
In which of the compounds, cross conjugation is present?
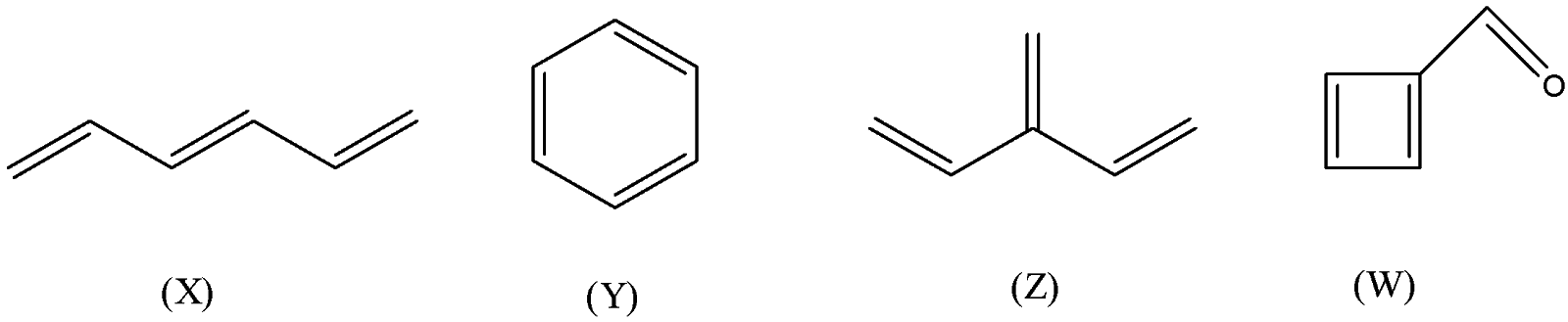
A.\[{{X,Y}}\]
B.\[{{Y,Z,W}}\]
C. \[{{X,Y,Z,W}}\]
D. \[{{only Z}}\]

Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint: Conjugation is the overlap of one p-orbital with another across an intervening sigma bond. In larger atoms d-orbitals can be involved. The compounds in which the bonds are conjugated (alternating multiple and single bonds) are slightly more stable than those in which they are isolated.
Complete step by step answer:
Cross conjugation is a special type of conjugation in a molecule. When in a set of three Pi bonds, only two Pi bonds interact with each other by conjugation and the third one is excluded from interaction.
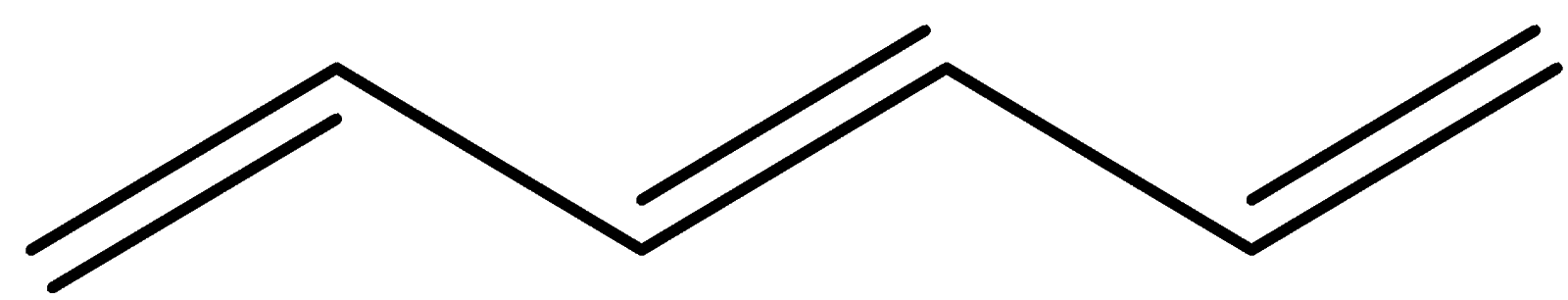
In this structure, there’s a double bond then a sigma bond and then a double bond and then a sigma bond. This is called conjugation. Here we can see overlap of one p-orbital with another p-orbital and also the sigma bond is intervening between the two.
