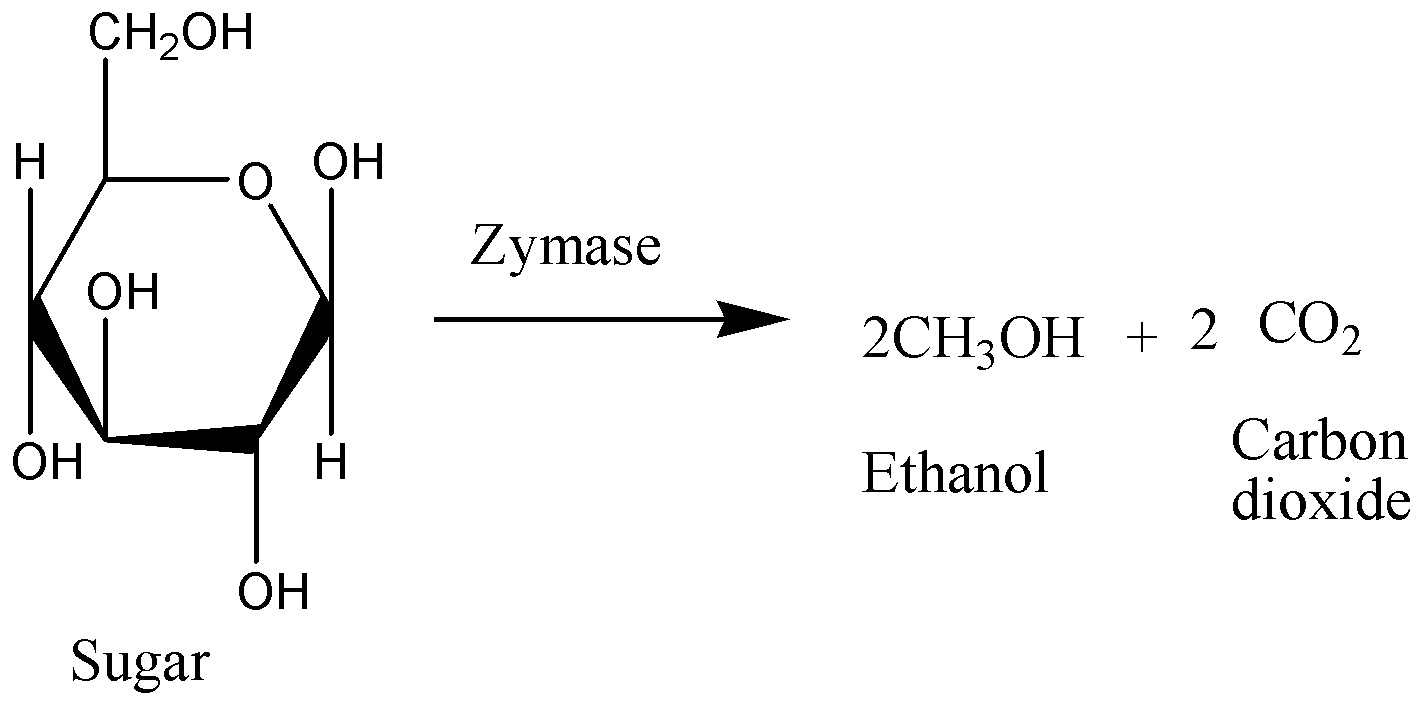
Therefore, the option C is incorrect.
The Kolbe reaction is properly a decarboxylative dimerization of two carboxylic acids or carboxylate ions. We can write a chemical equation for the above reaction as,
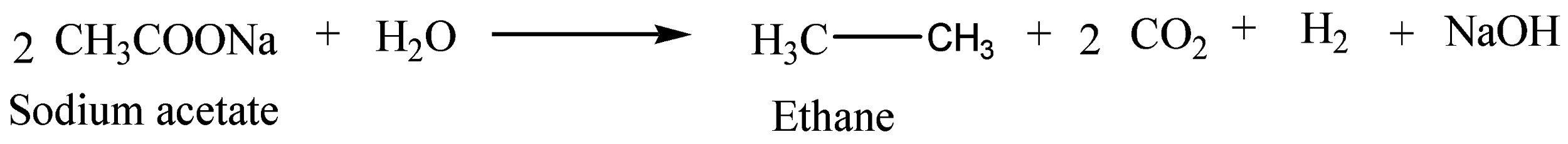
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: Don’t confuse Kolbe's electrolysis and Kolbe’s Schmitt reaction we know that reaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide is Kolbe’s Process and an aromatic hydroxy acid is obtained as the end product. In this reaction mechanism there is the nucleophilic addition of sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide to give salicylate
Complete step by step answer:
We must remember that the Sabatier-Senderens reaction is a reaction in which the large quantity of ethane is prepared by the catalytic hydrogenation of ethylene.
