
In this figure M is the midpoint of QR. \[\angle PRQ = {90^ \circ }\].
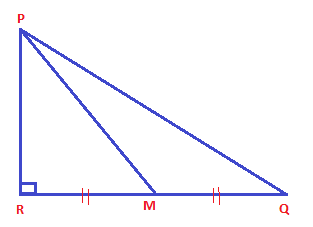
Prove that \[P{Q^2} = 4P{M^2} - 3P{R^2}\].

Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint:
Here in this geometrical problem we will take help of Pythagoras theorem. Because we are given that\[\angle PRQ = {90^ \circ }\]. So \[\vartriangle PRM = {90^ \circ }\] . Then we will modify the value of QR because we are given that M is the midpoint of QR.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s consider \[\vartriangle PRM,\]
Applying Pythagoras theorem,
\[{(PM)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + {\left( {RM} \right)^2} \to 1\]
Similarly for \[\vartriangle PRQ\]
\[{(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + {\left( {RQ} \right)^2} \to 2\]
But it is given that m is the midpoint of QR. So above equation2 can be written as,
\[
\Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + {\left( {RM + MQ} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + {\left( {2RM} \right)^2} \to \left( {\because RM = MQ} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + 4{\left( {RM} \right)^2} \\
\]
Now from equation1
\[{\left( {RM} \right)^2} = {\left( {PM} \right)^2} - {\left( {PR} \right)^2}\]
Putting this value of \[{\left( {RM} \right)^2}\] in above equation we will get,
\[ \Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + 4\left[ {{{\left( {PM} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {PR} \right)}^2}} \right]\]
Multiplying the bracket with 4
\[
\Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + 4{\left( {PM} \right)^2} - 4{\left( {PR} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = + 4{\left( {PM} \right)^2} - 3{\left( {PR} \right)^2} \\
\]
Hence we proved the statement.
Note:
For this problem using Pythagoras theorem is the best approach to solve. Always focus on given data because it is the best indicator for leading a problem solution. The thought process is to think how we can get PQ in terms of PM and PR.
Here in this geometrical problem we will take help of Pythagoras theorem. Because we are given that\[\angle PRQ = {90^ \circ }\]. So \[\vartriangle PRM = {90^ \circ }\] . Then we will modify the value of QR because we are given that M is the midpoint of QR.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s consider \[\vartriangle PRM,\]
Applying Pythagoras theorem,
\[{(PM)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + {\left( {RM} \right)^2} \to 1\]
Similarly for \[\vartriangle PRQ\]
\[{(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + {\left( {RQ} \right)^2} \to 2\]
But it is given that m is the midpoint of QR. So above equation2 can be written as,
\[
\Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + {\left( {RM + MQ} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + {\left( {2RM} \right)^2} \to \left( {\because RM = MQ} \right) \\
\Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + 4{\left( {RM} \right)^2} \\
\]
Now from equation1
\[{\left( {RM} \right)^2} = {\left( {PM} \right)^2} - {\left( {PR} \right)^2}\]
Putting this value of \[{\left( {RM} \right)^2}\] in above equation we will get,
\[ \Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + 4\left[ {{{\left( {PM} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {PR} \right)}^2}} \right]\]
Multiplying the bracket with 4
\[
\Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = {\left( {PR} \right)^2} + 4{\left( {PM} \right)^2} - 4{\left( {PR} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(PQ)^2} = + 4{\left( {PM} \right)^2} - 3{\left( {PR} \right)^2} \\
\]
Hence we proved the statement.
Note:
For this problem using Pythagoras theorem is the best approach to solve. Always focus on given data because it is the best indicator for leading a problem solution. The thought process is to think how we can get PQ in terms of PM and PR.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




