
In \[\vartriangle ABC\],\[m\angle A + m\angle C = m\angle B\]and \[AC:AB = 17:15\]. If \[BC = 12\], find the area of \[\vartriangle ABC\]
Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: We use the given condition of angles and use the property of sum of interior angles to calculate the measure of angle B. Using the value of angle B we form a right triangle. Use the given ratio of sides to write the length of one side in terms of length of the other side. Use Pythagoras theorem to calculate the value of one of the sides of the triangle. Use the formula of the area of the triangle to calculate the area.
* Sum of interior angles of a triangle is \[{180^ \circ }\]
* Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, the sum of square of base and square of height is equal to square of the hypotenuse. In the right triangle the largest side opposite to the right angle is the hypotenuse.
If we have a right angled triangle, \[\vartriangle ABC\]with right angle, \[\angle B = {90^ \circ }\]
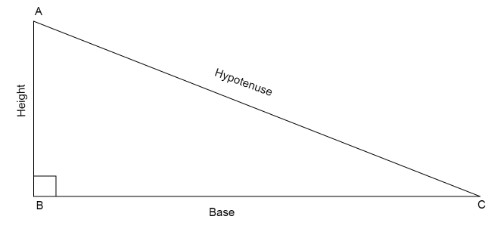
Then using the Pythagoras theorem we can write that \[A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\]
* Ratio of any number ‘x’ to ‘y’ is given by \[x:y = \dfrac{x}{y}\]
* Area of a triangle is given by the formula \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times \]Base\[ \times \]altitude.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We are given a triangle ABC with one side \[BC = 12\]and ratio of two other sides as\[AC:AB = 17:15\]
We are given the ratio of two sides \[AC:AB = 17:15\]
Use the concept of ratio to write ratio in fraction form
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AC}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{17}}{{15}}\]
Cross multiply the terms and write AB on one side of the equation and all other values on opposite side of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow AB = \dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC\].....................… (1)
In \[\vartriangle ABC\], \[m\angle A + m\angle C = m\angle B\]
We can remove ‘m’ from both sides of the equation as it just indicates the measure of the angles.
\[ \Rightarrow \angle A + \angle C = \angle B\]....................… (2)
Apply property of sum of interior angles to the \[\vartriangle ABC\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle A + \angle B + \angle C = {180^ \circ }\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\angle A + \angle C} \right) + \angle B = {180^ \circ }\]
Substitute the value of \[\angle A + \angle C = \angle B\]from equation (2) in LHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow \angle B + \angle B = {180^ \circ }\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\angle B = {180^ \circ }\]
Divide both sides of the equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2\angle B}}{2} = \dfrac{{{{180}^ \circ }}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle B = {90^ \circ }\]
So, in \[\vartriangle ABC\], \[\angle B = {90^ \circ }\]. This means \[\vartriangle ABC\] is a right angled triangle
We draw right triangle \[\vartriangle ABC\]
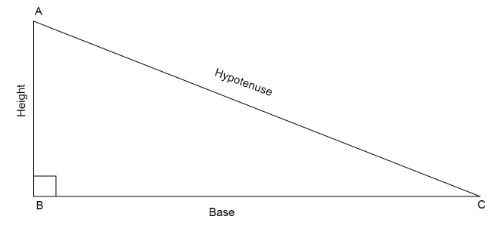
Since \[\vartriangle ABC\] is a right angled triangle, we can apply Pythagoras theorem here
\[{\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2}\]
Substitute the value of \[BC = 12\]and \[AB = \dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC\]from equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC} \right)^2} + {\left( {12} \right)^2}\]
Shift all values with variable AC to LHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {AC} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {12} \right)^2}\]
Write the square of each number
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} - \dfrac{{225A{C^2}}}{{289}} = 144\]
Take LCM in LHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{289A{C^2} - 225A{C^2}}}{{289}} = 144\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{64A{C^2}}}{{289}} = 144\]
Cross multiply all values except \[A{C^2}\]to RHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = \dfrac{{144 \times 289}}{{64}}\]
Write each term in RHS as square of a whole number
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = \dfrac{{{{12}^2} \times {{17}^2}}}{{{8^2}}}\]
Since power of each element is same we can multiply the base in RHS
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{12 \times 17}}{8}} \right)^2}\]
Take square root on both sides of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {A{C^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{{12 \times 17}}{8}} \right)}^2}} \]
Cancel square root by square power on both sides of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow AC = \left( {\dfrac{{12 \times 17}}{8}} \right)\]
Cancel same factors from numerator and denominator in RHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow AC = \left( {\dfrac{{3 \times 17}}{2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow AC = \left( {\dfrac{{3 \times 17}}{2}} \right)\]....................… (3)
Now we use the formula of area of triangle to calculate the area
Since area of a triangle is given by the formula \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times \]Base\[ \times \]altitude, in \[\vartriangle ABC\]altitude is AB and base is BC
\[ \Rightarrow \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \times AB\]
Substitute the value of \[BC = 12\]and \[AB = \dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC\]from equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 12 \times \dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC\]
Substitute the value of AC from equation (3)
\[ \Rightarrow \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 12 \times \dfrac{{15}}{{17}} \times \left( {\dfrac{{3 \times 17}}{2}} \right)\]
Cancel same factors from numerator and denominator in RHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC = 3 \times 15 \times 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC = 135\] square units
\[\therefore \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC\] is 135 square units
Note: The equation or relation between angles is given so that we use the property of right angle triangle and apply Pythagoras theorem. Also, while writing one side in terms of other using ratio don’t cross multiply value of constants to one side, write one side in terms of other i.e. keep one length at one side and rest values on other.
