
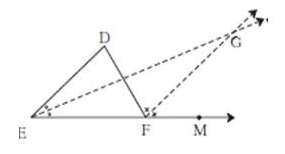
In the given figure, line $DE\ parallel $line $GF$ ray $EG$ and ray $FG$ are bisectors of $\angle DEF$ and $\angle DFM$ respectively. Prove that,
$\left( 1 \right)$$\ angle DEG = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle EDF$
$\left( 2 \right)$$EF = FG$

Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: In this question we will use the following properties:
If a line passes through the center of an angle then it divides the same angle into equal parts.
Sum of two interior angles of a triangle is equal to the opposite exterior angle of a triangle. Sum of all angles of the triangle is always equal to ${180^ \circ }$. Two triangles are said to be similar if the corresponding angles of two triangles are congruent and lengths of corresponding sides are proportional. Two triangles are said to be congruent if all the sides of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides of another triangle and the corresponding angles are equal.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, $DE\parallel GF$
Ray $EG$and ray $FG$ are bisectors of $\angle DEF$and$\angle DFM$.
Means $EG$and $FG$divides $\angle DEF$and$\angle DFM$respectively in two equal parts. So,
$ \Rightarrow \angle DEG = \angle GEF = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DEF$ ……..$1$
Also, $\angle DFG = \angle GFM = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DFM$……. $2$
Since, $DE\parallel GF$
So, $\angle EDF = \angle DFG$ ………$3$ ($\because $we know that alternate interior angles are equal to each other)
Also we can write, $\angle EDF = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DFM$$.....4$
Now, consider $\vartriangle DEF$
We know that the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of opposite two interior angles.
Therefore,
$\angle DFM = \angle DEF + \angle EDF$
From equation $4$$\angle EDF = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DFM$. We can also write this equation like this, $2\angle EDF = \angle DFM$ Therefore,
$ \Rightarrow 2\angle EDF = \angle DEF + \angle EDF$
We get, $\angle EDF = \angle DEF$
From equation $1$, $\angle DEG = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DEF$. We can also write this equation like this $2\angle DEG = \angle DEF$
$ \Rightarrow \angle EDF = 2\angle DEG$
So we get $\angle DEG = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle EDF$.
Hence proved.
Given, $DE\ parallel GF$
$\angle DEG = \angle EGF$…… $5$ ($\because $We know that alternate interior angles are equal to each other)
Now, From equation 1 , $\angle DEG = \angle GEF$
$\angle GEF = \angle EGF$
Since, the $\vartriangle EGF$sides opposite to equal angles are also equal.
$ \Rightarrow EF = FG$
Hence, proved
Note:While solving this question one should have remembered all the properties angles and triangles i.e. If a triangle has the same three angles then it has similar length of sides or vice versa and Bisectors always cut angle into two equal parts etc. Also should take care while doing calculation.
If a line passes through the center of an angle then it divides the same angle into equal parts.
Sum of two interior angles of a triangle is equal to the opposite exterior angle of a triangle. Sum of all angles of the triangle is always equal to ${180^ \circ }$. Two triangles are said to be similar if the corresponding angles of two triangles are congruent and lengths of corresponding sides are proportional. Two triangles are said to be congruent if all the sides of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides of another triangle and the corresponding angles are equal.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, $DE\parallel GF$
Ray $EG$and ray $FG$ are bisectors of $\angle DEF$and$\angle DFM$.
Means $EG$and $FG$divides $\angle DEF$and$\angle DFM$respectively in two equal parts. So,
$ \Rightarrow \angle DEG = \angle GEF = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DEF$ ……..$1$
Also, $\angle DFG = \angle GFM = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DFM$……. $2$
Since, $DE\parallel GF$
So, $\angle EDF = \angle DFG$ ………$3$ ($\because $we know that alternate interior angles are equal to each other)
Also we can write, $\angle EDF = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DFM$$.....4$
Now, consider $\vartriangle DEF$
We know that the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of opposite two interior angles.
Therefore,
$\angle DFM = \angle DEF + \angle EDF$
From equation $4$$\angle EDF = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DFM$. We can also write this equation like this, $2\angle EDF = \angle DFM$ Therefore,
$ \Rightarrow 2\angle EDF = \angle DEF + \angle EDF$
We get, $\angle EDF = \angle DEF$
From equation $1$, $\angle DEG = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DEF$. We can also write this equation like this $2\angle DEG = \angle DEF$
$ \Rightarrow \angle EDF = 2\angle DEG$
So we get $\angle DEG = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle EDF$.
Hence proved.
Given, $DE\ parallel GF$
$\angle DEG = \angle EGF$…… $5$ ($\because $We know that alternate interior angles are equal to each other)
Now, From equation 1 , $\angle DEG = \angle GEF$
$\angle GEF = \angle EGF$
Since, the $\vartriangle EGF$sides opposite to equal angles are also equal.
$ \Rightarrow EF = FG$
Hence, proved
Note:While solving this question one should have remembered all the properties angles and triangles i.e. If a triangle has the same three angles then it has similar length of sides or vice versa and Bisectors always cut angle into two equal parts etc. Also should take care while doing calculation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

The number of corners in a cube are A 4 B 6 C 8 D class 8 maths CBSE

Advantages and disadvantages of science

The pH of the gastric juices released during digestion class 8 biology CBSE

What are the methods of reducing friction. Explain




