
In which of the following molecules all atoms are not coplanar?
A.
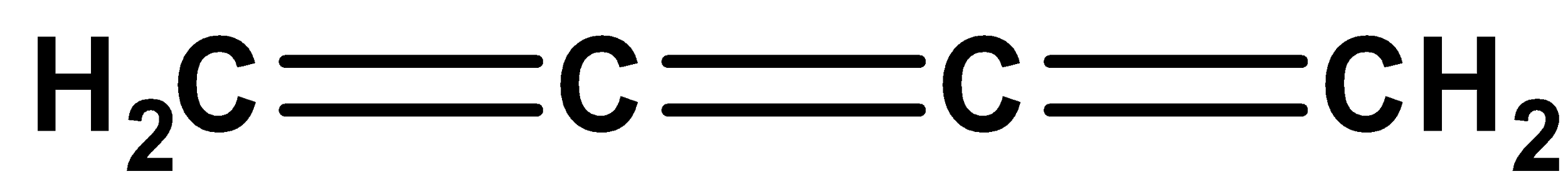
B.
C.
D.
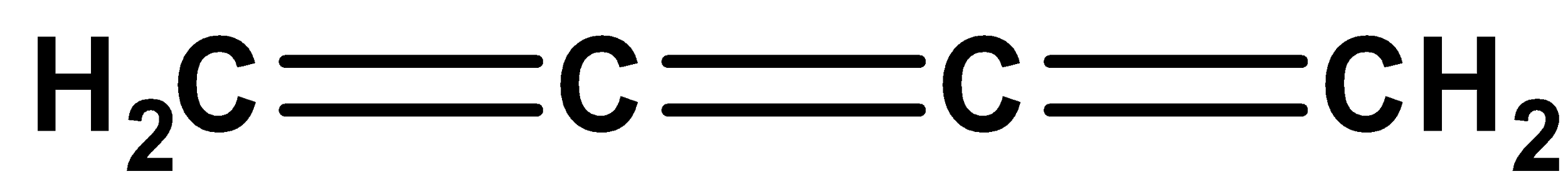



Answer
561k+ views
Hint: The molecule is said to be coplanar if they lie in the same plane. A double bond is restricted for rotation whereas a single bond is free to rotate. The geometry for \[s{p^3}\] rotation is tetrahedral and it