
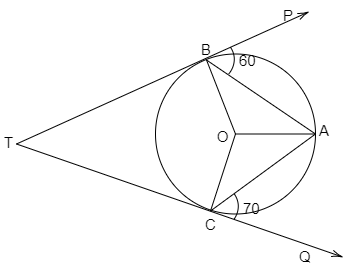
In the given figure, TBP and TCQ are tangents to the circle whose center is O. Also, $\angle PBA = 60^\circ $ and $\angle ACQ = 70^\circ $. Determine $\angle BAC$ and $\angle BTC$.
A. $50^\circ ,60^\circ $
B. $60^\circ ,70^\circ $
C. $50^\circ ,70^\circ $
D. $50^\circ ,80^\circ $

Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: Use the concept of radius making the right angle at the point of contact with the tangent to find the angle and using the property of isosceles triangle formed by radii of the circle to find the angle contributing to \[\angle BAC\]. After that use of the property, the angle subtended by an arc at the center of a circle is double that of the angle that the arc subtends at any other given point on the circle. After that use the property of the sum of opposite angles in a quadrilateral we find the value of $\angle BTC$.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given the measure of an angle $\angle PBA = 60^\circ $ and $\angle ACQ = 70^\circ $.
Use the property of tangents that the radius makes a right angle with the tangent at the point of contact.
$ \Rightarrow \angle OBP = 90^\circ $
We can write,
$\angle OBP = \angle OBA + \angle ABP$
Substitute the values,
$ \Rightarrow 90^\circ = \angle OBA + 60^\circ $
Bring all constant values to one side of the equation,
$ \Rightarrow \angle OBA = 90^\circ - 60^\circ $
Subtract the values,
$ \Rightarrow \angle OBA = 30^\circ $
Now we know that $OA = OB$ as they both are radii of the same circle.
So, triangle OAB is an isosceles triangle.
From the property of the isosceles triangle, the angles opposite to equal sides are equal.
\[ \Rightarrow \angle OAB = \angle OBA\]
Substitute the values,
\[ \Rightarrow \angle OAB = 30^\circ \] ….. (1)
Also, at point C,
$ \Rightarrow \angle OCQ = 90^\circ $
We can write,
$\angle OCQ = \angle OCA + \angle ACQ$
Substitute the values,
$ \Rightarrow 90^\circ = \angle OCA + 70^\circ $
Bring all constant values to one side of the equation,
$ \Rightarrow \angle OCA = 90^\circ - 60^\circ $
Subtract the values,
$ \Rightarrow \angle OCA = 20^\circ $
Now we know that $OA = OC$ as they both are radii of the same circle.
So, triangle OAC is an isosceles triangle.
From the property of the isosceles triangle, the angles opposite to equal sides are equal.
\[ \Rightarrow \angle OAC = \angle OCA\]
Substitute the values,
\[ \Rightarrow \angle OAC = 20^\circ \] ….. (2)
We know that,
\[ \Rightarrow \angle BAC = \angle OAB + \angle OAC\]
Substitute the values from equation (1) and (2),
\[ \Rightarrow \angle BAC = 30^\circ + 20^\circ \]
Add the terms,
\[ \Rightarrow \angle BAC = 50^\circ \]
From the property of the circle, the angle subtended by an arc at the center of a circle is double that of the angle that the arc subtends at any other given point on the circle.
$ \Rightarrow \angle BOC = 2\angle BAC$
Substitute the value of $\angle BAC$,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BOC = 2 \times 50^\circ $
Multiply the terms,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BOC = 100^\circ $
Now we have a quadrilateral OBTC. Then the sum of opposite angles is $180^\circ $.
We have opposite angles $\angle BTC$ and $\angle BOC$.
$ \Rightarrow \angle BTC + \angle BOC = 180^\circ $
Substitute the value of $\angle BOC$,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BTC + 100^\circ = 180^\circ $
Bring all constant values to one side of the equation,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BTC = 180^\circ - 100^\circ $
Subtract the values,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BTC = 80^\circ $
Thus, $\angle BAC = 50^\circ $ and $\angle BTC = 80^\circ $
Hence, option (D) is the correct answer.
Additional Information: The radius of the circle is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact.