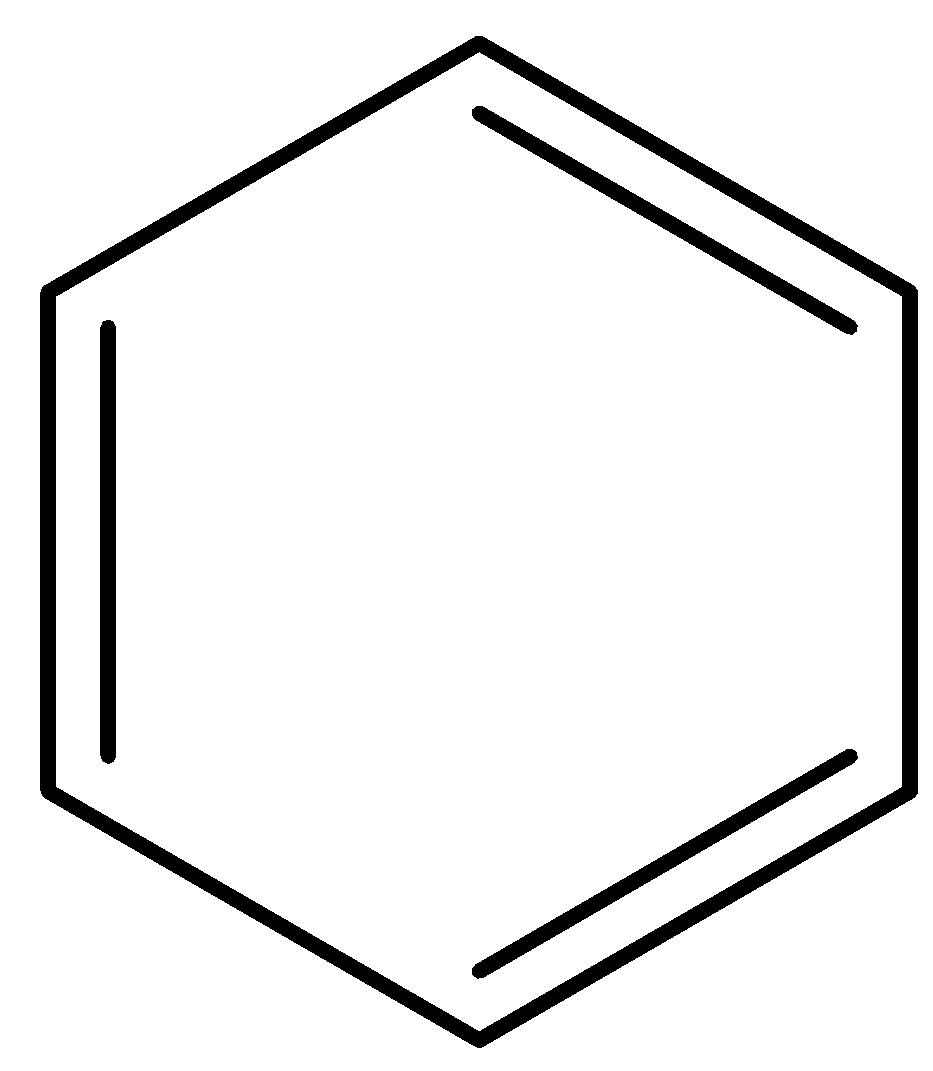
Even in this structure there’s conjugation as sigma bonds are intervening between the double bonds.