is not coplanar. When the carbon has \[s{p^2}(or)sp\] hybridization, then it will act as coplanar since double and triple bonds are restricted in rotation.
Complete step by step answer:
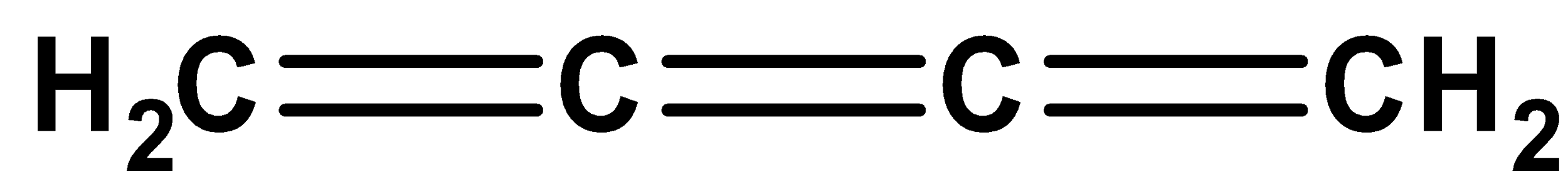
The given compound is coplanar since the hybridization for two terminal carbon atoms present in the given molecules is \[s{p^2}\] and for non-terminal atoms is Sp. Thus, it exists in coplanar
