
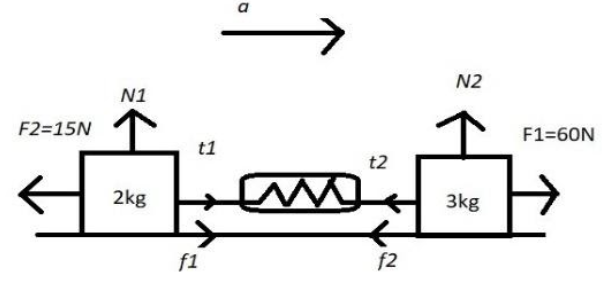
In the situation given, the reading of the spring balance is ($g = 10m/{s^2}$).
A). $30N$
B). $33N$
C). $39N$
D). $40N$

Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: In order to find the solution of the question, we need to draw a free body diagram of the above image including all the forces exerted on the body. Then we will find the tension in the spring balance to find the reading.
Complete step-by-step solution:
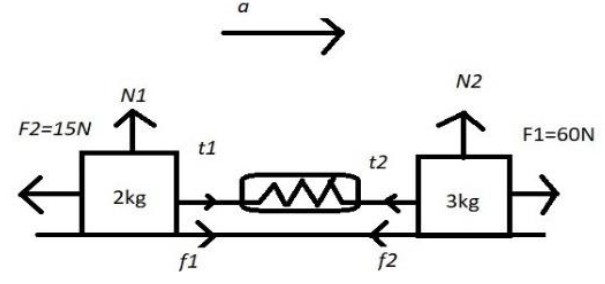
The free body diagram of the body is given as below:
The frictional force exerted by $2kg$ of body is
\[{f_1} = \mu {\rm N}\]
${f_1} = \mu mg
= 0.5 \times 2 \times 10 \\
= 10N $
The frictional force exerted by $3kg$ body is
$ {f_2} = \mu {\rm N} \\
\Rightarrow f_2^{} = \mu mg \\
= 0.5 \times 3 \times 10 \\
= 15N $
Then we need to find the acceleration find the tension between the spring:
$ {F_{net}} = ma \\
\Rightarrow 60N + 10N - 15N - 15N = (3 + 2)a \\
\Rightarrow 5a = 40 \\
\Rightarrow a = 8m/{s^2} $
Now, we will find the tension in the wire of spring of the $2kg$body:
$ {T_1} + {f_1} - 15N = 2a \\
\Rightarrow {T_1} + 10 - 15 = 2 \times 8 \\
\Rightarrow {T_1} = 21N $
Now, we will find the tension in the wire of spring of the$3kg$body:
$ 60N - {T_2} - {f_2} = 3a \\
\Rightarrow 60N - {T_2} - 15N = 24 \\
\Rightarrow {T_2} = 19N $
Now the reading of spring balance will be:
$ = {T_1} + {T_2} \\
= 21N + 19N \\
= 40N $
The reading in the spring balance in the above figure is $40N$.
Note: We need to keep some points in our mind while solving these problems:
> The free body diagram is the most important thing in these kinds of questions so that we get to know the magnitude and direction of all the forces exerted.
> We should have proper knowledge of laws of motion so that we can apply the accordingly.
> We should remember all the required formulae.
Complete step-by-step solution:

The free body diagram of the body is given as below:
The frictional force exerted by $2kg$ of body is
\[{f_1} = \mu {\rm N}\]
${f_1} = \mu mg
= 0.5 \times 2 \times 10 \\
= 10N $
The frictional force exerted by $3kg$ body is
$ {f_2} = \mu {\rm N} \\
\Rightarrow f_2^{} = \mu mg \\
= 0.5 \times 3 \times 10 \\
= 15N $
Then we need to find the acceleration find the tension between the spring:
$ {F_{net}} = ma \\
\Rightarrow 60N + 10N - 15N - 15N = (3 + 2)a \\
\Rightarrow 5a = 40 \\
\Rightarrow a = 8m/{s^2} $
Now, we will find the tension in the wire of spring of the $2kg$body:
$ {T_1} + {f_1} - 15N = 2a \\
\Rightarrow {T_1} + 10 - 15 = 2 \times 8 \\
\Rightarrow {T_1} = 21N $
Now, we will find the tension in the wire of spring of the$3kg$body:
$ 60N - {T_2} - {f_2} = 3a \\
\Rightarrow 60N - {T_2} - 15N = 24 \\
\Rightarrow {T_2} = 19N $
Now the reading of spring balance will be:
$ = {T_1} + {T_2} \\
= 21N + 19N \\
= 40N $
The reading in the spring balance in the above figure is $40N$.
Note: We need to keep some points in our mind while solving these problems:
> The free body diagram is the most important thing in these kinds of questions so that we get to know the magnitude and direction of all the forces exerted.
> We should have proper knowledge of laws of motion so that we can apply the accordingly.
> We should remember all the required formulae.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




