
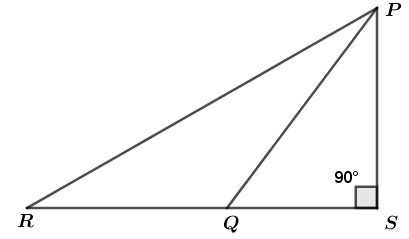
In the given figure, ∠PSR = 90°, PQ = 10 cm, QS = 6 cm and RQ = 9 cm. Calculate the length PR.
A. 16 cm
B. 17 cm
C. 18 cm
D. 19 cm

Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Here, first find the length of PS from triangle PSQ, using Pythagoras theorem. Then find the length of PR from triangle PSR, using Pythagoras theorem again, as we have the lengths of PS and RS (= RQ +QS) known.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that in figure, ∠PSR = 90°, PQ = 10 cm, QS = 6 cm and RQ = 9 cm.
First we have to find PS.
In triangle PSQ,
Hypotenuse = PQ, other two sides are PS and QS
$P{Q^2} = P{S^2} + Q{S^2}$ …(i) [Using Pythagoras Theorem]
[Pythagoras Theorem: Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, square of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides]
Here, we are given, PQ = 10 cm and QS = 6 cm
Putting values in equation (i), we get
\[{(10{\text{cm)}}^2} = P{S^2} + {(6{\text{cm}})^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow P{S^2} = 100{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2} - 36{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow P{S^2} = 64{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow PS = 8{\text{cm}}\]
Therefore, the length of side PS = 8 cm
Now, in triangle PSR,
$P{R^2} = P{S^2} + S{R^2}$ …(ii)
Hypotenuse = PR, other two sides are PS and SR
[Using Pythagoras theorem]
Here, SR = RQ + QS = (9 cm + 6 cm) = 15 cm and PS = 8 cm.
Putting values of SR and PS in equation (ii), we get
$P{R^2} = {(8{\text{cm}})^2} + {(15{\text{cm}})^2}$
$P{R^2} = 64{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2} + 225{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
$P{R^2} = 289{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Taking square root of both sides,
PR = 17 cm
The length of PR is 17 cm.
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note: Always use Pythagoras theorem to find the side of a right angled triangle, if two of the sides are known. Start with the smallest triangle and proceed by finding all the sides of the triangles one by one. Do not go for any trigonometric method as their calculations may be complicated.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that in figure, ∠PSR = 90°, PQ = 10 cm, QS = 6 cm and RQ = 9 cm.
First we have to find PS.
In triangle PSQ,
Hypotenuse = PQ, other two sides are PS and QS
$P{Q^2} = P{S^2} + Q{S^2}$ …(i) [Using Pythagoras Theorem]
[Pythagoras Theorem: Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, square of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides]
Here, we are given, PQ = 10 cm and QS = 6 cm
Putting values in equation (i), we get
\[{(10{\text{cm)}}^2} = P{S^2} + {(6{\text{cm}})^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow P{S^2} = 100{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2} - 36{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow P{S^2} = 64{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow PS = 8{\text{cm}}\]
Therefore, the length of side PS = 8 cm
Now, in triangle PSR,
$P{R^2} = P{S^2} + S{R^2}$ …(ii)
Hypotenuse = PR, other two sides are PS and SR
[Using Pythagoras theorem]
Here, SR = RQ + QS = (9 cm + 6 cm) = 15 cm and PS = 8 cm.
Putting values of SR and PS in equation (ii), we get
$P{R^2} = {(8{\text{cm}})^2} + {(15{\text{cm}})^2}$
$P{R^2} = 64{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2} + 225{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
$P{R^2} = 289{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Taking square root of both sides,
PR = 17 cm
The length of PR is 17 cm.
Hence, option (B) is correct.
Note: Always use Pythagoras theorem to find the side of a right angled triangle, if two of the sides are known. Start with the smallest triangle and proceed by finding all the sides of the triangles one by one. Do not go for any trigonometric method as their calculations may be complicated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




