
In the reaction below, State what is being oxidized and what is being reduced?
$ S{O_2} + {O_2} \to S{O_3} $
Answer
490.8k+ views
Hint: The process of oxidation that takes place is described by the loss of electrons by an atom or by a group of atoms. The process of reduction that takes place is described by the acceptance of electrons by an atom or by the group of atoms. Chemical reactions which include both of them are known as redox reactions.
Complete answer:
There are some ways to determine whether the process of oxidation occurs or not like:
$ \to $ Increase in positive charge over the atom indicates the oxidation
$ \to $ Decrease in the number of electrons over the atom indicates the oxidation.
$ \to $ Increase in oxidation number of the atom indicates the oxidation.
Similarly, the process of reduction is also determined:
$ \to $ decrease in positive charge over the atom indicates the reduction.
$ \to $ increase in the number of electrons over the atom indicates the reduction.
$ \to $ Decrease in oxidation number of the atom indicates the reduction.
In the given chemical reaction: $ S{O_2} + {O_2} \to S{O_3} $
Firstly, we have to calculate the oxidation number of each of the atoms present in the reaction.
Oxidation number of sulphur $ \left( S \right) $ in $ S{O_2} $ is: $ x + 2 \times \left( { - 2} \right) = 0 $
On solving the above equation, we get
$ x = + 4 $
Oxidation number of $ \left( S \right) $ in $ S{O_3} $ is: $ x + 3 \times \left( { - 2} \right) = 0 $
On solving the above equation, we get
$ x = + 6 $
As we see, the oxidation number of sulphur atoms increases $ \left( S \right) $ from $ \left( { + 4} \right) $ to $ \left( { + 6} \right) $ . Hence, $ S{O_2} $ gets oxidized to $ S{O_3} $ .
Oxidation number of Oxygen $ \left( O \right) $ in $ {O_2} $ is zero because the oxidation number of atoms in its natural or free state is considered as zero.
Oxidation number of Oxygen $ \left( O \right) $ in $ S{O_3} $ is: $ 6 + 3 \times \left( x \right) = 0 $
On solving, we get
$ 3x = \left( { - 6} \right) $
On calculating, we get
$ x = - 2 $
As we see, the oxidation number of oxygen atoms decreases from $ \left( 0 \right) $ to $ \left( { - 2} \right) $ . Hence, $ {O_2} $ gets reduced to $ S{O_3} $ .
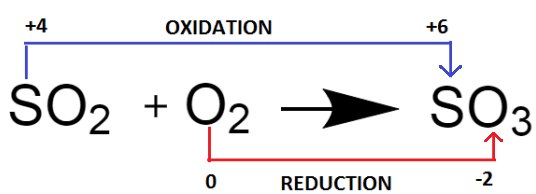
$ \Rightarrow $ In the chemical reaction: $ S{O_2} $ + $ {O_2} \to S{O_3} $ , sulphur gets oxidized and oxygen gets reduced.
Note:
Substances which tend to accept one or more electrons are known as oxidizing agents like $ KMn{O_4},{H_2}S{O_4} $ . Substances which tend to lose one or more electrons are known as reducing agents like $ Fe,Zn $ . Oxidation number of the atom may vary with change in reaction it may participate.
Complete answer:
There are some ways to determine whether the process of oxidation occurs or not like:
$ \to $ Increase in positive charge over the atom indicates the oxidation
$ \to $ Decrease in the number of electrons over the atom indicates the oxidation.
$ \to $ Increase in oxidation number of the atom indicates the oxidation.
Similarly, the process of reduction is also determined:
$ \to $ decrease in positive charge over the atom indicates the reduction.
$ \to $ increase in the number of electrons over the atom indicates the reduction.
$ \to $ Decrease in oxidation number of the atom indicates the reduction.
In the given chemical reaction: $ S{O_2} + {O_2} \to S{O_3} $
Firstly, we have to calculate the oxidation number of each of the atoms present in the reaction.
Oxidation number of sulphur $ \left( S \right) $ in $ S{O_2} $ is: $ x + 2 \times \left( { - 2} \right) = 0 $
On solving the above equation, we get
$ x = + 4 $
Oxidation number of $ \left( S \right) $ in $ S{O_3} $ is: $ x + 3 \times \left( { - 2} \right) = 0 $
On solving the above equation, we get
$ x = + 6 $
As we see, the oxidation number of sulphur atoms increases $ \left( S \right) $ from $ \left( { + 4} \right) $ to $ \left( { + 6} \right) $ . Hence, $ S{O_2} $ gets oxidized to $ S{O_3} $ .
Oxidation number of Oxygen $ \left( O \right) $ in $ {O_2} $ is zero because the oxidation number of atoms in its natural or free state is considered as zero.
Oxidation number of Oxygen $ \left( O \right) $ in $ S{O_3} $ is: $ 6 + 3 \times \left( x \right) = 0 $
On solving, we get
$ 3x = \left( { - 6} \right) $
On calculating, we get
$ x = - 2 $
As we see, the oxidation number of oxygen atoms decreases from $ \left( 0 \right) $ to $ \left( { - 2} \right) $ . Hence, $ {O_2} $ gets reduced to $ S{O_3} $ .

$ \Rightarrow $ In the chemical reaction: $ S{O_2} $ + $ {O_2} \to S{O_3} $ , sulphur gets oxidized and oxygen gets reduced.
Note:
Substances which tend to accept one or more electrons are known as oxidizing agents like $ KMn{O_4},{H_2}S{O_4} $ . Substances which tend to lose one or more electrons are known as reducing agents like $ Fe,Zn $ . Oxidation number of the atom may vary with change in reaction it may participate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




