
In what stage of meiosis does reduction division occur?
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: The significance of meiosis includes the formation of gamete cells which are responsible for sexual reproduction. Meiosis maintains the constant number of chromosomes by reducing it in half, therefore, called reductional division.
Complete answer:
Meiosis is a phenomenon that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms in which shuffling of genetic information takes place.
Meiosis is a type of cell division in which the chromosome number in the cells reduces by half that results in the production of haploid daughter cells, hence this cell division is known as a reduction division. It involves two rounds of nuclear and cell division known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated in the S-phase of the cell cycle. The meiotic event includes various stages to complete the cell division.
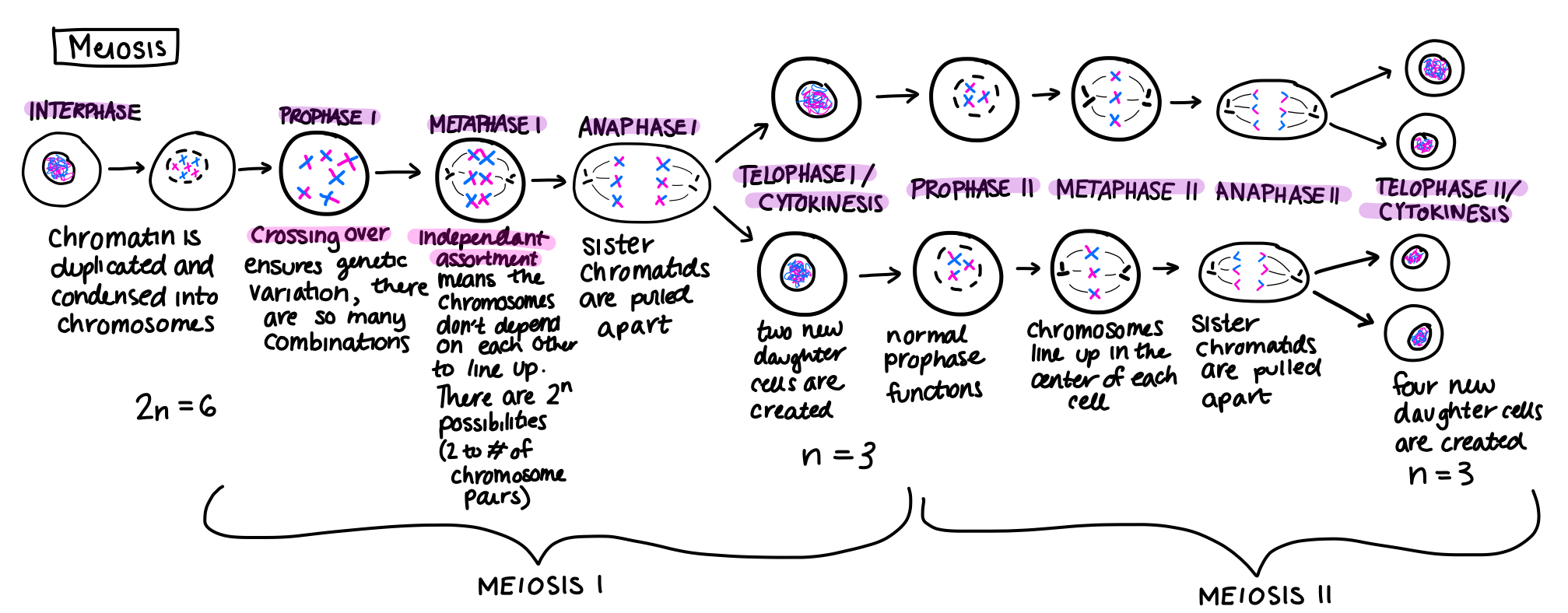
Meiosis involves two constitutive divisions resulting in cell division and namely Meiosis I and Meiosis II. Meiosis I is the reductional division where the chromosome number is reduced to half and Meiosis II is just the same as mitosis or, say, equational division. Meiosis I is divided into 4 stages namely the prophase, the metaphase, the anaphase, and the telophase. Prophase I is further divided into the 5 substages called leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
Prophase I signifies the chromosomal pairing.
Metaphase I, here, all the chromosomes align up at the equator via the spindle fibers.
Anaphase I, the homologous sister chromatids, pull apart and then enter into the telophase I stage where two new daughter cells are created.
In Meiosis I the homologous chromosome segregates at the anaphase I stage and that’s why it is called reductional division.
Meiosis II involves prophase II in which the two daughter cells perform normal prophase functions like chromatin condensation of sister chromatids.
In Metaphase II, chromosomes line up at the equator, and sister chromatids are pulled apart during the Anaphase II stage. Telophase II results in cell pinching off in 4 equal daughter cells.
Note:
Meiosis decreases the number of chromosomes to half in the daughter cells of the gamete-forming cells. It helps in the maintenance of the chromosome number constant for a species when a zygote is formed. The mixing of genetic material forms genetically unique gametes and each of them fuses with another unique gamete during the process of fertilization and forms a unique zygote of the upcoming generation. Haploid cells are produced in meiosis.
Complete answer:
Meiosis is a phenomenon that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms in which shuffling of genetic information takes place.
Meiosis is a type of cell division in which the chromosome number in the cells reduces by half that results in the production of haploid daughter cells, hence this cell division is known as a reduction division. It involves two rounds of nuclear and cell division known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated in the S-phase of the cell cycle. The meiotic event includes various stages to complete the cell division.

Meiosis involves two constitutive divisions resulting in cell division and namely Meiosis I and Meiosis II. Meiosis I is the reductional division where the chromosome number is reduced to half and Meiosis II is just the same as mitosis or, say, equational division. Meiosis I is divided into 4 stages namely the prophase, the metaphase, the anaphase, and the telophase. Prophase I is further divided into the 5 substages called leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
Prophase I signifies the chromosomal pairing.
Metaphase I, here, all the chromosomes align up at the equator via the spindle fibers.
Anaphase I, the homologous sister chromatids, pull apart and then enter into the telophase I stage where two new daughter cells are created.
In Meiosis I the homologous chromosome segregates at the anaphase I stage and that’s why it is called reductional division.
Meiosis II involves prophase II in which the two daughter cells perform normal prophase functions like chromatin condensation of sister chromatids.
In Metaphase II, chromosomes line up at the equator, and sister chromatids are pulled apart during the Anaphase II stage. Telophase II results in cell pinching off in 4 equal daughter cells.
Note:
Meiosis decreases the number of chromosomes to half in the daughter cells of the gamete-forming cells. It helps in the maintenance of the chromosome number constant for a species when a zygote is formed. The mixing of genetic material forms genetically unique gametes and each of them fuses with another unique gamete during the process of fertilization and forms a unique zygote of the upcoming generation. Haploid cells are produced in meiosis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