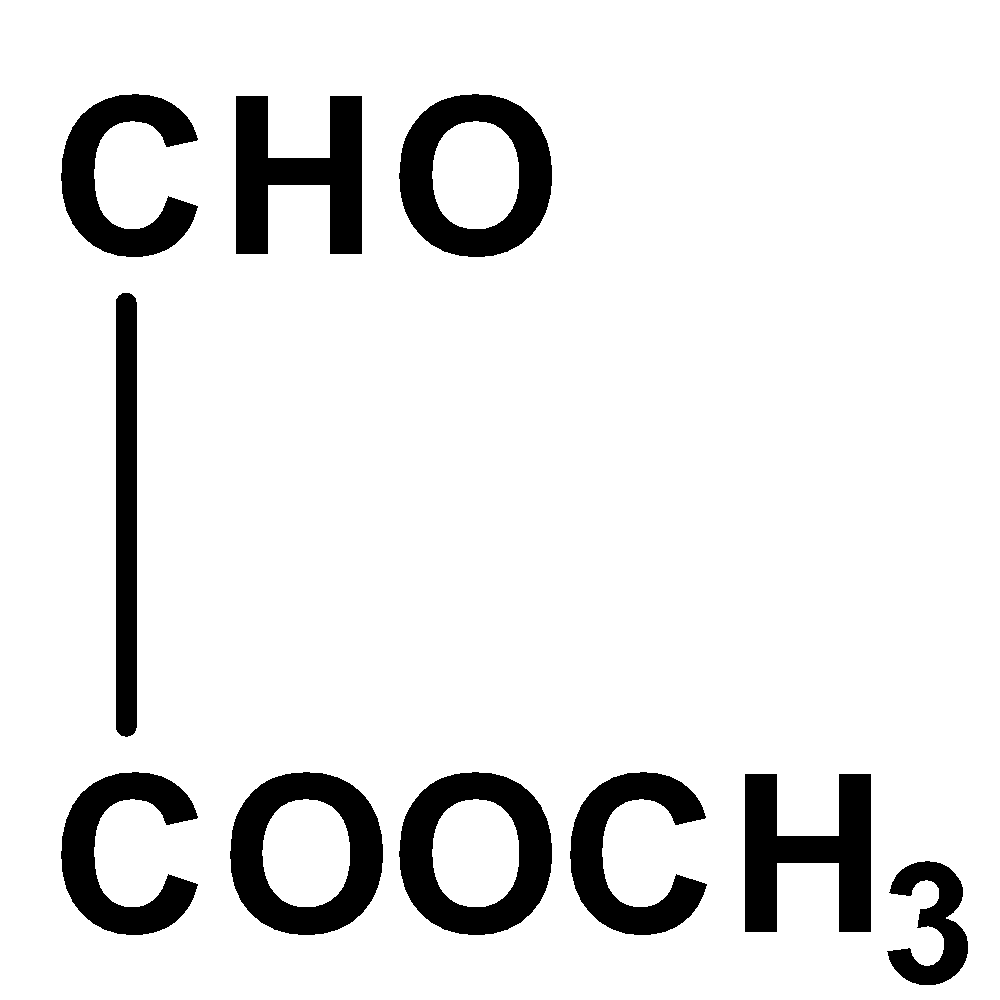
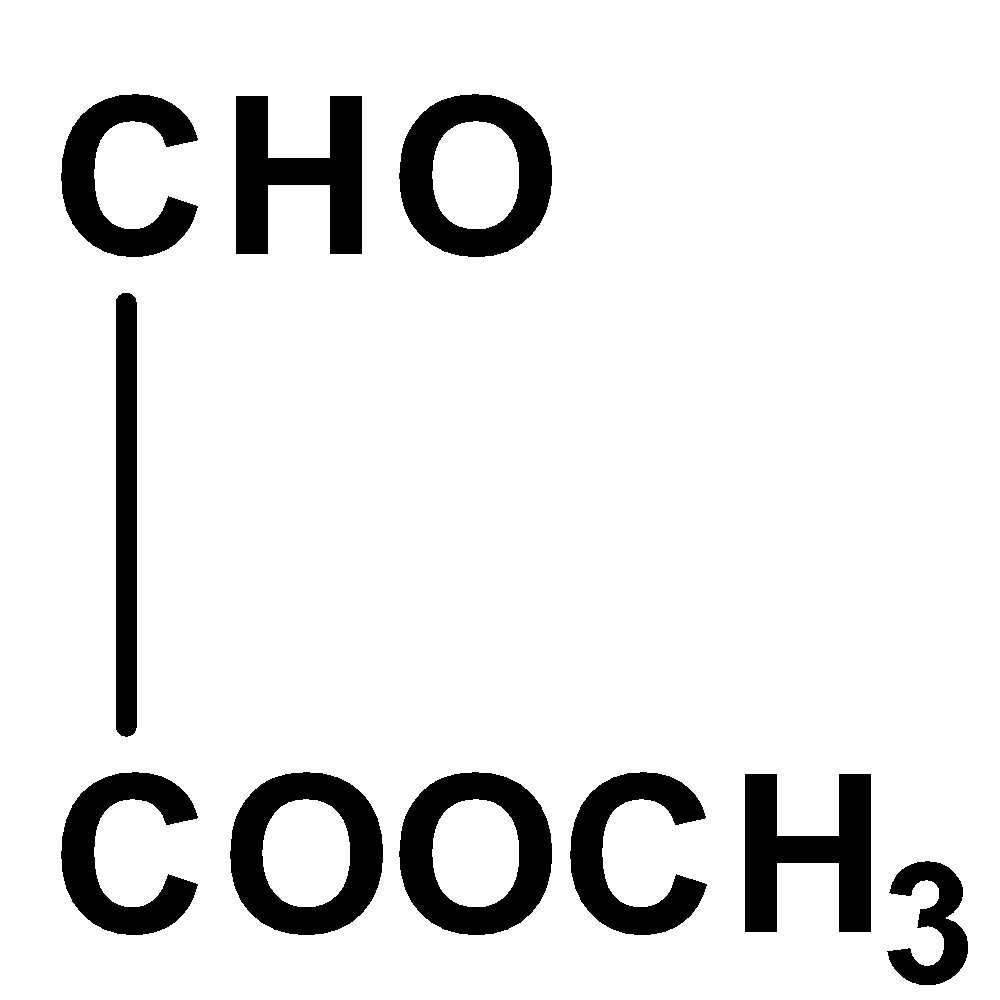
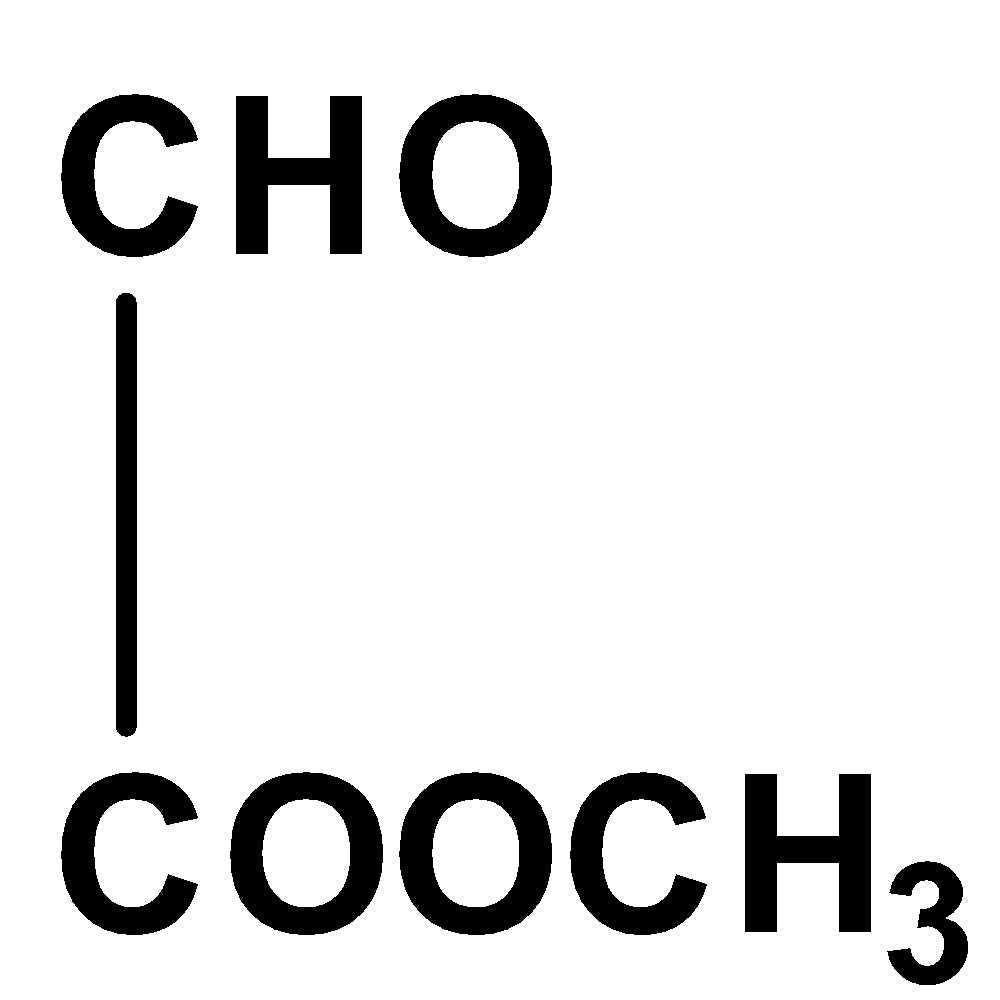
The given compound is not coplanar since the carbon in aldehyde group has hybridization \[s{p^2}\] and for methyl group in ester molecule, its hybridization is \[s{p^3}\] and thus, it would not exist in the same plane due to its unrestricted rotation.