The example of this reaction is given as,
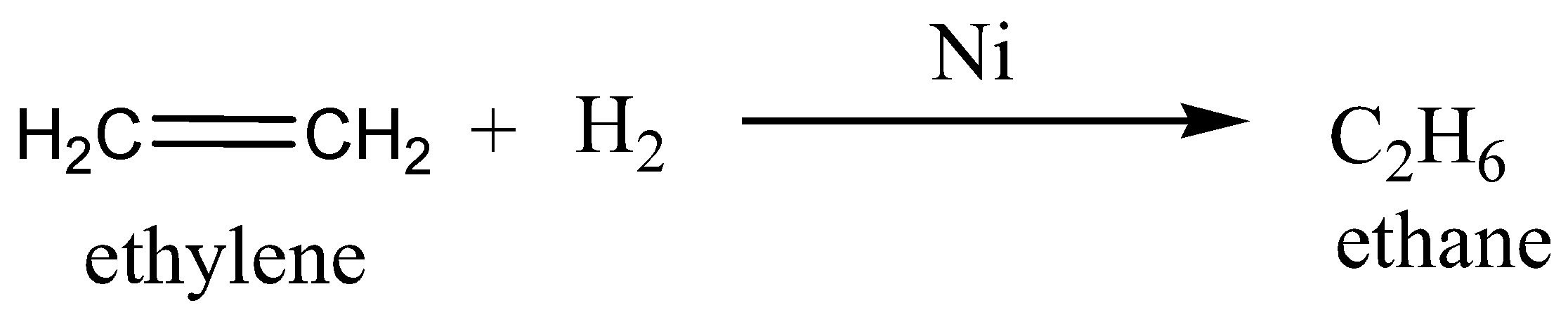
Therefore, the option A is incorrect.
When ethyl iodide reacts with \[\;Zn - {\text{ }}Cu\] couple and ethyl alcohol, iodide is reduced to yield ethane. We can write a chemical equation for the above reaction as,
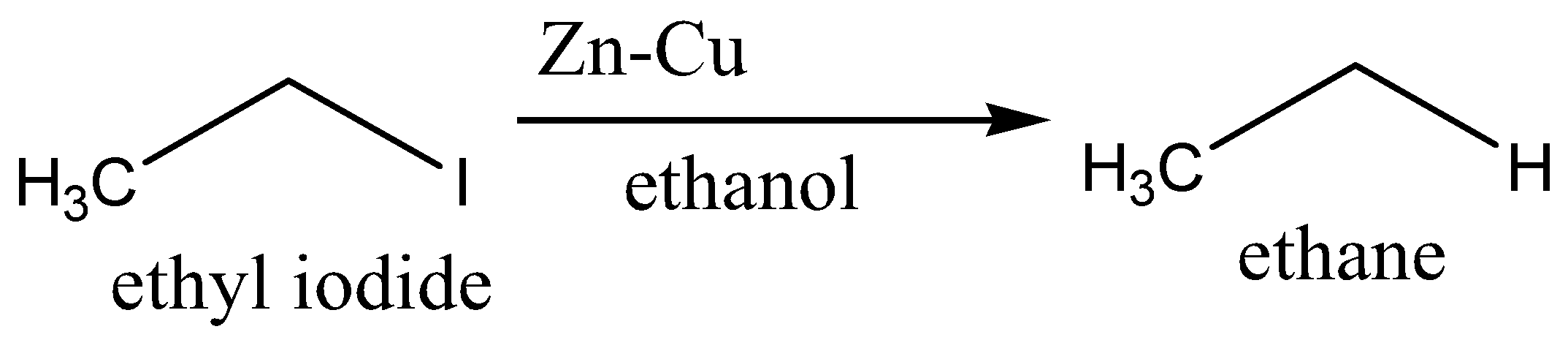
Therefore, the option B is incorrect.
As we know that the Decarboxylation reaction is defined as a reaction to eliminate a carboxyl and releases carbon dioxide. Decarboxylation generally refers to a reaction in which carboxylic acids remove an atom from a series of carbons. Carboxylation may be a total process which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, where Carbon dioxide is added to the compound. Whereas, Enzymes like zymase that catalyse decarboxylation are referred to as decarboxylases. We can write a chemical equation for the above reaction as,

Therefore, the option C is incorrect.
The Kolbe reaction is properly a decarboxylative dimerization of two carboxylic acids or carboxylate ions. We can write a chemical equation for the above reaction as,
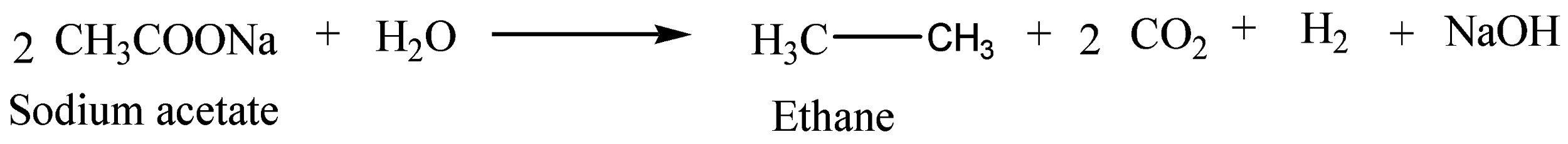
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: Don’t confuse Kolbe's electrolysis and Kolbe’s Schmitt reaction we know that reaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide is Kolbe’s Process and an aromatic hydroxy acid is obtained as the end product. In this reaction mechanism there is the nucleophilic addition of sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide to give salicylate
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




