
In the interval \[\left[ 0,3 \right]\] , the number of points at which the function \[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\sin \pi x\] ( \[\left[ . \right]\] is the usual integral part) is discontinuous are:
(a)\[4\]
(b)\[5\]
(c) \[6\]
(d) \[8\]
Answer
623.1k+ views
Hint: \[\left[ g\left( x \right) \right]\] is continuous only at those points at which \[g\left( x \right)\] does not attain an integer value . If \[g\left( x \right)\] attains an integer value , \[\left[ g\left( x \right) \right]\] becomes discontinuous .
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let the given function be \[f\left( x \right)\] . So, we can say \[f\left( x \right)=\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\sin \pi x\] .
Now , we know the greatest integer function is defined as a function which rounds down a real number to the nearest integer . Its graph is as given as
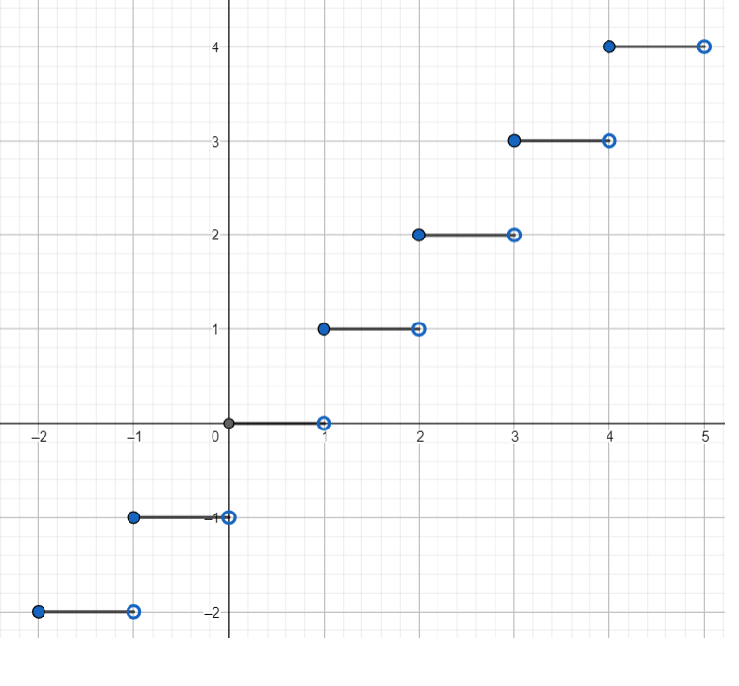
From the graph , we can clearly see that the graph is in the form of steps . So , from the graph we can conclude that the greatest integer function is discontinuous at integer points .
Now , we can define the function \[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\] as:
\[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]=\left\{ \begin{align}
& 0,\text{ }0\le x<1 \\
& 1,\text{ }1\le x<\sqrt{2} \\
& 2,\text{ }\sqrt{2}\le x<\sqrt{3} \\
& 3,\text{ }\sqrt{3}\le x<2 \\
& 4,\text{ }2\le x<\sqrt{5} \\
& 5,\text{ }\sqrt{5}\le x<\sqrt{6} \\
& 6,\text{ }\sqrt{6}\le x<\sqrt{7} \\
& 7,\text{ }\sqrt{7}\le x\sqrt{8} \\
& 8,\text{ }\sqrt{8}\le x<3 \\
& 9,\text{ }x=3 \\
\end{align} \right.\]
The graph of the function \[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\] is given as:
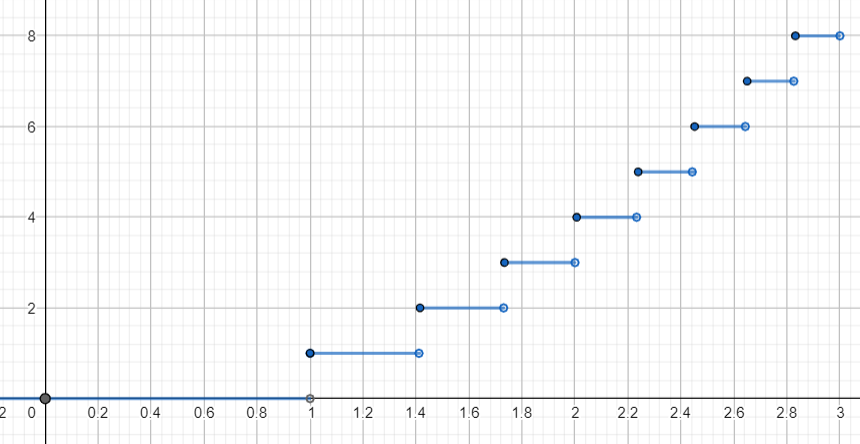
From the graph we can see that \[\left[ g\left( x \right) \right]\] is discontinuous at points where \[g\left( x \right)\] becomes an integer.
