
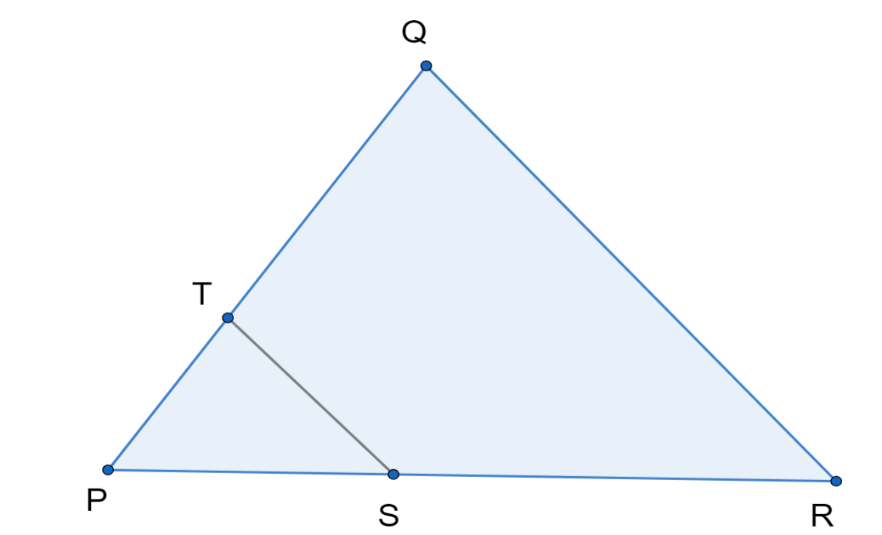
In the given figure $ST\parallel RQ$, $PS=3$cm and $SR=4$cm. Find the ratio of area of $\Delta PST$ to area of $\Delta PRQ$

Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: We are given that, $ST\parallel RQ$, $PS=3$cm and $SR=4$cm. Take two triangles, $\Delta PST$ and $\Delta PRQ$ and use AA similarity to prove the congruence. After that, use the property that if the triangles are similar then the ratio of area of triangles are equal to the ratio of corresponding sides.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that, $ST\parallel RQ$, $PS=3$cm and $SR=4$cm.
Now taking $\Delta PST$ and $\Delta PRQ$.
In $\Delta PRQ$ and $\Delta PRQ$,
$\angle QPR=\angle TPS$ ……….. (Common angle between both the triangles)
$\angle PRQ=\angle PST$ ………… (We know $ST\parallel RQ$ , hence corresponding angles are equal)
$\therefore \Delta PRQ\sim \Delta PST$ …… (By AA similarity)
Now we know that if the triangles are similar then the ratio of area of triangles are equal to the ratio of corresponding sides.
So,
$\Rightarrow$ $\dfrac{\text{area of }\vartriangle PST}{\text{area of }\vartriangle PRQ}={{\left( \dfrac{PS}{PR} \right)}^{2}}$
We are given, $PS=3$cm and $SR=4$cm.
Now, we can see in figure, $PR=PS+SR=3+4$.
$\Rightarrow$ $\dfrac{\text{area of }\vartriangle PST}{\text{area of }\vartriangle PRQ}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{3+4} \right)}^{2}}$
Simplifying we get,
$\Rightarrow$ $\dfrac{\text{area of }\vartriangle PST}{\text{area of }\vartriangle PRQ}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{7} \right)}^{2}}$
Now we know that, ${{(3)}^{2}}=9$ and ${{(7)}^{2}}=49$.
$\Rightarrow$ $\dfrac{\text{area of }\vartriangle PST}{\text{area of }\vartriangle PRQ}=\left( \dfrac{9}{49} \right)$
The ratio of area of $\Delta PST$ to area of $\Delta PRQ$ is $9:49$.
Additional information:
Similar triangles are the triangles which have the same shape, but their sizes may vary. All equilateral triangles, squares of any side lengths are examples of similar objects. In other words, if two triangles are similar, then their corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding sides are in equal proportion. Triangle is the three-sided polygon. In Geometry, a triangle is a three-sided polygon that consists of three edges and three vertices. The most important property of a triangle is that the sum of the internal angles of a triangle is equal to $180$ degrees. This property is called the angle sum property of triangles.
Note: If any two angles of a triangle are equal to any two angles of another triangle, then the two triangles are similar to each other.The condition for the similarity of triangles is;
i) Corresponding angles of both the triangles are equal, and
ii) Corresponding sides of both the triangles are in proportion to each other.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that, $ST\parallel RQ$, $PS=3$cm and $SR=4$cm.
Now taking $\Delta PST$ and $\Delta PRQ$.
In $\Delta PRQ$ and $\Delta PRQ$,
$\angle QPR=\angle TPS$ ……….. (Common angle between both the triangles)
$\angle PRQ=\angle PST$ ………… (We know $ST\parallel RQ$ , hence corresponding angles are equal)
$\therefore \Delta PRQ\sim \Delta PST$ …… (By AA similarity)
Now we know that if the triangles are similar then the ratio of area of triangles are equal to the ratio of corresponding sides.
So,
$\Rightarrow$ $\dfrac{\text{area of }\vartriangle PST}{\text{area of }\vartriangle PRQ}={{\left( \dfrac{PS}{PR} \right)}^{2}}$
We are given, $PS=3$cm and $SR=4$cm.
Now, we can see in figure, $PR=PS+SR=3+4$.
$\Rightarrow$ $\dfrac{\text{area of }\vartriangle PST}{\text{area of }\vartriangle PRQ}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{3+4} \right)}^{2}}$
Simplifying we get,
$\Rightarrow$ $\dfrac{\text{area of }\vartriangle PST}{\text{area of }\vartriangle PRQ}={{\left( \dfrac{3}{7} \right)}^{2}}$
Now we know that, ${{(3)}^{2}}=9$ and ${{(7)}^{2}}=49$.
$\Rightarrow$ $\dfrac{\text{area of }\vartriangle PST}{\text{area of }\vartriangle PRQ}=\left( \dfrac{9}{49} \right)$
The ratio of area of $\Delta PST$ to area of $\Delta PRQ$ is $9:49$.
Additional information:
Similar triangles are the triangles which have the same shape, but their sizes may vary. All equilateral triangles, squares of any side lengths are examples of similar objects. In other words, if two triangles are similar, then their corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding sides are in equal proportion. Triangle is the three-sided polygon. In Geometry, a triangle is a three-sided polygon that consists of three edges and three vertices. The most important property of a triangle is that the sum of the internal angles of a triangle is equal to $180$ degrees. This property is called the angle sum property of triangles.
Note: If any two angles of a triangle are equal to any two angles of another triangle, then the two triangles are similar to each other.The condition for the similarity of triangles is;
i) Corresponding angles of both the triangles are equal, and
ii) Corresponding sides of both the triangles are in proportion to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




