
In the given figure, PQL and PRM are two tangents to the circle with centre O at the point Q and R respectively. If S is a point on the circle such that the angle SQL = \[{{50}^{\circ }}\] and angle SRM =\[{{60}^{\circ }}\]. Find the reflex angle QOR.
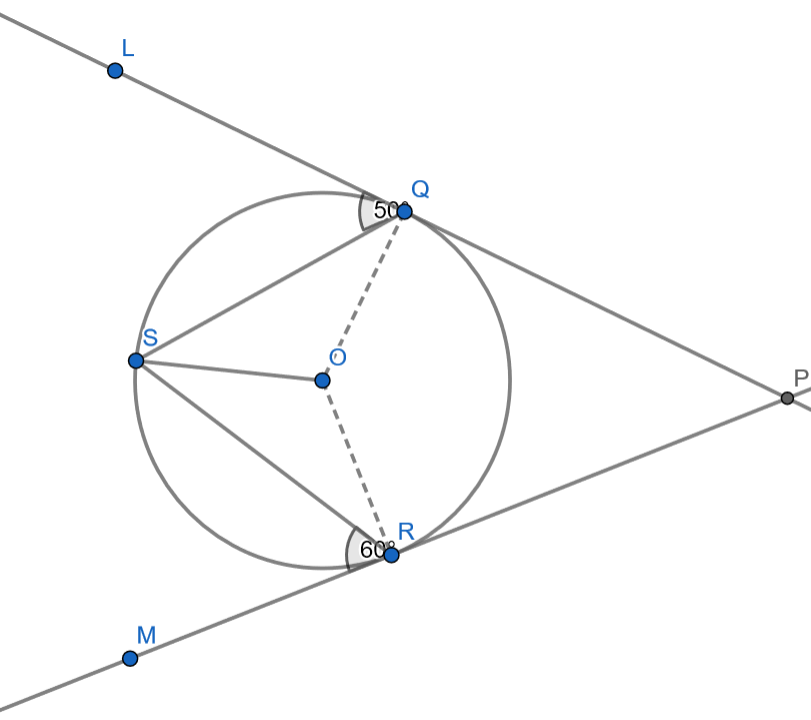

Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: In this type of question we have to use the properties of a circle. We know that the tangent to the circle forms an angle of \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] with the radius of the circle, so by using this we can find the measure of the angles \[\angle SQO\] and \[\angle SRO\]. Also we know that, angles opposite to equal sides are equal. By using this we can obtain the required result.
Complete step by step answer:
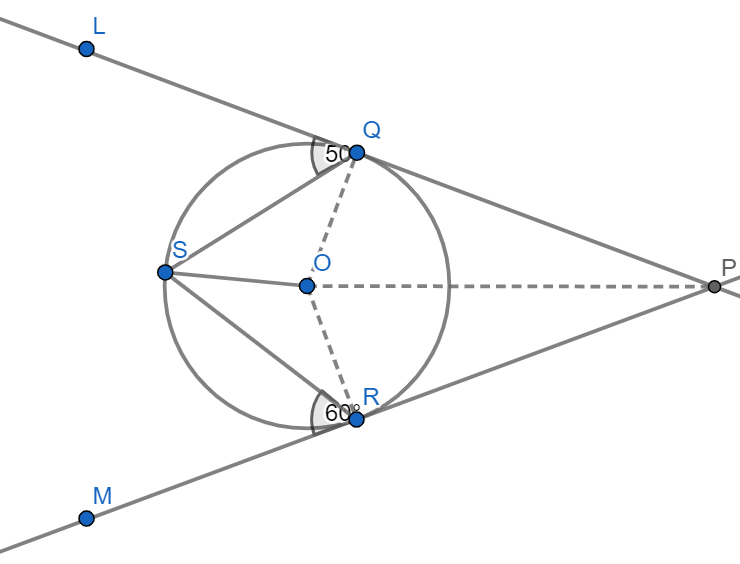
Now we have to find the angle \[QOR\], for this let us draw the diagram again by joining the centre O with the point P.
