
In triangle ABC, let AD, BE and CF be the internal angle bisectors with D, E and F on the sides BC, CA and AB respectively. Suppose AD, BE and CF concur at I and B, D, I, F are con-cyclic, then $\angle IFD$ has measure:
$\left( a \right){15^o}$
$\left( b \right){30^o}$
$\left( c \right){45^o}$
$\left( d \right)$ Any value $ \leqslant {90^o}$
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: In this question use the property of cyclic quadrilateral i.e. the sum of the opposite angles of the quadrilateral is ${180^o}$ and the property of triangle that the sum of angles of a triangle is ${180^o}$. Use this to find the value of $\angle IFD$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
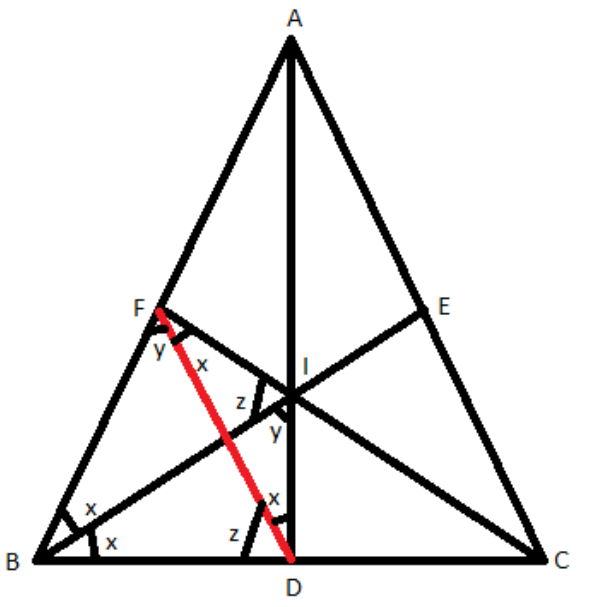
According to the question, ABC let AD, BE and CF be the internal angle bisectors with D, E, and F on the sides BC, CA, and AB respectively as shown in the figure and we have to find.
Let, $\angle IBF = x,\angle BID = y,\angle BIF = z$ as shown in the above figure.
$\therefore \angle IBF = \angle IBD = \angle IDF = \angle IFD = x$, Using angles in the same arc have the same measure and BE is the angle bisector of $\angle ABC$
Similarly, $\angle BID = \angle BFD = y$,
And $\angle BIF = \angle BDF = z$
Since points B, D, I and F are con-cyclic, $\angle FBD + \angle FID = {180^o}$ (i.e. in cyclic quadrilateral the sum of the opposite angles of the quadrilateral is ${180^o}$)
$ \Rightarrow 2x + y + z = {180^o}$.................. (1)
Now as we know that in any triangle the sum of all angles is equal to 180 degrees.
So in triangle BCF,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BCF + \angle BFC + \angle CBF = {180^o}$
Now substitute the values from the figure we have,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BCF = {180^o} - y - x - 2x$
$ \Rightarrow \angle BCF = {180^o} - y - 3x$........... (2)
Similarly in triangle BAD we have,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BAD = {180^o} - z - 3x$............. (3)
Now in triangle ABC, we have,
$ \Rightarrow \angle ABC + \angle ACB + \angle BAC = {180^o}$
$ \Rightarrow 2\angle ABE + 2\angle BCF + 2\angle BAD = {180^o}$ (As, AD, CE and CF are bisectors of angles A, B and C respectively).
Now substitute the values from equation (2) and (3) we have,
$ \Rightarrow 2x + 2\left( {{{180}^o} - y - 3x} \right) + 2\left( {{{180}^o} - z - 3x} \right) = {180^o}$
$ \Rightarrow x + \left( {{{180}^o} - y - 3x} \right) + \left( {{{180}^o} - z - 3x} \right) = {90^o}$
$ \Rightarrow - 5x + {360^o} - y - z = {90^o}$
$ \Rightarrow 5x + y + z = {270^o}$.................. (4)
Now subtract equation (1) from equation (4) we have,
$ \Rightarrow 5x + y + z - \left( {2x + y + z} \right) = {270^o} - {180^o}$
$ \Rightarrow 3x = {90^o}$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{{{90}^o}}}{3} = {30^o}$
Hence $\angle IFD = {30^o}$
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall basic properties in shapes related questions such as angles in the same arc have the same measure and if we draw any bisector from any vertex the bisector divides the angles into two equal half’s.
Complete step-by-step solution:

According to the question, ABC let AD, BE and CF be the internal angle bisectors with D, E, and F on the sides BC, CA, and AB respectively as shown in the figure and we have to find.
Let, $\angle IBF = x,\angle BID = y,\angle BIF = z$ as shown in the above figure.
$\therefore \angle IBF = \angle IBD = \angle IDF = \angle IFD = x$, Using angles in the same arc have the same measure and BE is the angle bisector of $\angle ABC$
Similarly, $\angle BID = \angle BFD = y$,
And $\angle BIF = \angle BDF = z$
Since points B, D, I and F are con-cyclic, $\angle FBD + \angle FID = {180^o}$ (i.e. in cyclic quadrilateral the sum of the opposite angles of the quadrilateral is ${180^o}$)
$ \Rightarrow 2x + y + z = {180^o}$.................. (1)
Now as we know that in any triangle the sum of all angles is equal to 180 degrees.
So in triangle BCF,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BCF + \angle BFC + \angle CBF = {180^o}$
Now substitute the values from the figure we have,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BCF = {180^o} - y - x - 2x$
$ \Rightarrow \angle BCF = {180^o} - y - 3x$........... (2)
Similarly in triangle BAD we have,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BAD = {180^o} - z - 3x$............. (3)
Now in triangle ABC, we have,
$ \Rightarrow \angle ABC + \angle ACB + \angle BAC = {180^o}$
$ \Rightarrow 2\angle ABE + 2\angle BCF + 2\angle BAD = {180^o}$ (As, AD, CE and CF are bisectors of angles A, B and C respectively).
Now substitute the values from equation (2) and (3) we have,
$ \Rightarrow 2x + 2\left( {{{180}^o} - y - 3x} \right) + 2\left( {{{180}^o} - z - 3x} \right) = {180^o}$
$ \Rightarrow x + \left( {{{180}^o} - y - 3x} \right) + \left( {{{180}^o} - z - 3x} \right) = {90^o}$
$ \Rightarrow - 5x + {360^o} - y - z = {90^o}$
$ \Rightarrow 5x + y + z = {270^o}$.................. (4)
Now subtract equation (1) from equation (4) we have,
$ \Rightarrow 5x + y + z - \left( {2x + y + z} \right) = {270^o} - {180^o}$
$ \Rightarrow 3x = {90^o}$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{{{90}^o}}}{3} = {30^o}$
Hence $\angle IFD = {30^o}$
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall basic properties in shapes related questions such as angles in the same arc have the same measure and if we draw any bisector from any vertex the bisector divides the angles into two equal half’s.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What type of cell is found in the Seminiferous tub class 10 biology CBSE

What are the public facilities provided by the government? Also explain each facility




