
In which of the following, functional group isomerism is not possible?
A.Alcohols
B.Aldehyde
C.Alkyl halides
D.Cyanides
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Functional isomers are a type of structural isomers having different functional groups. This isomerism thus results in significantly different physical and chemical properties.
In other words, functional isomerism occurs when the substances have the same molecular formula but different functional groups.
Complete step by step answer:
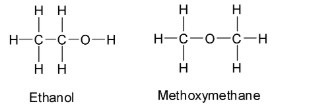
Alcohols are functional group isomers with ethers. The functional group in alcohols is the hydroxyl group, ${\text{ - OH}}$ whereas, the functional group in ethers is the ${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ - O - }}{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}$ group. The symbols ${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}$ and ${{\text{R}}_2}$ represents alkyl groups. They also represent the structure of the rest of the molecule. The alkyl groups can be same or different. If one of the alkyl groups is hydrogen, then the compound contains a hydroxyl group and is not an ether.
For example, let us consider ethanol and methoxymethane. Both of them contain the same molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}}$ but have different functional groups which are hydroxyl group and ${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ - O - }}{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}$ group respectively. So they are functional isomers of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}}$ .
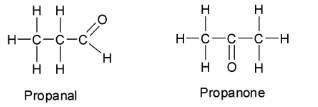
Aldehydes are functional group isomers with ketones. Aldehydes as well as ketones have the carbonyl group ${\text{ - C = O}}$ . In case of aldehydes, the functional group is attached to one or two hydrogens and in case of ketones, the functional group is attached to two carbon atoms. For example, propanal and propanone have the same molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}}$ but different functional groups ${\text{ - C}}\left( {{\text{ = O}}} \right){\text{H}}$ and ${\text{ - C}}\left( {{\text{ = O}}} \right){\text{C}}$ respectively and so they are functional isomers of ${{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}}$.
Cyanides are functional isomers with isocyanides as they both have the same molecular formula but different functional groups ${\text{ - CN}}$ and ${\text{ - NC}}$ respectively.
Alkyl halides do not have any functional group isomers as there is only one way to attach a halogen to a carbon atom via a single bond.
So, C is the correct option.
Note:
Another pair of functional isomers is carboxylic acids and esters. Carboxylic acids have the functional group ${\text{ - COOH}}$ and esters have the functional group ${{\text{R}}_1}{\text{ - COO}}{{\text{R}}_2}$ where${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}$ and ${{\text{R}}_2}$ represents alkyl groups.
In other words, functional isomerism occurs when the substances have the same molecular formula but different functional groups.
Complete step by step answer:
Alcohols are functional group isomers with ethers. The functional group in alcohols is the hydroxyl group, ${\text{ - OH}}$ whereas, the functional group in ethers is the ${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ - O - }}{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}$ group. The symbols ${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}$ and ${{\text{R}}_2}$ represents alkyl groups. They also represent the structure of the rest of the molecule. The alkyl groups can be same or different. If one of the alkyl groups is hydrogen, then the compound contains a hydroxyl group and is not an ether.
For example, let us consider ethanol and methoxymethane. Both of them contain the same molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}}$ but have different functional groups which are hydroxyl group and ${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ - O - }}{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}$ group respectively. So they are functional isomers of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}}$ .

Aldehydes are functional group isomers with ketones. Aldehydes as well as ketones have the carbonyl group ${\text{ - C = O}}$ . In case of aldehydes, the functional group is attached to one or two hydrogens and in case of ketones, the functional group is attached to two carbon atoms. For example, propanal and propanone have the same molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}}$ but different functional groups ${\text{ - C}}\left( {{\text{ = O}}} \right){\text{H}}$ and ${\text{ - C}}\left( {{\text{ = O}}} \right){\text{C}}$ respectively and so they are functional isomers of ${{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}}$.

Cyanides are functional isomers with isocyanides as they both have the same molecular formula but different functional groups ${\text{ - CN}}$ and ${\text{ - NC}}$ respectively.
Alkyl halides do not have any functional group isomers as there is only one way to attach a halogen to a carbon atom via a single bond.
So, C is the correct option.
Note:
Another pair of functional isomers is carboxylic acids and esters. Carboxylic acids have the functional group ${\text{ - COOH}}$ and esters have the functional group ${{\text{R}}_1}{\text{ - COO}}{{\text{R}}_2}$ where${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}$ and ${{\text{R}}_2}$ represents alkyl groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