So , \[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\] should be discontinuous at \[x=0,x=1,x=\sqrt{2},x=\sqrt{3},x=2,x=\sqrt{5},x=\sqrt{6},x=\sqrt{7},x=\sqrt{8}\] and \[x=3\] .
But , since \[f\left( x \right)\] is defined in the interval \[x\in \left[ 0,3 \right]\] , \[f\left( x \right)\] does not exist to the left of \[x=0\] and to right of \[x=3\] .
So , continuity of function \[f\left( x \right)\] cannot be discussed at \[x=0\] and at \[x=3\] .
Now , in the interval \[\left[ 0,3 \right]\] , we can see there are \[8\] points at which \[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\] is discontinuous i.e. \[{{x}^{2}}\] attains an integer value.
These points are \[x=1,\text{ }x=\sqrt{2},\text{ }x=\sqrt{3},\text{ }x=2,\text{ }x=\sqrt{5},\text{ }x=\sqrt{6},\text{ }x=\sqrt{7}\] and \[x=\sqrt{8}\] .
Hence, the function \[f\left( x \right)=\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\sin \pi x\] is discontinuous at these \[8\] points.
Note: The critical points for the function \[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\]are \[x=0,x=1,x=\sqrt{2},x=\sqrt{3},x=2,x=\sqrt{5},x=\sqrt{6},x=\sqrt{7},x=\sqrt{8}\] and \[x=3\] and not \[x=0,x=1,x=2,x=3,x=4,x=5,x=6,x=7,x=8\] and \[x=9\] as in GIF there is square of x so the domain will contains those value whose square is an integer. Students often make this mistake. Due to such mistakes , they end up getting a wrong answer . So , such mistakes should be avoided .
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let the given function be \[f\left( x \right)\] . So, we can say \[f\left( x \right)=\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\sin \pi x\] .
Now , we know the greatest integer function is defined as a function which rounds down a real number to the nearest integer . Its graph is as given as

From the graph , we can clearly see that the graph is in the form of steps . So , from the graph we can conclude that the greatest integer function is discontinuous at integer points .
Now , we can define the function \[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\] as:
\[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]=\left\{ \begin{align}
& 0,\text{ }0\le x<1 \\
& 1,\text{ }1\le x<\sqrt{2} \\
& 2,\text{ }\sqrt{2}\le x<\sqrt{3} \\
& 3,\text{ }\sqrt{3}\le x<2 \\
& 4,\text{ }2\le x<\sqrt{5} \\
& 5,\text{ }\sqrt{5}\le x<\sqrt{6} \\
& 6,\text{ }\sqrt{6}\le x<\sqrt{7} \\
& 7,\text{ }\sqrt{7}\le x\sqrt{8} \\
& 8,\text{ }\sqrt{8}\le x<3 \\
& 9,\text{ }x=3 \\
\end{align} \right.\]
The graph of the function \[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\] is given as:

From the graph we can see that \[\left[ g\left( x \right) \right]\] is discontinuous at points where \[g\left( x \right)\] becomes an integer.
So , \[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\] should be discontinuous at \[x=0,x=1,x=\sqrt{2},x=\sqrt{3},x=2,x=\sqrt{5},x=\sqrt{6},x=\sqrt{7},x=\sqrt{8}\] and \[x=3\] .
But , since \[f\left( x \right)\] is defined in the interval \[x\in \left[ 0,3 \right]\] , \[f\left( x \right)\] does not exist to the left of \[x=0\] and to right of \[x=3\] .
So , continuity of function \[f\left( x \right)\] cannot be discussed at \[x=0\] and at \[x=3\] .
Now , in the interval \[\left[ 0,3 \right]\] , we can see there are \[8\] points at which \[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\] is discontinuous i.e. \[{{x}^{2}}\] attains an integer value.
These points are \[x=1,\text{ }x=\sqrt{2},\text{ }x=\sqrt{3},\text{ }x=2,\text{ }x=\sqrt{5},\text{ }x=\sqrt{6},\text{ }x=\sqrt{7}\] and \[x=\sqrt{8}\] .
Hence, the function \[f\left( x \right)=\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\sin \pi x\] is discontinuous at these \[8\] points.
Note: The critical points for the function \[\left[ {{x}^{2}} \right]\]are \[x=0,x=1,x=\sqrt{2},x=\sqrt{3},x=2,x=\sqrt{5},x=\sqrt{6},x=\sqrt{7},x=\sqrt{8}\] and \[x=3\] and not \[x=0,x=1,x=2,x=3,x=4,x=5,x=6,x=7,x=8\] and \[x=9\] as in GIF there is square of x so the domain will contains those value whose square is an integer. Students often make this mistake. Due to such mistakes , they end up getting a wrong answer . So , such mistakes should be avoided .
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




