
In the hysteresis cycle, the value of H needed to make the intensity of magnetism zero is called
A. Retentivity
B. Coercive force
C. Lorentz force
D. None of the above
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: In this question, we first see the hysteresis loop and see the point of saturation, the point of retentivity, and the point of coercivity. From the hysteresis, we see that the residual magnetism is called retentivity and the point where the magnetism becomes zero is called coercivity.
Step-By-Step answer:
The hysteresis loop is the graph plotted between the intensity of Magnetization M and the magnetizing field intensity H. this loop is made because when a ferromagnetic material is magnetized to some value, it will not return back to the initial zero magnetization after the applied field is removed hence resulting in a loop called as the hysteresis loop.
Now seeing the plot of the hysteresis loop in figure 1 we will see each part one by one that is,
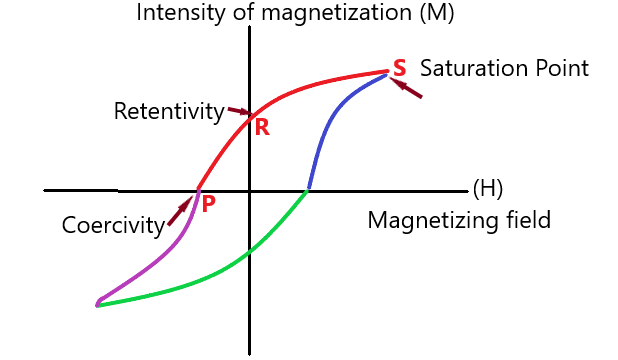
Figure 1
First, we apply a magnetic field intensity (H) and due to this, the intensity of Magnetization (M) starts rising from the initial value that is zero. After that The intensity of Magnetization(M) eventually reaches a point S where it gets saturated hence, known as saturation point.
Then we start reducing the magnetic field intensity (H) due to this the magnetism (M) also starts to reduce but it follows a different path and because of this at point R when (H) becomes zero the (M) does not become zero that is the material still retains some magnetism known as residual magnetism or Retentivity of the material.
So to demagnetize the material completely we need to apply a negative magnetic field intensity and at point P the magnetism becomes zero. This force which is needed to remove the Retentivity is called Coercive force and it is also known as the coercivity of the material.
Therefore from the above explanation, we can see that the value of H needed to make M zero is the coercive force, so the correct option is C.
Note: For these types of questions we need to know about the different types of magnetic material that are paramagnetic, diamagnetic, antiferromagnetic, ferromagnetic, and ferrimagnetic materials. Then we need to know about the mechanism of magnetism, demagnetism, magnetic dipole, magnetic domains, and hysteresis loop.
Step-By-Step answer:
The hysteresis loop is the graph plotted between the intensity of Magnetization M and the magnetizing field intensity H. this loop is made because when a ferromagnetic material is magnetized to some value, it will not return back to the initial zero magnetization after the applied field is removed hence resulting in a loop called as the hysteresis loop.
Now seeing the plot of the hysteresis loop in figure 1 we will see each part one by one that is,

Figure 1
First, we apply a magnetic field intensity (H) and due to this, the intensity of Magnetization (M) starts rising from the initial value that is zero. After that The intensity of Magnetization(M) eventually reaches a point S where it gets saturated hence, known as saturation point.
Then we start reducing the magnetic field intensity (H) due to this the magnetism (M) also starts to reduce but it follows a different path and because of this at point R when (H) becomes zero the (M) does not become zero that is the material still retains some magnetism known as residual magnetism or Retentivity of the material.
So to demagnetize the material completely we need to apply a negative magnetic field intensity and at point P the magnetism becomes zero. This force which is needed to remove the Retentivity is called Coercive force and it is also known as the coercivity of the material.
Therefore from the above explanation, we can see that the value of H needed to make M zero is the coercive force, so the correct option is C.
Note: For these types of questions we need to know about the different types of magnetic material that are paramagnetic, diamagnetic, antiferromagnetic, ferromagnetic, and ferrimagnetic materials. Then we need to know about the mechanism of magnetism, demagnetism, magnetic dipole, magnetic domains, and hysteresis loop.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




