
In triangle \[ABC,\angle A = \dfrac{\pi }{3}\] and it’s encircle is of units radius. If the radius of the circle touching the sides \[AB,AC\] internally and encircle externally is x, then the value of x is
(A) \[\dfrac{1}{2}\]
(B) \[\dfrac{1}{4}\]
(C) \[\dfrac{1}{3}\]
(D) None of these
Answer
471.3k+ views
Hint: First, we have to draw a circle with the given conditions. Then we compare the sides and angles for some similarity using trigonometric values and solve for \[x\]and \[y\]. An acute angle is extensively used in this solution.
Complete answer:
First, we draw a circle with a unit radius.
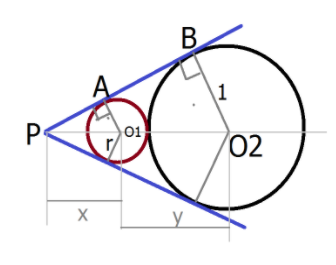
Secondly, we mark the radius as 1 with center \[o2\]
Forming a triangle ABC we see that the circle with unit radius touches the circle at abs and AC
Again we draw an encircle with radius x with center \[o1\]
Hence we get the above diagram
From the above diagram we get right-angled triangles \[APO1\] AND \[ABO2\]
Hence we can write it as
\[(x + y)\sin (30) = 1\]
We write \[\sin (30)\]because the angle formed is \[\sin (30)\]
Hence we know that \[\sin 30 = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Substituting the values we get,
\[(x + y)\sin 30 = 1\]
\[(x + y)\dfrac{1}{2} = 1 \]
\[x + y = 2 \]
Again we know that
\[x\sin 30 = r\]
Because the angle formed by the encircling has a radius \[r\]
Therefore we have:
\[x = 2r\]
Again for \[y = 1 + r\]
Solving this we get
\[x + y = 2 \]
\[2r + 1 + r = 2 \]
\[3r + 1 = 2 \]
\[3r = 2 - 1 \]
\[3r = 1 \]
\[r = \dfrac{1}{3} \]
Hence the correct option is (C) i.e. \[\dfrac{1}{3}\]
Additional information:
Triangles and their properties are an essential part of solving questions as such. The trigonometric application adds to the sum to give the final answer.
Note:
Geometry and construction of triangles should be clear along with a clear understanding of their properties and formulas. Trigonometric formula i.e. \[\sin (30)\]is an essential part to proceed as it forms an angle with the triangle. The knowledge of adjacent sides along with values of trigonometric is essential.
Complete answer:
First, we draw a circle with a unit radius.

Secondly, we mark the radius as 1 with center \[o2\]
Forming a triangle ABC we see that the circle with unit radius touches the circle at abs and AC
Again we draw an encircle with radius x with center \[o1\]
Hence we get the above diagram
From the above diagram we get right-angled triangles \[APO1\] AND \[ABO2\]
Hence we can write it as
\[(x + y)\sin (30) = 1\]
We write \[\sin (30)\]because the angle formed is \[\sin (30)\]
Hence we know that \[\sin 30 = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Substituting the values we get,
\[(x + y)\sin 30 = 1\]
\[(x + y)\dfrac{1}{2} = 1 \]
\[x + y = 2 \]
Again we know that
\[x\sin 30 = r\]
Because the angle formed by the encircling has a radius \[r\]
Therefore we have:
\[x = 2r\]
Again for \[y = 1 + r\]
Solving this we get
\[x + y = 2 \]
\[2r + 1 + r = 2 \]
\[3r + 1 = 2 \]
\[3r = 2 - 1 \]
\[3r = 1 \]
\[r = \dfrac{1}{3} \]
Hence the correct option is (C) i.e. \[\dfrac{1}{3}\]
Additional information:
Triangles and their properties are an essential part of solving questions as such. The trigonometric application adds to the sum to give the final answer.
Note:
Geometry and construction of triangles should be clear along with a clear understanding of their properties and formulas. Trigonometric formula i.e. \[\sin (30)\]is an essential part to proceed as it forms an angle with the triangle. The knowledge of adjacent sides along with values of trigonometric is essential.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