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length and the angles opposite to equal sides are equal in measure.
The angle subtended by an arc at the center of a circle is double that of the angle that the arc subtends at any other given point on the circle.
In any quadrilateral, the sum of opposite sides is equal to $180^\circ $.
Note: Students many times get confused with angles given in the diagram i.e. $\angle PBA = 60^\circ $ and $\angle ACQ = 70^\circ $ as the angles made by radius with the tangents. Keep in mind radius is always perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact. Always change the sign from negative to positive and vice versa when shifting the values from one side to another.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given the measure of an angle $\angle PBA = 60^\circ $ and $\angle ACQ = 70^\circ $.
Use the property of tangents that the radius makes a right angle with the tangent at the point of contact.
$ \Rightarrow \angle OBP = 90^\circ $
We can write,
$\angle OBP = \angle OBA + \angle ABP$
Substitute the values,
$ \Rightarrow 90^\circ = \angle OBA + 60^\circ $
Bring all constant values to one side of the equation,
$ \Rightarrow \angle OBA = 90^\circ - 60^\circ $
Subtract the values,
$ \Rightarrow \angle OBA = 30^\circ $
Now we know that $OA = OB$ as they both are radii of the same circle.
So, triangle OAB is an isosceles triangle.
From the property of the isosceles triangle, the angles opposite to equal sides are equal.
\[ \Rightarrow \angle OAB = \angle OBA\]
Substitute the values,
\[ \Rightarrow \angle OAB = 30^\circ \] ….. (1)
Also, at point C,
$ \Rightarrow \angle OCQ = 90^\circ $
We can write,
$\angle OCQ = \angle OCA + \angle ACQ$
Substitute the values,
$ \Rightarrow 90^\circ = \angle OCA + 70^\circ $
Bring all constant values to one side of the equation,
$ \Rightarrow \angle OCA = 90^\circ - 60^\circ $
Subtract the values,
$ \Rightarrow \angle OCA = 20^\circ $
Now we know that $OA = OC$ as they both are radii of the same circle.
So, triangle OAC is an isosceles triangle.
From the property of the isosceles triangle, the angles opposite to equal sides are equal.
\[ \Rightarrow \angle OAC = \angle OCA\]
Substitute the values,
\[ \Rightarrow \angle OAC = 20^\circ \] ….. (2)
We know that,
\[ \Rightarrow \angle BAC = \angle OAB + \angle OAC\]
Substitute the values from equation (1) and (2),
\[ \Rightarrow \angle BAC = 30^\circ + 20^\circ \]
Add the terms,
\[ \Rightarrow \angle BAC = 50^\circ \]
From the property of the circle, the angle subtended by an arc at the center of a circle is double that of the angle that the arc subtends at any other given point on the circle.
$ \Rightarrow \angle BOC = 2\angle BAC$
Substitute the value of $\angle BAC$,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BOC = 2 \times 50^\circ $
Multiply the terms,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BOC = 100^\circ $
Now we have a quadrilateral OBTC. Then the sum of opposite angles is $180^\circ $.
We have opposite angles $\angle BTC$ and $\angle BOC$.
$ \Rightarrow \angle BTC + \angle BOC = 180^\circ $
Substitute the value of $\angle BOC$,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BTC + 100^\circ = 180^\circ $
Bring all constant values to one side of the equation,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BTC = 180^\circ - 100^\circ $
Subtract the values,
$ \Rightarrow \angle BTC = 80^\circ $
Thus, $\angle BAC = 50^\circ $ and $\angle BTC = 80^\circ $
Hence, option (D) is the correct answer.
Additional Information: The radius of the circle is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact.
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length and the angles opposite to equal sides are equal in measure.
The angle subtended by an arc at the center of a circle is double that of the angle that the arc subtends at any other given point on the circle.
In any quadrilateral, the sum of opposite sides is equal to $180^\circ $.
Note: Students many times get confused with angles given in the diagram i.e. $\angle PBA = 60^\circ $ and $\angle ACQ = 70^\circ $ as the angles made by radius with the tangents. Keep in mind radius is always perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact. Always change the sign from negative to positive and vice versa when shifting the values from one side to another.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




