
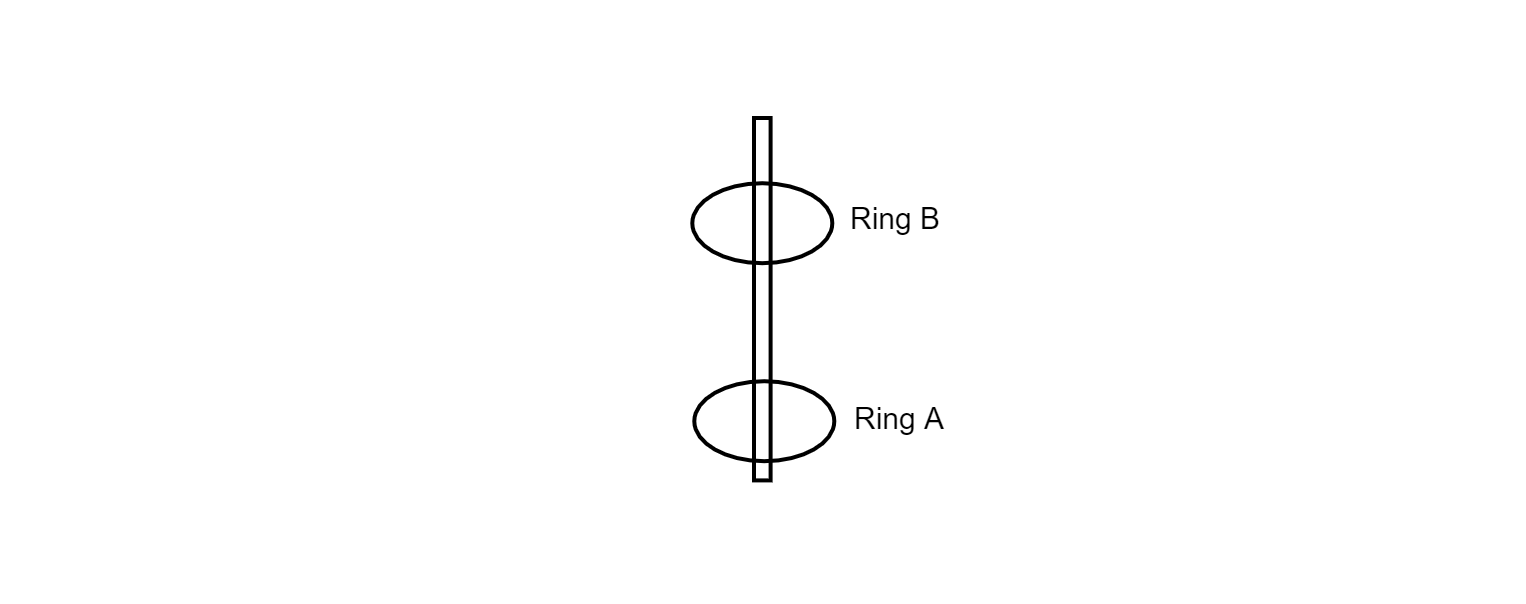
In the given picture the ring $A$ at the bottom is positively charged. Another ring $B$ is brought and placed over it. Ring $B$ hovers at a certain height above $A$. What would be the charge on ring $B$.

Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to know the different ways in which charge is induced from a charged body to a neutral body. Charge can be transferred in three ways i.e., friction, conduction and induction. Here that method is used in which charge is transferred without the contact of the charged body with the neutral body.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first discuss the ways in which charge can be induced to an uncharged object.
Charge transfer by friction: In this method, two uncharged bodies are taken and rubbed together. When they are rubbed together both the bodies acquire opposite charges.
Charge transfer by conduction: In this method when an uncharged conductive body is touched with a charged body, the same charge travels from the charged body to the uncharged body. Thus, in this method there is a movement of charge from one body to another on contact.
Charge transfer by induction: In this method an uncharged body is brought close to the charged body without touching it. The uncharged body acquires an opposite charge as that of the charged body.
In the question it is given that the ring $A$ at the bottom is positively charged and another ring $B$ hovers at a certain height above $A$. Since ring $A$ is charged while ring $B$ is placed at a distance from it, charge transfer by induction will take place and ring $B$ will acquire an opposite charge as that of ring $A$, i.e., it will be negatively charged.
Note: One example of charge transfer by induction is when a metal strip that is negatively charged by rubbing it on animal fur and brought near paper bits, then these paper bits get positively charged and get attracted to the scale and stick to it. Charge transfer by induction takes place without any contact.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first discuss the ways in which charge can be induced to an uncharged object.
Charge transfer by friction: In this method, two uncharged bodies are taken and rubbed together. When they are rubbed together both the bodies acquire opposite charges.
Charge transfer by conduction: In this method when an uncharged conductive body is touched with a charged body, the same charge travels from the charged body to the uncharged body. Thus, in this method there is a movement of charge from one body to another on contact.
Charge transfer by induction: In this method an uncharged body is brought close to the charged body without touching it. The uncharged body acquires an opposite charge as that of the charged body.
In the question it is given that the ring $A$ at the bottom is positively charged and another ring $B$ hovers at a certain height above $A$. Since ring $A$ is charged while ring $B$ is placed at a distance from it, charge transfer by induction will take place and ring $B$ will acquire an opposite charge as that of ring $A$, i.e., it will be negatively charged.
Note: One example of charge transfer by induction is when a metal strip that is negatively charged by rubbing it on animal fur and brought near paper bits, then these paper bits get positively charged and get attracted to the scale and stick to it. Charge transfer by induction takes place without any contact.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




