
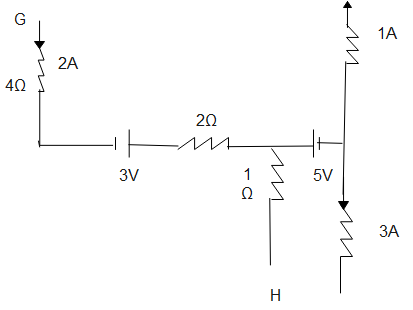
In the part of a circuit shown in fig, the potential difference $\left( {{V_H} - {V_G}} \right)$ between points G and H will be
1)1V
2)-1V
3)7V
4)-7V

Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: First we have to observe the given circuit diagram. To solve this question apply the first law of kirchhoff's junction which states that the current going into a junction must equal the current coming out. Here we have to find the potential difference between given points G and H.
Complete answer:
Kirchhoff's first law is also known as kirchhoff's current law. It states that the current going into a junction must equal the current coming out. So, in the given circuit diagram there is 4A current coming out of the junction (3A+1A). According to Kirchhoff's first law, the current is 4A.
From the point G there is a flowing 2A current and other remaining 2A current came from the point H. So, total incoming current is 2A+2A= 4A. Finally we get the total current of the select branch of the junction from points G to H.
Focus on the branch of junction from points G to H. Here we have to remember Kirchhoff's voltage law; it states that the algebraic sum of all voltages within the loop must be equal to zero. Starting from point G we consider potential is ${V_G}$ there is a drop of potential as we see in the circuit diagram.
In the question mentioned to find potential difference between points G and H. So, we select the branch of the junction from G to H.
$ {V_G} - 2A \times 4\Omega + 3V - 2A \times 2\Omega + 2A \times 1\Omega = {V_H} \\
\Rightarrow {V_G} - 8 + 3 - 4 + 2 = {V_H} \\
\Rightarrow - 8 + 3 - 4 + 2 = {V_H} - {V_G} \\
\therefore - 7 = {V_H} - {V_G} \\ $
Hence the correct answer is -7 that is in the option 4.
Note:
In these types of questions we need to observe circuit diagrams where the current is added and where the current is dropped. We know that ohm's law which states that electric current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance in other words we can write V=IR.
Complete answer:
Kirchhoff's first law is also known as kirchhoff's current law. It states that the current going into a junction must equal the current coming out. So, in the given circuit diagram there is 4A current coming out of the junction (3A+1A). According to Kirchhoff's first law, the current is 4A.
From the point G there is a flowing 2A current and other remaining 2A current came from the point H. So, total incoming current is 2A+2A= 4A. Finally we get the total current of the select branch of the junction from points G to H.
Focus on the branch of junction from points G to H. Here we have to remember Kirchhoff's voltage law; it states that the algebraic sum of all voltages within the loop must be equal to zero. Starting from point G we consider potential is ${V_G}$ there is a drop of potential as we see in the circuit diagram.
In the question mentioned to find potential difference between points G and H. So, we select the branch of the junction from G to H.
$ {V_G} - 2A \times 4\Omega + 3V - 2A \times 2\Omega + 2A \times 1\Omega = {V_H} \\
\Rightarrow {V_G} - 8 + 3 - 4 + 2 = {V_H} \\
\Rightarrow - 8 + 3 - 4 + 2 = {V_H} - {V_G} \\
\therefore - 7 = {V_H} - {V_G} \\ $
Hence the correct answer is -7 that is in the option 4.
Note:
In these types of questions we need to observe circuit diagrams where the current is added and where the current is dropped. We know that ohm's law which states that electric current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance in other words we can write V=IR.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




