
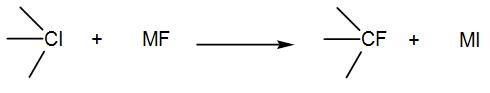
In the given replacement reaction, the reaction will be most favourable if M happens to be:
[A] K
[B] Rb
[C] Li
[D] Na

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this, think about the factors that affect strength of a bond. Here, for the replacement to be favourable, MF bond should be weak so that it can break easily and then replacement takes place via substitution mechanism.
Complete answer:
Here, we have a chlorine iodine compound which upon reaction with a metal fluoride undergoes replacement and gives us a metal iodide.
For this reaction to be feasible, the metal and fluorine bond should be weak so that the metal leaves the fluoride ion readily. The fluoride ion will attack on the carbocation and the reaction will proceed via ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Here for the M – F bond to be weak, it should have a lower lattice energy.
There are two factors that affect the lattice energy of any substance. Firstly it is the charge on the ions and second is the radius of the ions. Higher is the charge on each ion, higher will be the lattice energy. Lower the internuclear distances among the ions in an ionic crystal, higher will be their lattice energy i.e. closer the two ions are, higher is the force of attraction between them.
If the compound is LiF, then due to smaller size and higher lattice energy of lithium, the compound is very stable and therefore, Li – F bond breaking will not be feasible.
However, if the compound is Rb – F, due to the larger size of Rb, the bond length increases and bond strength decreases. So, breaking the Rb –F bond will be most favourable.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [B] Rb.
Note:
Here we can also approach using the HSAB principle that is the Hard Soft Acid Base principle. According to this principle, hard acids will prefer binding with hard bases and soft acids will prefer binding with soft bases.
According to this, for the reaction to take place, the M should be soft-centred so that it will leave the hard centre i.e. fluorine for a comparatively softer centre MI. Among the given elements, Rb is the softest and Li is the hardest. So, the correct answer would be Rb in this case too. However, we ignored the tertiary halide here and just concentrated on the metal halide.
Complete answer:
Here, we have a chlorine iodine compound which upon reaction with a metal fluoride undergoes replacement and gives us a metal iodide.
For this reaction to be feasible, the metal and fluorine bond should be weak so that the metal leaves the fluoride ion readily. The fluoride ion will attack on the carbocation and the reaction will proceed via ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism.
Here for the M – F bond to be weak, it should have a lower lattice energy.
There are two factors that affect the lattice energy of any substance. Firstly it is the charge on the ions and second is the radius of the ions. Higher is the charge on each ion, higher will be the lattice energy. Lower the internuclear distances among the ions in an ionic crystal, higher will be their lattice energy i.e. closer the two ions are, higher is the force of attraction between them.
If the compound is LiF, then due to smaller size and higher lattice energy of lithium, the compound is very stable and therefore, Li – F bond breaking will not be feasible.
However, if the compound is Rb – F, due to the larger size of Rb, the bond length increases and bond strength decreases. So, breaking the Rb –F bond will be most favourable.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [B] Rb.
Note:
Here we can also approach using the HSAB principle that is the Hard Soft Acid Base principle. According to this principle, hard acids will prefer binding with hard bases and soft acids will prefer binding with soft bases.
According to this, for the reaction to take place, the M should be soft-centred so that it will leave the hard centre i.e. fluorine for a comparatively softer centre MI. Among the given elements, Rb is the softest and Li is the hardest. So, the correct answer would be Rb in this case too. However, we ignored the tertiary halide here and just concentrated on the metal halide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




