
In which of the following mitochondria is not found?
(a) Leucocytes
(b) Hepatocytes
(c) Erythrocytes
(d) Adipose cells
Answer
595.2k+ views
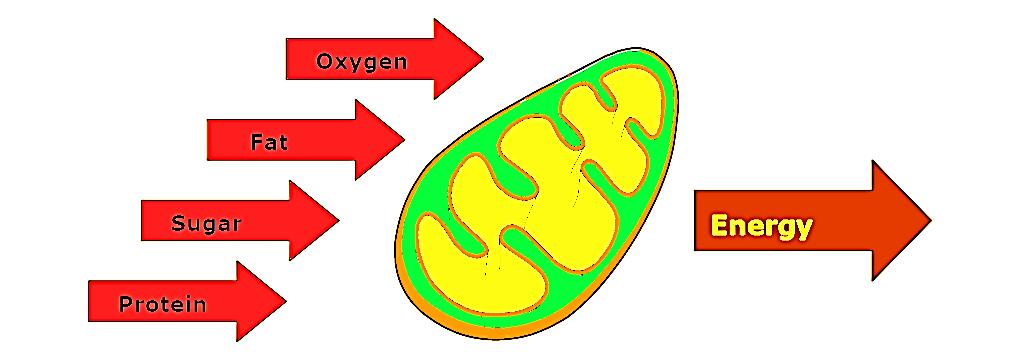
Hint: Mitochondria uses oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP. Cells that respire anaerobically don't require oxygen for energy production.
Complete answer:
RBCs (Erythrocytes) carry oxygen for metabolic functions. The mitochondria use oxygen to produce ATP for cells. In order to preserve oxygen, the RBCs respire anaerobically and don’t contain mitochondria.
Additional Information:
-Mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of almost all eukaryotic cells.
- Its primary function is to generate large quantities of energy in the form of ATP.
- The only Eukaryotic organism which does not have mitochondria is the oxymonad Monocercomonoides species.
-Cells that require a lot of energy can contain thousands of mitochondria. For example, Muscle cells.
-Prokaryotic organisms do not have mitochondria.
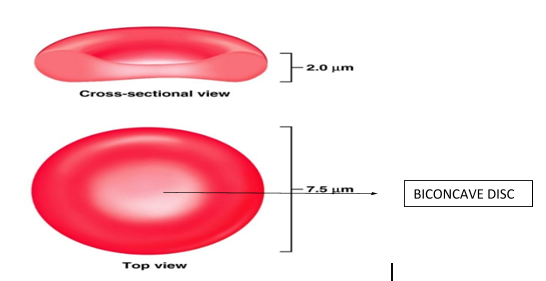
-Mammalian RBCs are typically biconcave disc-flattened and depressed in center and are very flexible so that they can squeeze through the tiny capillaries.
-RBCs lack mitochondria and nucleus.
-The removal of mitochondria and nucleus from the RBCs makes more space for hemoglobin to be carried.
-RBCs respire anaerobically. Thus, it doesn’t utilize oxygen for energy production.
-Since RBCs lack mitochondria, they use glycolysis of glucose and lactic acid fermentation to produce ATP.
-RBCs don’t have much role in biosynthesis (like replication, transcription, and translation). Therefore, its viability doesn’t go forever unlike other differentiated cells.
-RBCs have a lifetime of about 120 days.
So, the correct answer is, 'Erythrocytes'
Note: RBCs have mitochondria, nuclei, and other cell organelles during the early phases of erythropoiesis. Extrudes them during the development as they mature (at the stage of late normoblast).
Normal red blood cell: -
Complete answer:
RBCs (Erythrocytes) carry oxygen for metabolic functions. The mitochondria use oxygen to produce ATP for cells. In order to preserve oxygen, the RBCs respire anaerobically and don’t contain mitochondria.
Additional Information:
-Mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of almost all eukaryotic cells.
- Its primary function is to generate large quantities of energy in the form of ATP.
- The only Eukaryotic organism which does not have mitochondria is the oxymonad Monocercomonoides species.
-Cells that require a lot of energy can contain thousands of mitochondria. For example, Muscle cells.
-Prokaryotic organisms do not have mitochondria.
-Mammalian RBCs are typically biconcave disc-flattened and depressed in center and are very flexible so that they can squeeze through the tiny capillaries.
-RBCs lack mitochondria and nucleus.
-The removal of mitochondria and nucleus from the RBCs makes more space for hemoglobin to be carried.
-RBCs respire anaerobically. Thus, it doesn’t utilize oxygen for energy production.
-Since RBCs lack mitochondria, they use glycolysis of glucose and lactic acid fermentation to produce ATP.
-RBCs don’t have much role in biosynthesis (like replication, transcription, and translation). Therefore, its viability doesn’t go forever unlike other differentiated cells.
-RBCs have a lifetime of about 120 days.
So, the correct answer is, 'Erythrocytes'
Note: RBCs have mitochondria, nuclei, and other cell organelles during the early phases of erythropoiesis. Extrudes them during the development as they mature (at the stage of late normoblast).

Normal red blood cell: -

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




