
In the three - dimensional structure of methane, \[C{H_4}\], where are hydrogen atoms attached to a carbon atom aligned?
Answer
503.1k+ views
Hint: We have to know that methane is a chemical compound having the chemical formula,\[C{H_4}\] and these are found on earth's surface in small quantities. Among the hydrocarbon compounds, methane is the very simplest hydrocarbon and alkane. Here, it only contains one carbon atom. And four hydrogen atoms are attached with the carbon atoms. The methane gas is highly flammable and it is a powerful greenhouse gas.
Complete answer:
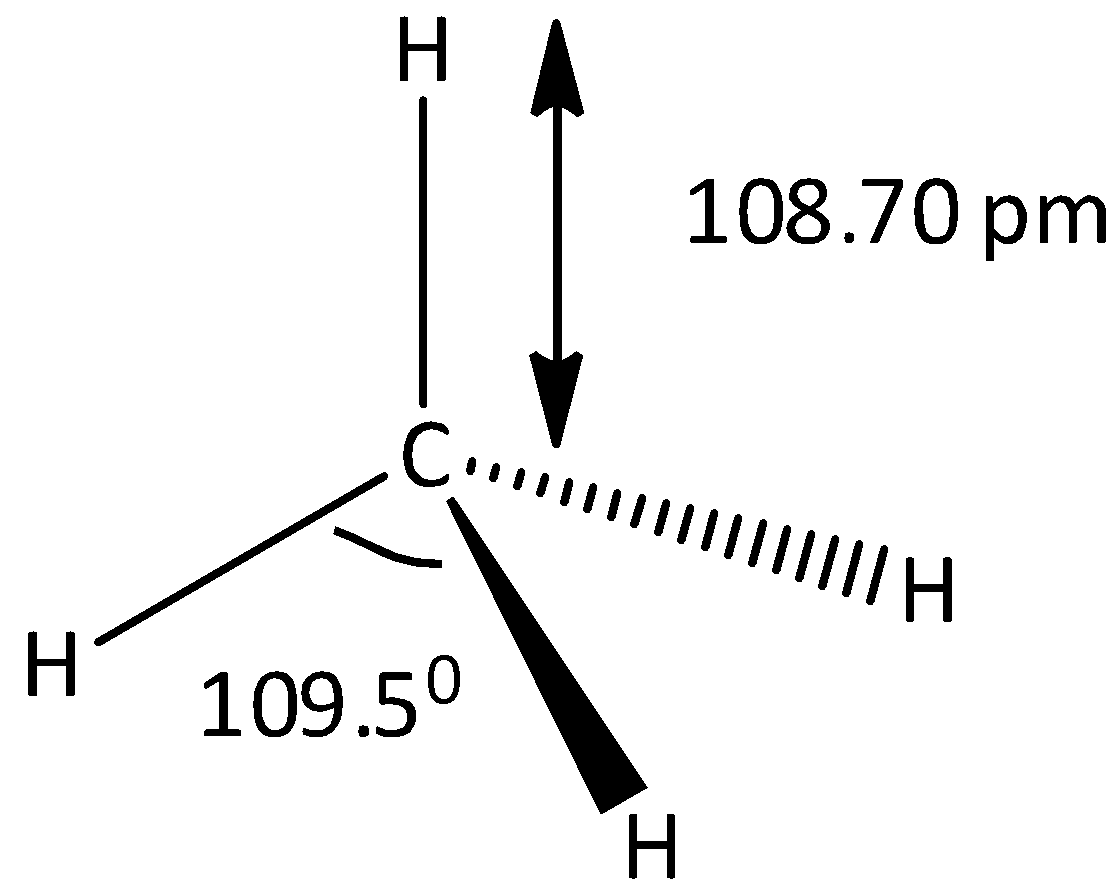
As we know that many of the organic molecules are not planar, including all the alkanes. But these are characterized by three dimensional structures. In the case of methane, the shape of methane is a regular tetrahedron and the carbon is located at the center and the hydrogen atoms are attached on each corner of the tetrahedron. The methane compound contains a total four carbon – hydrogen bonds. And the angles of \[H - C - H\] are equal to \[109.5^\circ \]. When all the hydrogen atoms are interchanged by using the symmetry operation, then all the hydrogens atoms present in the methane become equivalent. Let’s see the structure of methane,
Note:
The three dimensional structure is also known as tertiary structure. The methane is a tetrahedral compound and it contains four equivalent carbon – hydrogen bonds. The central atom is carbon and it is attached with four hydrogen atoms by covalent bond. Here the outer shells of both hydrogen and carbon atoms will share completely and the atoms become more stable. Methane is an odorless gas which is mainly used as fuel.
Complete answer:
As we know that many of the organic molecules are not planar, including all the alkanes. But these are characterized by three dimensional structures. In the case of methane, the shape of methane is a regular tetrahedron and the carbon is located at the center and the hydrogen atoms are attached on each corner of the tetrahedron. The methane compound contains a total four carbon – hydrogen bonds. And the angles of \[H - C - H\] are equal to \[109.5^\circ \]. When all the hydrogen atoms are interchanged by using the symmetry operation, then all the hydrogens atoms present in the methane become equivalent. Let’s see the structure of methane,

Note:
The three dimensional structure is also known as tertiary structure. The methane is a tetrahedral compound and it contains four equivalent carbon – hydrogen bonds. The central atom is carbon and it is attached with four hydrogen atoms by covalent bond. Here the outer shells of both hydrogen and carbon atoms will share completely and the atoms become more stable. Methane is an odorless gas which is mainly used as fuel.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




