
In the given figure, $ST\parallel RQ,{\text{ }}PS = 3{\text{ cm and }}SR = 4{\text{ cm}}$ . Find the ratio of the area of $\Delta PST$ to the area of $\Delta PRQ$ .

Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Draw a figure using all the given information. Use the property of parallel lines that state that the corresponding angles for a transverse of parallel lines are equal. This way you can prove the two non-common pairs of angles equal for both triangles. Now use the AAA similarity rule, conclude that these triangles are similar. And similar triangles have their areas in the ratio of the square of corresponding sides. Make a relation using that theorem and find the required ratio.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the question, here we have two triangles $\Delta PRQ{\text{ and }}\Delta PST$ with a common angle $\angle P$ . Length of $PS = 3{\text{ cm and }}SR = 4{\text{ cm}}$. The opposite side to the angle $\angle P$ is parallel for both the triangles.
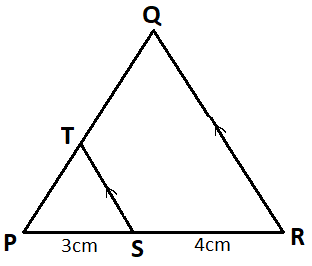
So from the given information, we get the above figure.
Now as we know that sides ST and RQ are parallel and this makes the side PT and PQ as transverse lines.
As we know that the corresponding angles for two parallel lines are equal. And here angle $\angle PTS{\text{ and }}\angle PQR$ is a pair of corresponding angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle PTS = \angle PQR$
Similarly, if we consider sides ST and RQ as parallel and side PR as transverse to these parallel lines. Here we get the corresponding angles as $\angle PST{\text{ and }}\angle PRQ$.
Therefore, we can say: $\angle PST = \angle PRQ$
Hence, in the triangle $\Delta PRQ{\text{ and }}\Delta PST$, we can say $\angle PTS = \angle PQR$, $\angle PST = \angle PRQ$ and $\angle TPS = \angle QPR = \angle P$ . Thus we can say that all three angles of these two triangles are equal.
According to the AAA similarity rule, which says that if two or more angles of a pair of triangles are the same(congruent), then the triangles will be similar.
Therefore, triangles by AAA similarity rule $\Delta PRQ{\text{ and }}\Delta PST$ are similar triangles.
Also, we know the theorem, which states if two triangles are similar, then the ratio of the area of both triangles is proportional to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides. This proves that the ratio of the area of two similar triangles is proportional to the squares of the corresponding sides of both the triangles.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area of }}\Delta PST}}{{{\text{Area of }}\Delta PRQ}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{PS}}{{PR}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{ST}}{{RQ}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{TP}}{{QP}}} \right)^2}$
We already have $PS = 3{\text{ cm and }}SR = 4{\text{ cm}}$, after substituting these values, we get:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area of }}\Delta PST}}{{{\text{Area of }}\Delta PRQ}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{PS}}{{PR}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{PS}}{{PS + SR}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{3}{{3 + 4}}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{{3^2}}}{{{7^2}}} = \dfrac{9}{{49}}$
Hence, we got the required ratio of the area of a triangle $\Delta PRQ{\text{ and }}\Delta PST$ as $9:49$.
Note: Utilizing the knowledge of similarity rules was the most crucial part of the solution. Drawing a figure with all the given information will help you visualise the problem in a better way. Be careful while substituting the values in the relationship formed for the required ratio. An alternative approach is to use the AA similarity rule, using just two pairs of equal angles in the triangle $\Delta PRQ{\text{ and }}\Delta PST$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the question, here we have two triangles $\Delta PRQ{\text{ and }}\Delta PST$ with a common angle $\angle P$ . Length of $PS = 3{\text{ cm and }}SR = 4{\text{ cm}}$. The opposite side to the angle $\angle P$ is parallel for both the triangles.

So from the given information, we get the above figure.
Now as we know that sides ST and RQ are parallel and this makes the side PT and PQ as transverse lines.
As we know that the corresponding angles for two parallel lines are equal. And here angle $\angle PTS{\text{ and }}\angle PQR$ is a pair of corresponding angles.
$ \Rightarrow \angle PTS = \angle PQR$
Similarly, if we consider sides ST and RQ as parallel and side PR as transverse to these parallel lines. Here we get the corresponding angles as $\angle PST{\text{ and }}\angle PRQ$.
Therefore, we can say: $\angle PST = \angle PRQ$
Hence, in the triangle $\Delta PRQ{\text{ and }}\Delta PST$, we can say $\angle PTS = \angle PQR$, $\angle PST = \angle PRQ$ and $\angle TPS = \angle QPR = \angle P$ . Thus we can say that all three angles of these two triangles are equal.
According to the AAA similarity rule, which says that if two or more angles of a pair of triangles are the same(congruent), then the triangles will be similar.
Therefore, triangles by AAA similarity rule $\Delta PRQ{\text{ and }}\Delta PST$ are similar triangles.
Also, we know the theorem, which states if two triangles are similar, then the ratio of the area of both triangles is proportional to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides. This proves that the ratio of the area of two similar triangles is proportional to the squares of the corresponding sides of both the triangles.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area of }}\Delta PST}}{{{\text{Area of }}\Delta PRQ}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{PS}}{{PR}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{ST}}{{RQ}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{TP}}{{QP}}} \right)^2}$
We already have $PS = 3{\text{ cm and }}SR = 4{\text{ cm}}$, after substituting these values, we get:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area of }}\Delta PST}}{{{\text{Area of }}\Delta PRQ}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{PS}}{{PR}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{{PS}}{{PS + SR}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{3}{{3 + 4}}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{{3^2}}}{{{7^2}}} = \dfrac{9}{{49}}$
Hence, we got the required ratio of the area of a triangle $\Delta PRQ{\text{ and }}\Delta PST$ as $9:49$.
Note: Utilizing the knowledge of similarity rules was the most crucial part of the solution. Drawing a figure with all the given information will help you visualise the problem in a better way. Be careful while substituting the values in the relationship formed for the required ratio. An alternative approach is to use the AA similarity rule, using just two pairs of equal angles in the triangle $\Delta PRQ{\text{ and }}\Delta PST$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Convert 40circ C to Fahrenheit A 104circ F B 107circ class 8 maths CBSE

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE