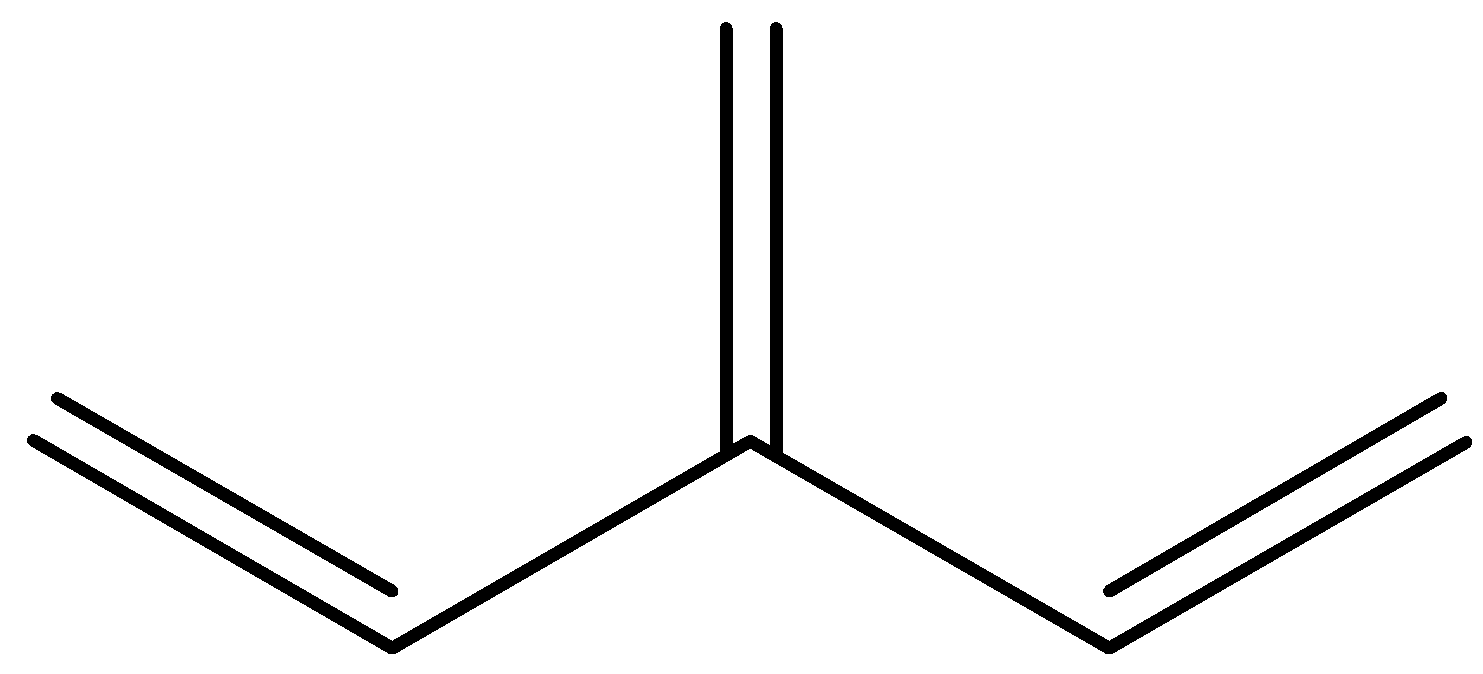
Here, out of a set of three Pi bonds only two interact with each other by conjugation, while the third one is excluded from interaction. Here we have a double bonded unit single bonded to one of the middle atoms of another conjugated chain. In other words, one of the double bonds branches off rather than continuing consecutively. Hence, a main chain is conjugated and part of that same main chain is conjugated with the side group, but all parts are not conjugated together. So, this structure is cross conjugated.