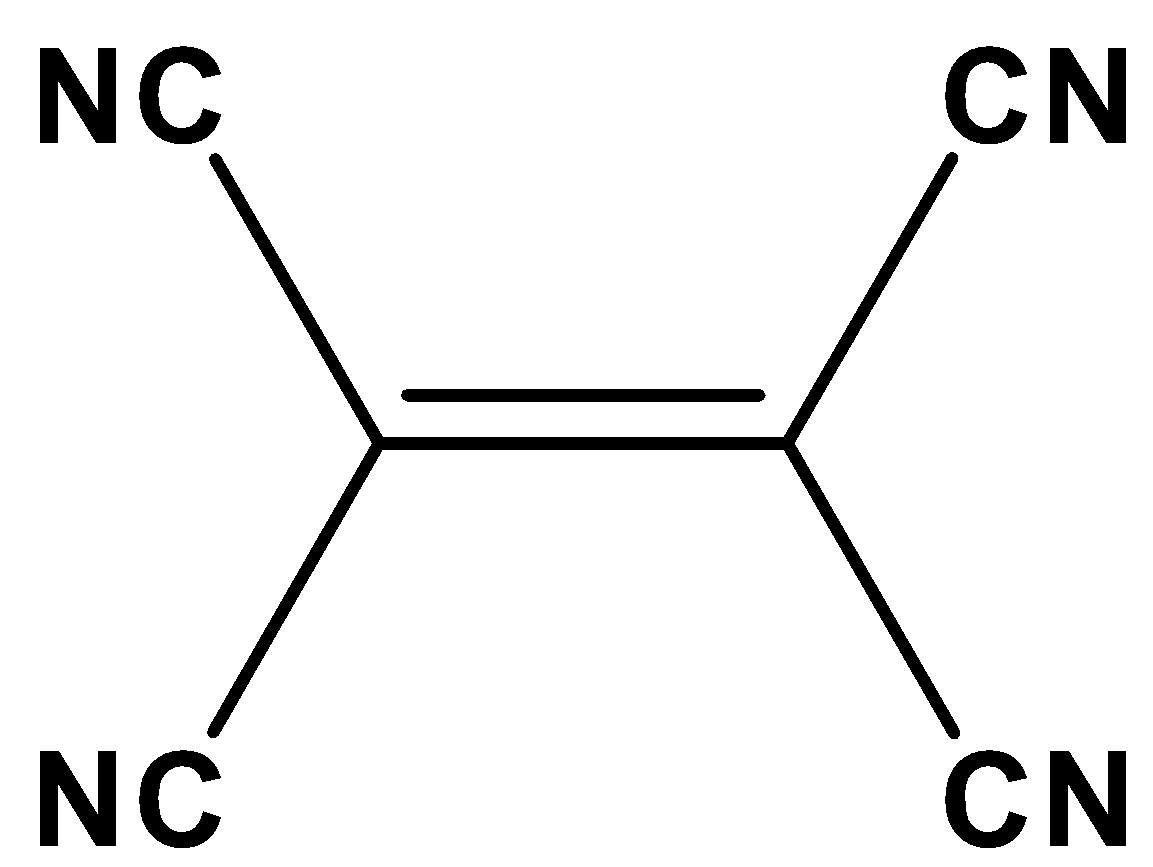
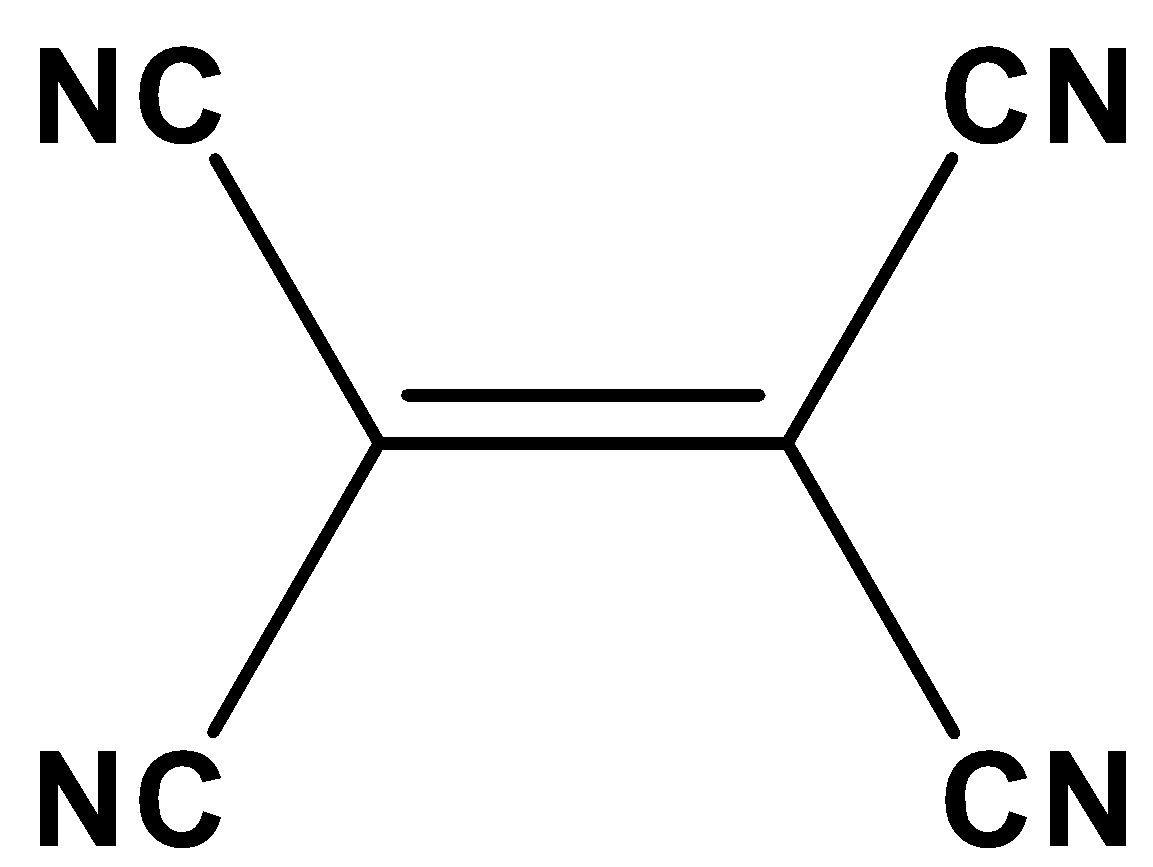
The given compound is coplanar since the carbon atom present in the cyanide atom of the given molecule has Sp hybridization and carbon present between double bonds of the given molecule has \[s{p^2}\] hybridization. Thus, it remains as coplanar.
