
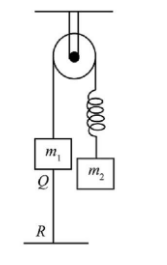
In the shown system ${m_1} > {m_2}$. Thread $QR$ is holding the system. If this thread is cut, then just after cutting:
(A) Acceleration of mass ${m_1}$ is zero and that of ${m_2}$ is direct upward
(B) Acceleration of mass ${m_2}$ is zero and that of ${m_1}$ is direct upward
(C) Acceleration of both the blocks will be same
(D) Acceleration of the system is given by $\dfrac{{\left( {{m_1} - {m_2}} \right)}}{{\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}\;kg$, where k is a spring factor

Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: The given problem is based upon the application of Newton's motion. So here we will use the concept of a spring mass system. In the given problem figure, we can see that the mass of block ${m_1}$ is more than that of block ${m_2}$. As the thread QR is cut, then the resultant force on mass ${m_1}$ becomes equal to zero.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Two blocks of different masses are given in the problem figure. The mass of one block attached to spring is ${m_2}$ and the mass of another block attached to thread QR is ${m_2}$.
In the given figure, the thread QR holds the system, then it says that the thread is cut, then just after cutting the resultant force on mass ${m_1}$ becomes equal to zero because we can see it is balanced by the tension in the spring. So the acceleration of the mass ${m_1}$ is zero.
${a_1} = 0$
Here, ${a_1}$ is the acceleration of mass ${m_1}$.
Now, we write the resultant force acting on mass ${m_2}$
${F_2} = \left( {{m_1} - {m_2}} \right)g$
Here, g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Now, we write the equation for acceleration acting in upward direction on mass ${m_2}$.
${a_2} = \dfrac{{{F_2}}}{{{m_2}}}$
Now, we substitute the value of ${F_2}$ in above relation.
${a_2} = \dfrac{{\left( {{m_1} - {m_2}} \right)g}}{{{m_2}}}$
Therefore, the acceleration of mass ${m_1}$ is zero and the acceleration of mass ${m_2}$ is directed upward and the correct option from the given options is option (A).
Note:In this type of problem we should know that the spring balances the system. If the thread is cut then, the mass at which the sting or thread is attached experiences zero resultant force and there is no change in the spring force.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Two blocks of different masses are given in the problem figure. The mass of one block attached to spring is ${m_2}$ and the mass of another block attached to thread QR is ${m_2}$.
In the given figure, the thread QR holds the system, then it says that the thread is cut, then just after cutting the resultant force on mass ${m_1}$ becomes equal to zero because we can see it is balanced by the tension in the spring. So the acceleration of the mass ${m_1}$ is zero.
${a_1} = 0$
Here, ${a_1}$ is the acceleration of mass ${m_1}$.
Now, we write the resultant force acting on mass ${m_2}$
${F_2} = \left( {{m_1} - {m_2}} \right)g$
Here, g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Now, we write the equation for acceleration acting in upward direction on mass ${m_2}$.
${a_2} = \dfrac{{{F_2}}}{{{m_2}}}$
Now, we substitute the value of ${F_2}$ in above relation.
${a_2} = \dfrac{{\left( {{m_1} - {m_2}} \right)g}}{{{m_2}}}$
Therefore, the acceleration of mass ${m_1}$ is zero and the acceleration of mass ${m_2}$ is directed upward and the correct option from the given options is option (A).
Note:In this type of problem we should know that the spring balances the system. If the thread is cut then, the mass at which the sting or thread is attached experiences zero resultant force and there is no change in the spring force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