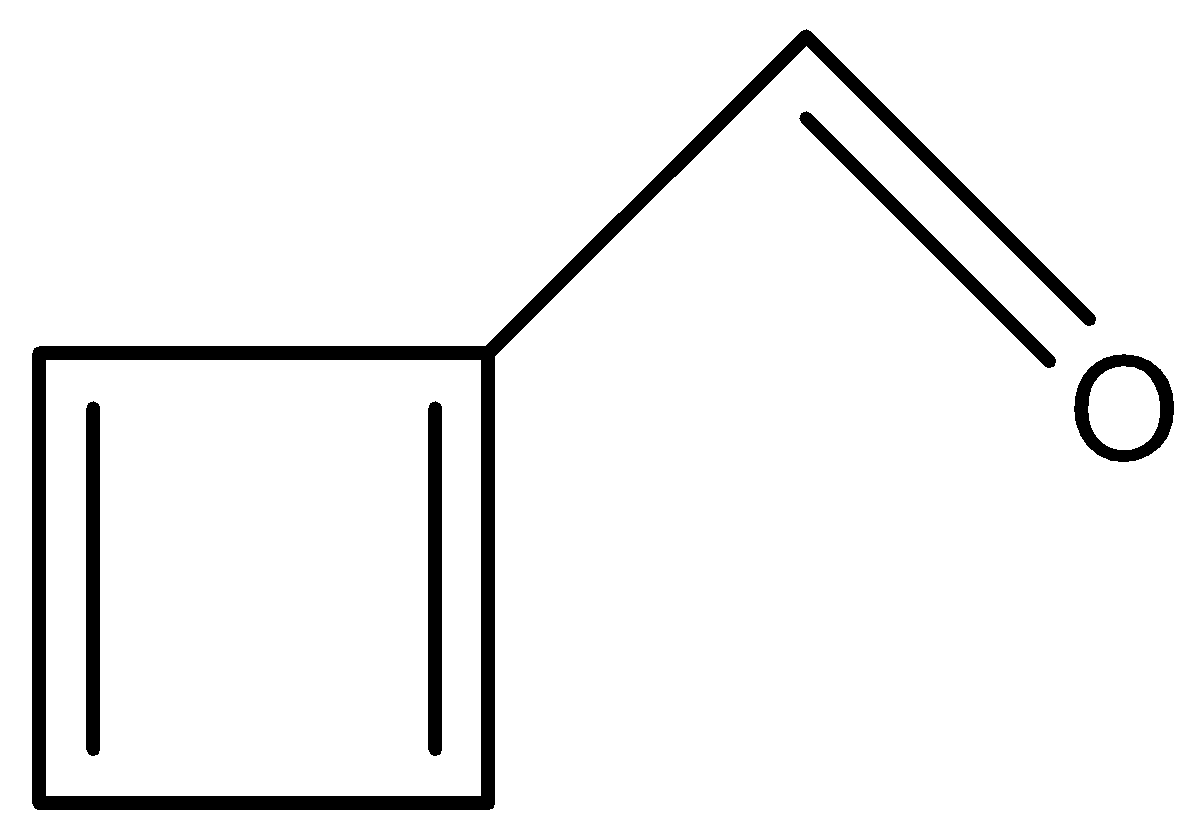
In this option, we see conjugation again.
Hence the correct answer is D.
Note: Cross conjugation has an important impact on reactivity and molecular electronic transition.Examples are Benzophenone, Divinyl ketone, p-quinone.Due to the cross conjugation, the extent of resonance decreases slightly.
Complete step by step answer:
Cross conjugation is a special type of conjugation in a molecule. When in a set of three Pi bonds, only two Pi bonds interact with each other by conjugation and the third one is excluded from interaction.

In this structure, there’s a double bond then a sigma bond and then a double bond and then a sigma bond. This is called conjugation. Here we can see overlap of one p-orbital with another p-orbital and also the sigma bond is intervening between the two.

Even in this structure there’s conjugation as sigma bonds are intervening between the double bonds.

Here, out of a set of three Pi bonds only two interact with each other by conjugation, while the third one is excluded from interaction. Here we have a double bonded unit single bonded to one of the middle atoms of another conjugated chain. In other words, one of the double bonds branches off rather than continuing consecutively. Hence, a main chain is conjugated and part of that same main chain is conjugated with the side group, but all parts are not conjugated together. So, this structure is cross conjugated.

In this option, we see conjugation again.
Hence the correct answer is D.
Note: Cross conjugation has an important impact on reactivity and molecular electronic transition.Examples are Benzophenone, Divinyl ketone, p-quinone.Due to the cross conjugation, the extent of resonance decreases slightly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




