
In two right triangles one side and an acute angle of one are equal to the corresponding side and angle of the other. Prove that the triangles are congruent.
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: The Angle-Angle-Side criteria (AAS) specifies that if any two angles and a opposite of any one of the angle is given then triangles can be equated or can form congruence when two angles and side is common value in both the triangles like given in the diagram below:
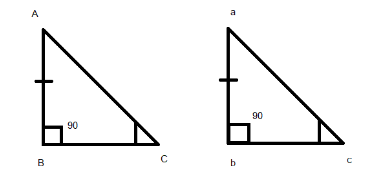
where \[\angle C=\angle c\] and AB is equal to ab.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To prove congruency one must form equal angles or/and side with another triangle. In case when two angles and a side are the same then we can say that the triangles are in AAS congruency or Angle-Angle-Side congruence. There is a difference between AAS (Angle-Angle-Side) and ASA (Angle- Side- Angle) with ASA, the side which is equal in both tends to have the two angles which are similar in both the triangles like shown below:
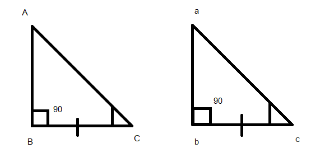
Here the sides and the angles are in same section or part whereas in AAS as shown below:
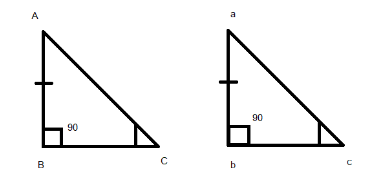
The sides are corresponding to the angles given in the above diagram. Hence by AAS criteria we can say that the angle \[\angle ABC=\angle abc\] , \[\angle ACB=\angle acb\] and sides AB is equal to ab. Therefore, yes both the triangles are congruent on the basis of AAS (Angle-Angle-Side).
Note: Students may think both ASA and AAS are same but in hindsight both are different as the side’s position is different in both of them and the most appropriate congruency in this case is that of AAS.

where \[\angle C=\angle c\] and AB is equal to ab.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To prove congruency one must form equal angles or/and side with another triangle. In case when two angles and a side are the same then we can say that the triangles are in AAS congruency or Angle-Angle-Side congruence. There is a difference between AAS (Angle-Angle-Side) and ASA (Angle- Side- Angle) with ASA, the side which is equal in both tends to have the two angles which are similar in both the triangles like shown below:

Here the sides and the angles are in same section or part whereas in AAS as shown below:

The sides are corresponding to the angles given in the above diagram. Hence by AAS criteria we can say that the angle \[\angle ABC=\angle abc\] , \[\angle ACB=\angle acb\] and sides AB is equal to ab. Therefore, yes both the triangles are congruent on the basis of AAS (Angle-Angle-Side).
Note: Students may think both ASA and AAS are same but in hindsight both are different as the side’s position is different in both of them and the most appropriate congruency in this case is that of AAS.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




