
In the given system which mass (in kg) will move with acceleration greater than acceleration due to gravity $ (g) $ .
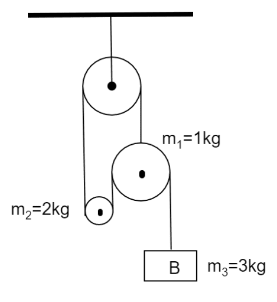

Answer
478.2k+ views
Hint: Tension is the pulling force acting along a stretched flexible connector, such as a rope or cable. When a rope holds the weight of an object at rest, the rope's tension is equal to the object's weight. Using this we will find the acceleration of the different masses hence the answer to our question.
Complete answer:
When items rest on a surface, the surface exerts a force on the object, which helps it to support its weight. This sustaining force works perpendicular to the surface and away from it. There is a pulling force acting along a stretched flexible connector that is known as a normal force.
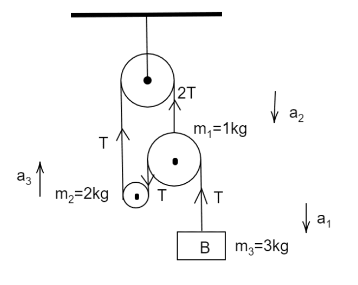
let a downward acceleration on the $ 3kg $ block be $ {a_1} $
Let $ T $ be tensioned in each part of the string. The equation of motion on the block
For $ 3kg $ mass is
$ 3{a_1} = 3g - T $ ………………… $ (1) $
For $ 1kg $ mass
$ 1 \times {a_2} = 2T - 2T + g $
$ \Rightarrow {a_2} = g $ ………………………. $ (2) $
For $ 2kg $ mass
$ 2{a_3} = 2T - 2g $ ………………….. $ (3) $
Hence relation between all the acceleration will be,
$ {a_1} = 2{a_2} + 2{a_3} $
Putting value of $ {a_2} $ we get,
$ \Rightarrow {a_1} = 2g + 2{a_3} $
$ \Rightarrow {a_1} = 2(g + {a_3}) $
Solving the above equations we get,
$ 6g + 6{a_3} = 3g - T $
$ \Rightarrow 3g + 6{a_3} = - T $
$ 2{a_3} = - 9g - 12{a_3} $
$ \Rightarrow {a_3} = \dfrac{{ - 9g}}{{14}} $
$ {a_1} = 2 \times \left( {\dfrac{{4 - 9}}{{14}}} \right)g $
$ \Rightarrow {a_1} = \dfrac{{10g}}{{14}} $
$ \Rightarrow {a_2} = g $
So mass $ {a_2} $ is moving with the speed of acceleration in the given system.
Note:
It’s crucial to remember that tension in a connector refers to a pull. Take, for example, the expression "You can't push a rope." A rope's two ends are pulled outward by the tension force. All we have to do to create a lot of tension is apply a force perpendicular to a flexible connector.
Complete answer:
When items rest on a surface, the surface exerts a force on the object, which helps it to support its weight. This sustaining force works perpendicular to the surface and away from it. There is a pulling force acting along a stretched flexible connector that is known as a normal force.

let a downward acceleration on the $ 3kg $ block be $ {a_1} $
Let $ T $ be tensioned in each part of the string. The equation of motion on the block
For $ 3kg $ mass is
$ 3{a_1} = 3g - T $ ………………… $ (1) $
For $ 1kg $ mass
$ 1 \times {a_2} = 2T - 2T + g $
$ \Rightarrow {a_2} = g $ ………………………. $ (2) $
For $ 2kg $ mass
$ 2{a_3} = 2T - 2g $ ………………….. $ (3) $
Hence relation between all the acceleration will be,
$ {a_1} = 2{a_2} + 2{a_3} $
Putting value of $ {a_2} $ we get,
$ \Rightarrow {a_1} = 2g + 2{a_3} $
$ \Rightarrow {a_1} = 2(g + {a_3}) $
Solving the above equations we get,
$ 6g + 6{a_3} = 3g - T $
$ \Rightarrow 3g + 6{a_3} = - T $
$ 2{a_3} = - 9g - 12{a_3} $
$ \Rightarrow {a_3} = \dfrac{{ - 9g}}{{14}} $
$ {a_1} = 2 \times \left( {\dfrac{{4 - 9}}{{14}}} \right)g $
$ \Rightarrow {a_1} = \dfrac{{10g}}{{14}} $
$ \Rightarrow {a_2} = g $
So mass $ {a_2} $ is moving with the speed of acceleration in the given system.
Note:
It’s crucial to remember that tension in a connector refers to a pull. Take, for example, the expression "You can't push a rope." A rope's two ends are pulled outward by the tension force. All we have to do to create a lot of tension is apply a force perpendicular to a flexible connector.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




