
In two step pulley arrangement meant for a load \[W\], the ratio between force \[P\] and \[W\] equilibrium position, when radii of pulleys are \[{r_1}\] and \[{r_2}\] :
\[\left( {\text{A}} \right){\text{ }}\dfrac{{{r_{\text{2}}}}}{{{r_r}{\text{ - }}{r_{\text{2}}}}}\]
\[\left( {\text{B}} \right){\text{ }}\dfrac{{{r_1} - {r_2}}}{{{r_2}}}\]
\[\left( {\text{C}} \right){\text{ }}\dfrac{{{r_1}}}{{{r_2} - {r_1}}}\]
\[\left( {\text{D}} \right){\text{ }}\dfrac{{{r_2} - {r_1}}}{{{r_1}}}\]

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint:The two pulley arrangement is given force \[P\] and also the work is done at the centre of the pulley. The pulley remains constant means it doesn’t change its position due to the force and the load. Therefore the effect of load and the force is equal and opposite.
Complete step by answer:
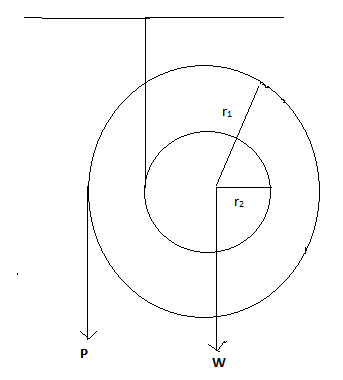
From the question, the ratio of a small circle in the pulley is \[{r_2}\]. And the load \[W\] concentrates at the centre of both the pulleys which is \[{r_2}\]. Due to the effect of the load \[W\], the pulley rotates at a small angle called \[{r_2}\theta \]
The force \[P\] is given to the circle of radius \[{r_1} - {r_2}\]. Due to the force \[P\] the pulley experiences the rotation equals to \[({r_1} - {r_2})\theta \]
The condition given is that the pulley remains in the equilibrium position. Hence the resultant action by the force \[P\] and the load \[W\]is equal and opposite. Therefore,
\[P\left[ {({r_1} - {r_2})\theta } \right] - W({r_2}\theta ) = 0\]
We have to write the terms as equate form
\[ \rightarrow P\left[ {({r_1} - {r_2})\theta } \right] = W({r_2}\theta )\]
Also, write it as the fraction term so we divided the terms we get,
\[ \rightarrow \dfrac{P}{W} = \dfrac{{{r_2}\theta }}{{({r_1} - {r_2})\theta }}\]
Cancel the same term we get,
\[\therefore \dfrac{P}{W} = \dfrac{{{r_2}}}{{({r_1} - {r_2})}}\]
Hence, the ratio between the force \[P\] and the load \[W\] in equilibrium is \[\dfrac{{{r_2}}}{{{r_1} - {r_2}}}\].
Therefore the correct option is A.
Note:Pulleys are used for the mechanism to lift the weight. It reduces the force required for lifting the weight. In two pulley arrangements, one pulley is fixed at its centre point and another pulley is movable. As the weight is loaded on the pulley, the pulley should be two times heavier than the load. Pulleys have many applications in our day to day life. It is used in wells to carry water from the well using the bucket; elevators have multiple pulleys, etc.
Complete step by answer:
From the question, the ratio of a small circle in the pulley is \[{r_2}\]. And the load \[W\] concentrates at the centre of both the pulleys which is \[{r_2}\]. Due to the effect of the load \[W\], the pulley rotates at a small angle called \[{r_2}\theta \]
The force \[P\] is given to the circle of radius \[{r_1} - {r_2}\]. Due to the force \[P\] the pulley experiences the rotation equals to \[({r_1} - {r_2})\theta \]
The condition given is that the pulley remains in the equilibrium position. Hence the resultant action by the force \[P\] and the load \[W\]is equal and opposite. Therefore,
\[P\left[ {({r_1} - {r_2})\theta } \right] - W({r_2}\theta ) = 0\]
We have to write the terms as equate form
\[ \rightarrow P\left[ {({r_1} - {r_2})\theta } \right] = W({r_2}\theta )\]
Also, write it as the fraction term so we divided the terms we get,
\[ \rightarrow \dfrac{P}{W} = \dfrac{{{r_2}\theta }}{{({r_1} - {r_2})\theta }}\]
Cancel the same term we get,
\[\therefore \dfrac{P}{W} = \dfrac{{{r_2}}}{{({r_1} - {r_2})}}\]
Hence, the ratio between the force \[P\] and the load \[W\] in equilibrium is \[\dfrac{{{r_2}}}{{{r_1} - {r_2}}}\].
Therefore the correct option is A.
Note:Pulleys are used for the mechanism to lift the weight. It reduces the force required for lifting the weight. In two pulley arrangements, one pulley is fixed at its centre point and another pulley is movable. As the weight is loaded on the pulley, the pulley should be two times heavier than the load. Pulleys have many applications in our day to day life. It is used in wells to carry water from the well using the bucket; elevators have multiple pulleys, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