* Sum of interior angles of a triangle is \[{180^ \circ }\]
* Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, the sum of square of base and square of height is equal to square of the hypotenuse. In the right triangle the largest side opposite to the right angle is the hypotenuse.
If we have a right angled triangle, \[\vartriangle ABC\]with right angle, \[\angle B = {90^ \circ }\]

Then using the Pythagoras theorem we can write that \[A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\]
* Ratio of any number ‘x’ to ‘y’ is given by \[x:y = \dfrac{x}{y}\]
* Area of a triangle is given by the formula \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times \]Base\[ \times \]altitude.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We are given a triangle ABC with one side \[BC = 12\]and ratio of two other sides as\[AC:AB = 17:15\]
We are given the ratio of two sides \[AC:AB = 17:15\]
Use the concept of ratio to write ratio in fraction form
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AC}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{17}}{{15}}\]
Cross multiply the terms and write AB on one side of the equation and all other values on opposite side of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow AB = \dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC\].....................… (1)
In \[\vartriangle ABC\], \[m\angle A + m\angle C = m\angle B\]
We can remove ‘m’ from both sides of the equation as it just indicates the measure of the angles.
\[ \Rightarrow \angle A + \angle C = \angle B\]....................… (2)
Apply property of sum of interior angles to the \[\vartriangle ABC\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle A + \angle B + \angle C = {180^ \circ }\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\angle A + \angle C} \right) + \angle B = {180^ \circ }\]
Substitute the value of \[\angle A + \angle C = \angle B\]from equation (2) in LHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow \angle B + \angle B = {180^ \circ }\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\angle B = {180^ \circ }\]
Divide both sides of the equation by 2
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2\angle B}}{2} = \dfrac{{{{180}^ \circ }}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle B = {90^ \circ }\]
So, in \[\vartriangle ABC\], \[\angle B = {90^ \circ }\]. This means \[\vartriangle ABC\] is a right angled triangle
We draw right triangle \[\vartriangle ABC\]

Since \[\vartriangle ABC\] is a right angled triangle, we can apply Pythagoras theorem here
\[{\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2}\]
Substitute the value of \[BC = 12\]and \[AB = \dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC\]from equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC} \right)^2} + {\left( {12} \right)^2}\]
Shift all values with variable AC to LHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {AC} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {12} \right)^2}\]
Write the square of each number
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} - \dfrac{{225A{C^2}}}{{289}} = 144\]
Take LCM in LHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{289A{C^2} - 225A{C^2}}}{{289}} = 144\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{64A{C^2}}}{{289}} = 144\]
Cross multiply all values except \[A{C^2}\]to RHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = \dfrac{{144 \times 289}}{{64}}\]
Write each term in RHS as square of a whole number
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = \dfrac{{{{12}^2} \times {{17}^2}}}{{{8^2}}}\]
Since power of each element is same we can multiply the base in RHS
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{12 \times 17}}{8}} \right)^2}\]
Take square root on both sides of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {A{C^2}} = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{{12 \times 17}}{8}} \right)}^2}} \]
Cancel square root by square power on both sides of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow AC = \left( {\dfrac{{12 \times 17}}{8}} \right)\]
Cancel same factors from numerator and denominator in RHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow AC = \left( {\dfrac{{3 \times 17}}{2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow AC = \left( {\dfrac{{3 \times 17}}{2}} \right)\]....................… (3)
Now we use the formula of area of triangle to calculate the area
Since area of a triangle is given by the formula \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times \]Base\[ \times \]altitude, in \[\vartriangle ABC\]altitude is AB and base is BC
\[ \Rightarrow \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times BC \times AB\]
Substitute the value of \[BC = 12\]and \[AB = \dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC\]from equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 12 \times \dfrac{{15}}{{17}}AC\]
Substitute the value of AC from equation (3)
\[ \Rightarrow \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 12 \times \dfrac{{15}}{{17}} \times \left( {\dfrac{{3 \times 17}}{2}} \right)\]
Cancel same factors from numerator and denominator in RHS of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC = 3 \times 15 \times 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC = 135\] square units
\[\therefore \]Area of \[\vartriangle ABC\] is 135 square units
Note: The equation or relation between angles is given so that we use the property of right angle triangle and apply Pythagoras theorem. Also, while writing one side in terms of other using ratio don’t cross multiply value of constants to one side, write one side in terms of other i.e. keep one length at one side and rest values on other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