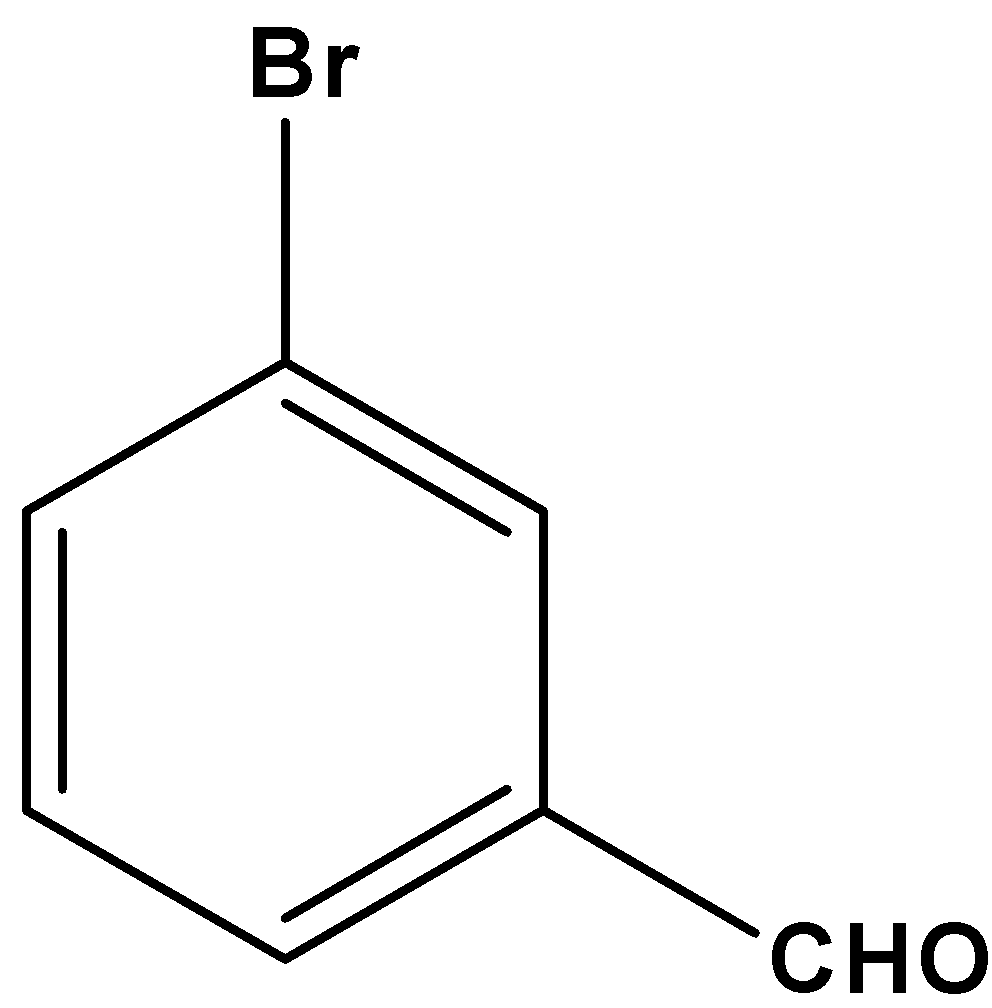
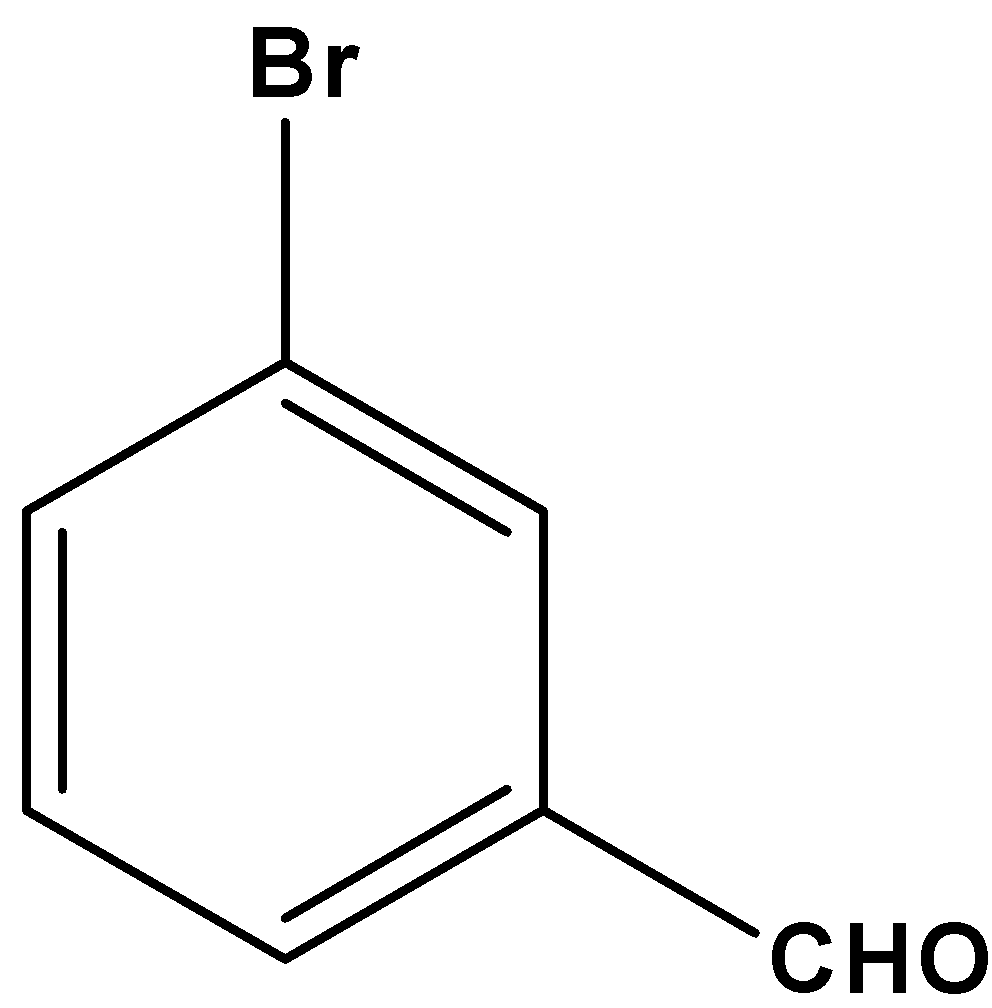
The given compound is coplanar since all the carbon atoms present in the given molecule are \[s{p^2}\] hybridized. Thus, it remains on the same plane.
Thus, the compound is not coplanar.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: The hybridization of any organic compounds can be easily identified by the number of single (sigma) bonds present in the given compound. If the compound has three sigma bonds, then its hybridization will be \[s{p^2}\] and the best example is ethylene. If the compound has two sigma bonds, then its hybridization will be \[sp\] and the best example is ethyne. If the compound has four sigma bonds, then its hybridization will be \[s{p^3}\] and the best example is methane.
Complete step by step answer:
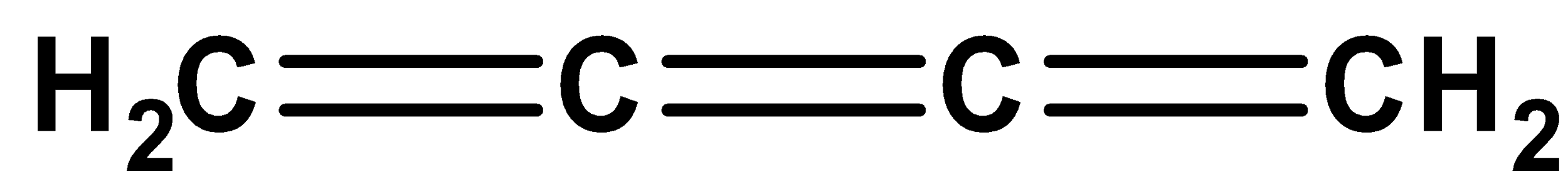
The given compound is coplanar since the hybridization for two terminal carbon atoms present in the given molecules is \[s{p^2}\] and for non-terminal atoms is Sp. Thus, it exists in coplanar

The given compound is not coplanar since the carbon in aldehyde group has hybridization \[s{p^2}\] and for methyl group in ester molecule, its hybridization is \[s{p^3}\] and thus, it would not exist in the same plane due to its unrestricted rotation.

The given compound is coplanar since the carbon atom present in the cyanide atom of the given molecule has Sp hybridization and carbon present between double bonds of the given molecule has \[s{p^2}\] hybridization. Thus, it remains as coplanar.

The given compound is coplanar since all the carbon atoms present in the given molecule are \[s{p^2}\] hybridized. Thus, it remains on the same plane.
Thus, the compound is not coplanar.

So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: The hybridization of any organic compounds can be easily identified by the number of single (sigma) bonds present in the given compound. If the compound has three sigma bonds, then its hybridization will be \[s{p^2}\] and the best example is ethylene. If the compound has two sigma bonds, then its hybridization will be \[sp\] and the best example is ethyne. If the compound has four sigma bonds, then its hybridization will be \[s{p^3}\] and the best example is methane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




