
In which of the following +M effect is in operative mode:
(A)
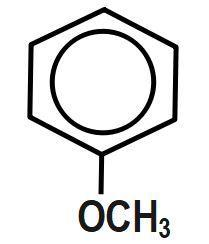
(B)
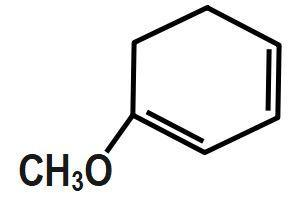
(C)
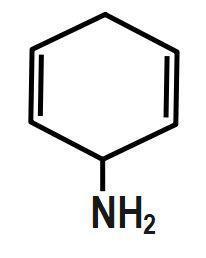
(D) ALL



Answer
513.3k+ views
Hint :We know that in order to solve this question we have to know the mesomeric effect than we will be checking one by one all the options and check the $ +M $ effect and we will find in how of it will be showing the mesomeric effect or else To get the appropriate answer of this question, first of all try to explain what inductive effect, mesomeric effect and Baker Nathan effect (also called as electromeric effect).
Complete Step By Step Answer:
First of all, let us know some of the terms before going to know the answer to this question. So, coming to the term inductive effect: Inductive effect: Inductive effect occurs in a molecule because of the unequal sharing of the bonding electrons within the molecule. The inductive effect is seen by sigma bonds while the electromeric effect is seen by pi-bonds only. Mesomeric effect: The polarity developed between atoms of a conjugated system by the electron transfer or pi-bond electron transfer is known as the mesomeric effect. This occurs when pi electrons move away from or towards a substituent group in a conjugated orbital system. Baker effect: The Baker effect or ‘electromeric effect’ or hyperconjugation, is a temporary effect mainly experienced in the presence of an attacking reagent in the vicinity of an organic compound having multiple bonds (a double or triple bond).
The mesomeric effect in chemistry is a property of substituents or functional groups in a chemical compound. It is defined as the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi bonds or between a pi bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacent atom. Now we will be reading $ +M $ effect and $ -M $ effect: $ +M $ effect: When the electrons are transferred from a particular group towards a conjugate system, this increases the electron density of the conjugate system then such a phenomenon is known as $ +M $ effect electron donating mesomeric effect. For the $ +M $ effect the group should have a lone pair or negative charge.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Additional Information:
In this effect, the complete transfer of a shared pair of pi electrons to one of the atoms joined by multiple bonds on the demand of an attacking reagent takes place. So, here in the question let us consider all molecules one by one. For the first option, there is no Baker effect or mesomeric effect while in the second and third option; the molecules are all alkyl groups. Hence, there will be no inductive effect. And in the fourth option, the respective molecule shows all the effects.
Note :
Remember that the inductive effect is seen where there is presence of electronegative atom while mesomeric effect is seen by a molecule due to presence of conjugated double or triple bonds and Baker effect is due to the presence of free pi orbitals.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
First of all, let us know some of the terms before going to know the answer to this question. So, coming to the term inductive effect: Inductive effect: Inductive effect occurs in a molecule because of the unequal sharing of the bonding electrons within the molecule. The inductive effect is seen by sigma bonds while the electromeric effect is seen by pi-bonds only. Mesomeric effect: The polarity developed between atoms of a conjugated system by the electron transfer or pi-bond electron transfer is known as the mesomeric effect. This occurs when pi electrons move away from or towards a substituent group in a conjugated orbital system. Baker effect: The Baker effect or ‘electromeric effect’ or hyperconjugation, is a temporary effect mainly experienced in the presence of an attacking reagent in the vicinity of an organic compound having multiple bonds (a double or triple bond).
The mesomeric effect in chemistry is a property of substituents or functional groups in a chemical compound. It is defined as the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi bonds or between a pi bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacent atom. Now we will be reading $ +M $ effect and $ -M $ effect: $ +M $ effect: When the electrons are transferred from a particular group towards a conjugate system, this increases the electron density of the conjugate system then such a phenomenon is known as $ +M $ effect electron donating mesomeric effect. For the $ +M $ effect the group should have a lone pair or negative charge.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Additional Information:
In this effect, the complete transfer of a shared pair of pi electrons to one of the atoms joined by multiple bonds on the demand of an attacking reagent takes place. So, here in the question let us consider all molecules one by one. For the first option, there is no Baker effect or mesomeric effect while in the second and third option; the molecules are all alkyl groups. Hence, there will be no inductive effect. And in the fourth option, the respective molecule shows all the effects.
Note :
Remember that the inductive effect is seen where there is presence of electronegative atom while mesomeric effect is seen by a molecule due to presence of conjugated double or triple bonds and Baker effect is due to the presence of free pi orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




