
In the stomach, what is the role of chief cells and parietal cells?
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: The two main types of exocrine secretory cells that are present in the stomach are the parietal cells and chief cells. Parietal cells secrete hydrochloric acid while the chief cells secrete digestive enzymes such as pepsin. These cells secrete their products when activated by signals from the body like hormones and neurotransmitters.
Complete answer:
Parietal cells are the exocrine cells of the stomach that secretes hydrochloric acid. The acid which is secreted by the cells helps in the digestion of food by causing them to unfold. The secretion of the parietal cells contains three million times more hydrogen ions than there are hydrogen ions in the bloodstream. Parietal cells secrete hydrochloric acid when they are stimulated by hormones such as gastrin, molecules such as histamine, which causes allergies and neurotransmitters from nerve cells such as acetylcholine.
Chief cells are the other type of exocrine secretory cell present in the stomach. They secrete digestive enzymes that break down the proteins in food into smaller pieces. Pepsin is secreted as an inactive enzyme which is called pepsinogen that is secreted by the chief cell. Pepsinogen becomes active when it comes in contact with an acidic environment and is cut apart. Chief cells start secreting digestive enzymes when they are activated by hormones and neurotransmitters. Activating hormones comprises secretin, vasoactive intestinal peptide and gastrin.
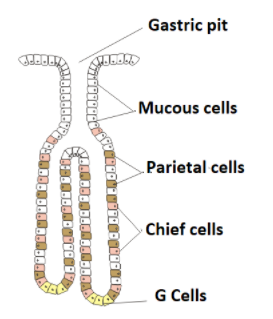
Note: Parietal cells are the epithelial cells that secrete hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor. They are situated in the gastric glands which are found inlining of the fundus and stomach. The gastric chief cells are cells in the stomach that releases pepsinogen and chymosin. They synthesize and secrete hydrolytic enzymes which are activated at an acidic medium. These are situated, in clusters at the base of the gastric glands.
Complete answer:
Parietal cells are the exocrine cells of the stomach that secretes hydrochloric acid. The acid which is secreted by the cells helps in the digestion of food by causing them to unfold. The secretion of the parietal cells contains three million times more hydrogen ions than there are hydrogen ions in the bloodstream. Parietal cells secrete hydrochloric acid when they are stimulated by hormones such as gastrin, molecules such as histamine, which causes allergies and neurotransmitters from nerve cells such as acetylcholine.
Chief cells are the other type of exocrine secretory cell present in the stomach. They secrete digestive enzymes that break down the proteins in food into smaller pieces. Pepsin is secreted as an inactive enzyme which is called pepsinogen that is secreted by the chief cell. Pepsinogen becomes active when it comes in contact with an acidic environment and is cut apart. Chief cells start secreting digestive enzymes when they are activated by hormones and neurotransmitters. Activating hormones comprises secretin, vasoactive intestinal peptide and gastrin.

Note: Parietal cells are the epithelial cells that secrete hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor. They are situated in the gastric glands which are found inlining of the fundus and stomach. The gastric chief cells are cells in the stomach that releases pepsinogen and chymosin. They synthesize and secrete hydrolytic enzymes which are activated at an acidic medium. These are situated, in clusters at the base of the gastric glands.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




