
In what ratio is the line segment joining the points (-3, 2) and (6, 1) is divided by y – axis?
A. \[1:3\]
B. \[2:1\]
C. \[1:2\]
D. \[3:1\]
Answer
618k+ views
Hint: Consider any point on the y – axis of the form \[\left( 0,a \right)\]. Assume that this point divides the points \[\left( -3,2 \right)\] and \[\left( 6,1 \right)\] in the ratio \[m:1\]. Use the section formula for finding the coordinates of points which divides two points \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] in the ratio \[u:v\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have two points \[\left( -3,2 \right)\] and \[\left( 6,1 \right)\]. We have to find the ratio in which line joining these two points is divided by the y – axis.
Let’s assume that the point on the y – axis is of the form \[\left( 0,a \right)\]. Let’s assume that the point \[\left( 0,a \right)\] divides the line joining \[\left( -3,2 \right)\] and \[\left( 6,1 \right)\] in the ratio \[m:1\].
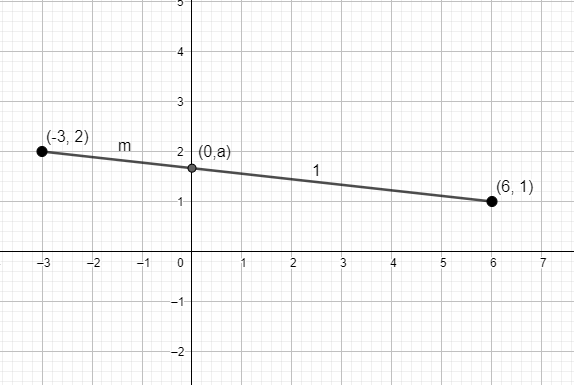
We will now use section formula to find the value of m. We know that the co-ordinates of point dividing two points \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] in the ratio \[u:v\] is \[\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}v+{{x}_{2}}u}{u+v},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}v+{{y}_{2}}u}{u+v} \right)\].
Substituting \[{{x}_{1}}=-3,{{x}_{2}}=6,{{y}_{1}}=2,{{y}_{2}}=1,u=m,v=1\] in the above equation, the co-ordinates of point dividing \[\left( -3,2 \right)\] and \[\left( 6,1 \right)\] in the ratio \[m:1\] is \[\left( \dfrac{-3\left( 1 \right)+6m}{m+1},\dfrac{2\left( 1 \right)+m}{m+1} \right)\].
However, we know that the co-ordinates of point dividing \[\left( -3,2 \right)\] and \[\left( 6,1 \right)\] in the ratio \[m:1\] is \[\left( 0,a \right)\].
Thus, we have \[\left( 0,a \right)=\left( \dfrac{-3\left( 1 \right)+6m}{m+1},\dfrac{2\left( 1 \right)+m}{m+1} \right)\].
By equation terms , we have \[0=\dfrac{-3+6m}{m+1},a=\dfrac{2+m}{m+1}\].
Solving the equation \[0=\dfrac{-3+6m}{m+1}\] by cross multiplying the terms, we have \[-3+6m=0\].
Thus, we have \[m=\dfrac{1}{2}\].
Hence, the ratio in which the line joining \[\left( -3,2 \right)\] and \[\left( 6,1 \right)\] is divided by y – axis is \[m:1=\dfrac{1}{2}:1=1:2\], which is option (c).
Note: We don’t have to find the exact coordinates of the point on the y – axis which divides the points. However, if we wish to do so, we can substitute the value of m in the other equation and find the value of a. Section formula tells us the coordinates of the point which divides a given line segment with two end points in a fixed ratio.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have two points \[\left( -3,2 \right)\] and \[\left( 6,1 \right)\]. We have to find the ratio in which line joining these two points is divided by the y – axis.
Let’s assume that the point on the y – axis is of the form \[\left( 0,a \right)\]. Let’s assume that the point \[\left( 0,a \right)\] divides the line joining \[\left( -3,2 \right)\] and \[\left( 6,1 \right)\] in the ratio \[m:1\].

We will now use section formula to find the value of m. We know that the co-ordinates of point dividing two points \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] in the ratio \[u:v\] is \[\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}v+{{x}_{2}}u}{u+v},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}v+{{y}_{2}}u}{u+v} \right)\].
Substituting \[{{x}_{1}}=-3,{{x}_{2}}=6,{{y}_{1}}=2,{{y}_{2}}=1,u=m,v=1\] in the above equation, the co-ordinates of point dividing \[\left( -3,2 \right)\] and \[\left( 6,1 \right)\] in the ratio \[m:1\] is \[\left( \dfrac{-3\left( 1 \right)+6m}{m+1},\dfrac{2\left( 1 \right)+m}{m+1} \right)\].
However, we know that the co-ordinates of point dividing \[\left( -3,2 \right)\] and \[\left( 6,1 \right)\] in the ratio \[m:1\] is \[\left( 0,a \right)\].
Thus, we have \[\left( 0,a \right)=\left( \dfrac{-3\left( 1 \right)+6m}{m+1},\dfrac{2\left( 1 \right)+m}{m+1} \right)\].
By equation terms , we have \[0=\dfrac{-3+6m}{m+1},a=\dfrac{2+m}{m+1}\].
Solving the equation \[0=\dfrac{-3+6m}{m+1}\] by cross multiplying the terms, we have \[-3+6m=0\].
Thus, we have \[m=\dfrac{1}{2}\].
Hence, the ratio in which the line joining \[\left( -3,2 \right)\] and \[\left( 6,1 \right)\] is divided by y – axis is \[m:1=\dfrac{1}{2}:1=1:2\], which is option (c).
Note: We don’t have to find the exact coordinates of the point on the y – axis which divides the points. However, if we wish to do so, we can substitute the value of m in the other equation and find the value of a. Section formula tells us the coordinates of the point which divides a given line segment with two end points in a fixed ratio.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