By give we have, \[\angle SQL={{50}^{\circ }}\] and \[\angle SRM={{60}^{\circ }}\]
As we know that, the tangent to the circle forms an angle of \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] with the radius of the circle hence,
\[\Rightarrow \angle LQO=\angle MRO={{90}^{\circ }}\]
Thus we can obtain \[\angle SQO\] and \[\angle SRO\] as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle SQO=\angle LQO-\angle SQL \\
& \Rightarrow \angle SQO={{90}^{\circ }}-{{50}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle SQO={{40}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Similarly, we can write,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle SRO=\angle MRO-\angle SRM \\
& \Rightarrow \angle SRO={{90}^{\circ }}-{{60}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle SRO={{30}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Also as we know, angles opposite to equal sides are equal and \[OQ=OS\], \[OR=OS\] as they are the radius of the circle.
\[\Rightarrow \angle SQO=\angle QSO={{40}^{\circ }}\]and \[\angle SRO=\angle OSR={{30}^{\circ }}\]
Now by using the exterior angle property we can write,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle QOP=\angle QSO+\angle SQO \\
& \Rightarrow \angle QOP={{40}^{\circ }}+{{40}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle QOP={{80}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
As well as we can also write,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle ROP=\angle SRO+\angle OSR \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ROP={{30}^{\circ }}+{{30}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ROP={{60}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
From the figure, we can easily observe that, \[\angle QOR\] is formed by addition of \[\angle QOP\] and \[\angle ROP\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle QOR=\angle QOP+\angle ROP \\
& \Rightarrow \angle QOR={{80}^{\circ }}+{{60}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle QOR={{140}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Thus the measure of the angle \[QOR\] is \[{{140}^{\circ }}\].
Note: In this type of question students have to note different properties of angles like exterior angle property of opposite angle property etc. Also students have to remember to draw the line joining the centre of the circle and point of intersection of the tangents, so that it will become easy to find the angle \[QOR\].
Complete step by step answer:
Now we have to find the angle \[QOR\], for this let us draw the diagram again by joining the centre O with the point P.

By give we have, \[\angle SQL={{50}^{\circ }}\] and \[\angle SRM={{60}^{\circ }}\]
As we know that, the tangent to the circle forms an angle of \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] with the radius of the circle hence,
\[\Rightarrow \angle LQO=\angle MRO={{90}^{\circ }}\]
Thus we can obtain \[\angle SQO\] and \[\angle SRO\] as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle SQO=\angle LQO-\angle SQL \\
& \Rightarrow \angle SQO={{90}^{\circ }}-{{50}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle SQO={{40}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Similarly, we can write,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle SRO=\angle MRO-\angle SRM \\
& \Rightarrow \angle SRO={{90}^{\circ }}-{{60}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle SRO={{30}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Also as we know, angles opposite to equal sides are equal and \[OQ=OS\], \[OR=OS\] as they are the radius of the circle.
\[\Rightarrow \angle SQO=\angle QSO={{40}^{\circ }}\]and \[\angle SRO=\angle OSR={{30}^{\circ }}\]
Now by using the exterior angle property we can write,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle QOP=\angle QSO+\angle SQO \\
& \Rightarrow \angle QOP={{40}^{\circ }}+{{40}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle QOP={{80}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
As well as we can also write,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle ROP=\angle SRO+\angle OSR \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ROP={{30}^{\circ }}+{{30}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle ROP={{60}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
From the figure, we can easily observe that, \[\angle QOR\] is formed by addition of \[\angle QOP\] and \[\angle ROP\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle QOR=\angle QOP+\angle ROP \\
& \Rightarrow \angle QOR={{80}^{\circ }}+{{60}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle QOR={{140}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Thus the measure of the angle \[QOR\] is \[{{140}^{\circ }}\].
Note: In this type of question students have to note different properties of angles like exterior angle property of opposite angle property etc. Also students have to remember to draw the line joining the centre of the circle and point of intersection of the tangents, so that it will become easy to find the angle \[QOR\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




